
Cosmos 60
Encyclopedia
Soviet Union
The Soviet Union , officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics , was a constitutionally socialist state that existed in Eurasia between 1922 and 1991....
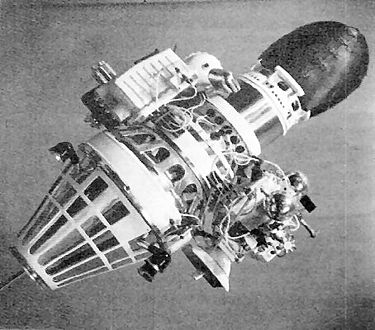
on March 12, 1965. It was the sixth attempt at a lunar
Moon
The Moon is Earth's only known natural satellite,There are a number of near-Earth asteroids including 3753 Cruithne that are co-orbital with Earth: their orbits bring them close to Earth for periods of time but then alter in the long term . These are quasi-satellites and not true moons. For more...
soft-landing mission, with a design similar to that of Luna 4
Luna 4
Luna 4 was the USSR's first successful spacecraft of their "second generation" Luna program. The spacecraft, rather than being sent on a straight trajectory toward the Moon, was placed first in a low Earth orbit and then the rocket stage reignited to send it on a curving path towards the...
. The spacecraft achieved Earth orbit
Orbit
In physics, an orbit is the gravitationally curved path of an object around a point in space, for example the orbit of a planet around the center of a star system, such as the Solar System...
(apogee 287 km, perigee 201 km, inclination 64.8 degrees, orbital period 89 minutes) but failed to leave orbit for its journey to the Moon due to a failure of the power supply in the control system, and was designated Kosmos 60. It had an on-orbit mass of 6530 kg (14,400 lb). The satellite reentered the Earth's atmosphere on 17 March 1965.
Kosmos 60 carried a 16-channel NaI(Tl) scintillator
Scintillator
A scintillator is a special material, which exhibits scintillation—the property of luminescence when excited by ionizing radiation. Luminescent materials, when struck by an incoming particle, absorb its energy and scintillate, i.e., reemit the absorbed energy in the form of light...
40 x 40 mm in size. It was surrounded in a charged particle rejection scintillator. The spacecraft weighed 1600 kg and the detector was located inside the vehicle. The detector was sensitive to 0.5-2.0 MeV photons.
Kosmos 60 measured the gamma-ray background flux density to be 1.7×104 quanta/(m2·s). As was seen by Ranger 3 and Lunas 10 & 12, the spectrum fell sharply up to 1.5 MeV and was flat for higher energies. Several peaks were observed in the spectra which were attributed to the inelastic interaction of cosmic protons with the materials in the satellite body.
The designation of this mission as an intended planetary probe is based on evidence from Soviet and non-Soviet sources and historical documents.

