
Darwin (unit)
Encyclopedia
The Darwin is a unit
of evolution
ary change, defined by J.B.S. Haldane in 1949. One Darwin is defined to be an e
-fold (about 2.718) change in a trait
over one million years. Haldane named the unit after Charles Darwin
.
 ) is:
) is:
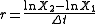
where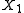 and
and 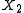 are the initial and final values of the trait and
are the initial and final values of the trait and 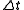 is the change in time in millions of years. An alternative form of this equation is:
is the change in time in millions of years. An alternative form of this equation is:
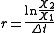
Since the difference between two natural logarithm
s is a dimension
less ratio
, the trait may be measured in any unit
. Also for this reason the Darwin is a specialist form of the inverse mega-annum (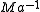 ).
).
s can be compared. Where this is used it is an indirect measure as it relies on phenotypic rather than genotypic data. Several data are required to overcome natural variation within a population. The Darwin only measures the evolution of a particular trait
rather than a lineage
; different traits may evolve at different rates within a lineage. The evolution of traits can however be used to infer as a proxy
the evolution of lineages.
Genetic information cannot be obtained from fossils, but modern (post-Haldane) techniques on extant organisms now rely on genetic data (q.v. phylogenetics
).
Units of measurement
A unit of measurement is a definite magnitude of a physical quantity, defined and adopted by convention and/or by law, that is used as a standard for measurement of the same physical quantity. Any other value of the physical quantity can be expressed as a simple multiple of the unit of...
of evolution
Evolution
Evolution is any change across successive generations in the heritable characteristics of biological populations. Evolutionary processes give rise to diversity at every level of biological organisation, including species, individual organisms and molecules such as DNA and proteins.Life on Earth...
ary change, defined by J.B.S. Haldane in 1949. One Darwin is defined to be an e
E (mathematical constant)
The mathematical constant ' is the unique real number such that the value of the derivative of the function at the point is equal to 1. The function so defined is called the exponential function, and its inverse is the natural logarithm, or logarithm to base...
-fold (about 2.718) change in a trait
Trait
Trait may refer to:* Trait, a characteristic or property of some object* Trait , which involve genes and characteristics of organisms* Trait theory, an approach to the psychological study of personality...
over one million years. Haldane named the unit after Charles Darwin
Charles Darwin
Charles Robert Darwin FRS was an English naturalist. He established that all species of life have descended over time from common ancestry, and proposed the scientific theory that this branching pattern of evolution resulted from a process that he called natural selection.He published his theory...
.
Equation
The equation for calculating evolutionary change in Darwins ( ) is:
) is: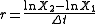
where
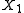 and
and 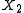 are the initial and final values of the trait and
are the initial and final values of the trait and 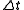 is the change in time in millions of years. An alternative form of this equation is:
is the change in time in millions of years. An alternative form of this equation is: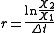
Since the difference between two natural logarithm
Natural logarithm
The natural logarithm is the logarithm to the base e, where e is an irrational and transcendental constant approximately equal to 2.718281828...
s is a dimension
Dimension
In physics and mathematics, the dimension of a space or object is informally defined as the minimum number of coordinates needed to specify any point within it. Thus a line has a dimension of one because only one coordinate is needed to specify a point on it...
less ratio
Ratio
In mathematics, a ratio is a relationship between two numbers of the same kind , usually expressed as "a to b" or a:b, sometimes expressed arithmetically as a dimensionless quotient of the two which explicitly indicates how many times the first number contains the second In mathematics, a ratio is...
, the trait may be measured in any unit
Units of measurement
A unit of measurement is a definite magnitude of a physical quantity, defined and adopted by convention and/or by law, that is used as a standard for measurement of the same physical quantity. Any other value of the physical quantity can be expressed as a simple multiple of the unit of...
. Also for this reason the Darwin is a specialist form of the inverse mega-annum (
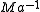 ).
).Application
The measure is most useful in palaeontology, where macroevolutionary changes in the dimensions of fossilFossil
Fossils are the preserved remains or traces of animals , plants, and other organisms from the remote past...
s can be compared. Where this is used it is an indirect measure as it relies on phenotypic rather than genotypic data. Several data are required to overcome natural variation within a population. The Darwin only measures the evolution of a particular trait
Trait (biology)
A trait is a distinct variant of a phenotypic character of an organism that may be inherited, environmentally determined or be a combination of the two...
rather than a lineage
Lineage (evolution)
An evolutionary lineage is a sequence of species, that form a line of descent, each new species the direct result of speciation from an immediate ancestral species. Lineages are subsets of the evolutionary tree of life. Lineages are often determined by the techniques of molecular systematics.-...
; different traits may evolve at different rates within a lineage. The evolution of traits can however be used to infer as a proxy
Proxy (statistics)
In statistics, a proxy variable is something that is probably not in itself of any great interest, but from which a variable of interest can be obtained...
the evolution of lineages.
Genetic information cannot be obtained from fossils, but modern (post-Haldane) techniques on extant organisms now rely on genetic data (q.v. phylogenetics
Phylogenetics
In biology, phylogenetics is the study of evolutionary relatedness among groups of organisms , which is discovered through molecular sequencing data and morphological data matrices...
).

