
Davidson correction
Encyclopedia
The Davidson correction is a simple correction that is often applied in calculations using the method of configuration interaction
, which is one of several post-Hartree–Fock ab initio quantum chemistry methods
in the field of computational chemistry
. It was introduced by Ernest R. Davidson
.
It allows one to estimate the value of the full configuration interaction
energy from a limited configuration interaction expansion result, although more precisely it estimates the energy of configuration interaction up to quadruple excitations (CISDTQ) from the energy of configuration interaction up to double excitations (CISD). It uses the formula
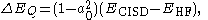
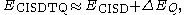
where a0 is the coefficient of the Hartree–Fock wavefunction
in the CISD expansion, ECISD and EHF are the energies of the CISD and Hartree–Fock wavefunctions respectively, and ΔEQ is the correction to estimate ECISDTQ, the energy of the CISDTQ wavefunction.
Configuration interaction
Configuration interaction is a post-Hartree–Fock linear variational method for solving the nonrelativistic Schrödinger equation within the Born–Oppenheimer approximation for a quantum chemical multi-electron system. Mathematically, configuration simply describes the linear combination...
, which is one of several post-Hartree–Fock ab initio quantum chemistry methods
Ab initio quantum chemistry methods
Ab initio quantum chemistry methods are computational chemistry methods based on quantum chemistry. The term ab initiowas first used in quantum chemistry by Robert Parr and coworkers, including David Craig in a semiempirical study on the excited states of benzene.The background is described by Parr...
in the field of computational chemistry
Computational chemistry
Computational chemistry is a branch of chemistry that uses principles of computer science to assist in solving chemical problems. It uses the results of theoretical chemistry, incorporated into efficient computer programs, to calculate the structures and properties of molecules and solids...
. It was introduced by Ernest R. Davidson
Ernest R. Davidson
Ernest R. Davidson, born October 12, 1936 in Terre Haute, Indiana, is Professor of Chemistry, University of Washington, Seattle, WA, USA. He graduated from Wiley High School, Terre Haute and Rose Polytechnic Institute....
.
It allows one to estimate the value of the full configuration interaction
Full configuration interaction
Full configuration interaction is a linear variational approach which provides numerically exact solutions to the electronic time-independent, non-relativistic Schrödinger equation....
energy from a limited configuration interaction expansion result, although more precisely it estimates the energy of configuration interaction up to quadruple excitations (CISDTQ) from the energy of configuration interaction up to double excitations (CISD). It uses the formula
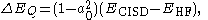
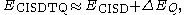
where a0 is the coefficient of the Hartree–Fock wavefunction
Wavefunction
Not to be confused with the related concept of the Wave equationA wave function or wavefunction is a probability amplitude in quantum mechanics describing the quantum state of a particle and how it behaves. Typically, its values are complex numbers and, for a single particle, it is a function of...
in the CISD expansion, ECISD and EHF are the energies of the CISD and Hartree–Fock wavefunctions respectively, and ΔEQ is the correction to estimate ECISDTQ, the energy of the CISDTQ wavefunction.

