
Coriolis frequency
Encyclopedia
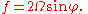
The Coriolis frequency ƒ, also called the Coriolis parameter or Coriolis coefficient, is equal to twice the rotation rate Ω of the Earth multiplied by the sine
of the latitude
φ.
The rotation rate of the Earth (Ω = 7.2921 × 10−5 rad/s) can be calculated as 2π / T radians per second, where T is the rotation period of the Earth which is one sidereal day (23 hr 56 m 4.1 s). Inertial oscillations
on the surface of the earth have this frequency
. These oscillation
s are the result of the Coriolis effect
.
Sine
In mathematics, the sine function is a function of an angle. In a right triangle, sine gives the ratio of the length of the side opposite to an angle to the length of the hypotenuse.Sine is usually listed first amongst the trigonometric functions....
of the latitude
Latitude
In geography, the latitude of a location on the Earth is the angular distance of that location south or north of the Equator. The latitude is an angle, and is usually measured in degrees . The equator has a latitude of 0°, the North pole has a latitude of 90° north , and the South pole has a...
φ.

The rotation rate of the Earth (Ω = 7.2921 × 10−5 rad/s) can be calculated as 2π / T radians per second, where T is the rotation period of the Earth which is one sidereal day (23 hr 56 m 4.1 s). Inertial oscillations
Inertial wave
Inertial waves, also known as inertial oscillations, are a type of mechanical wave possible in rotating fluids. Unlike surface gravity waves commonly seen at the beach or in the bathtub, inertial waves travel through the interior of the fluid, not at the surface...
on the surface of the earth have this frequency
Frequency
Frequency is the number of occurrences of a repeating event per unit time. It is also referred to as temporal frequency.The period is the duration of one cycle in a repeating event, so the period is the reciprocal of the frequency...
. These oscillation
Oscillation
Oscillation is the repetitive variation, typically in time, of some measure about a central value or between two or more different states. Familiar examples include a swinging pendulum and AC power. The term vibration is sometimes used more narrowly to mean a mechanical oscillation but sometimes...
s are the result of the Coriolis effect
Coriolis effect
In physics, the Coriolis effect is a deflection of moving objects when they are viewed in a rotating reference frame. In a reference frame with clockwise rotation, the deflection is to the left of the motion of the object; in one with counter-clockwise rotation, the deflection is to the right...
.
See also
- Beta planeBeta planeIn geophysical fluid dynamics, an approximation whereby the Coriolis parameter, f, is set to vary linearly in space is called a beta plane approximation...
- Earth's rotation
- Rossby-gravity wavesRossby-gravity wavesRossby-gravity waves are equatorially-trapped waves , meaning that they rapidly decay as their distance increases away from the equator . These waves have the same trapping scale as Kelvin waves, more commonly known as the equatorial Rossby deformation radius...

