
Compound of twelve pentagonal antiprisms with rotational freedom
Encyclopedia
| Compound of twelve pentagonal antiprisms with rotational freedom | |
|---|---|
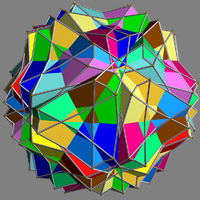 |
|
| Type | Uniform compound Uniform polyhedron compound A uniform polyhedron compound is a polyhedral compound whose constituents are identical uniform polyhedra, in an arrangement that is also uniform: the symmetry group of the compound acts transitively on the compound's vertices.The uniform polyhedron compounds were first enumerated by John Skilling... |
| Index | UC26 |
| Polyhedra | 12 pentagonal antiprism Pentagonal antiprism In geometry, the pentagonal antiprism is the third in an infinite set of antiprisms formed by an even-numbered sequence of triangle sides closed by two polygon caps. It consists of two pentagons joined to each other by a ring of 10 triangles for a total of 12 faces... s |
| Faces | 120 triangles, 24 pentagons |
| Edges | 240 |
| Vertices | 120 |
| Symmetry group Symmetry group The symmetry group of an object is the group of all isometries under which it is invariant with composition as the operation... |
icosahedral Icosahedral symmetry A regular icosahedron has 60 rotational symmetries, and a symmetry order of 120 including transformations that combine a reflection and a rotation... (Ih) |
| Subgroup Subgroup In group theory, given a group G under a binary operation *, a subset H of G is called a subgroup of G if H also forms a group under the operation *. More precisely, H is a subgroup of G if the restriction of * to H x H is a group operation on H... restricting to one constituent |
10-fold improper rotation Cyclic symmetries This article deals with the four infinite series of point groups in three dimensions with n-fold rotational symmetry about one axis , and no other rotational symmetry :Chiral:*Cn of order n - n-fold rotational symmetry... (S10) |
This uniform polyhedron compound
Uniform polyhedron compound
A uniform polyhedron compound is a polyhedral compound whose constituents are identical uniform polyhedra, in an arrangement that is also uniform: the symmetry group of the compound acts transitively on the compound's vertices.The uniform polyhedron compounds were first enumerated by John Skilling...
is a symmetric arrangement of 12 pentagonal antiprism
Pentagonal antiprism
In geometry, the pentagonal antiprism is the third in an infinite set of antiprisms formed by an even-numbered sequence of triangle sides closed by two polygon caps. It consists of two pentagons joined to each other by a ring of 10 triangles for a total of 12 faces...
s. It can be constructed by inscribing one pair of pentagonal antiprisms within an icosahedron
Icosahedron
In geometry, an icosahedron is a regular polyhedron with 20 identical equilateral triangular faces, 30 edges and 12 vertices. It is one of the five Platonic solids....
, in each of the six possible ways, and then rotating each by an equal and opposite angle θ.
When θ is 36 degrees, the antiprisms coincide in pairs to yield (two superimposed copies of) the compound of six pentagonal antiprisms
Compound of six pentagonal antiprisms
This uniform polyhedron compound is a symmetric arrangement of 6 pentagonal antiprisms. It can be constructed by inscribing within an icosahedron one pentagonal antiprism in each of the six possible ways, and then rotating each by 36 degrees about its axis .It shares its vertex arrangement with the...
(without rotational freedom).
This compound shares its vertices with the compound of twelve pentagrammic crossed antiprisms with rotational freedom
Compound of twelve pentagrammic crossed antiprisms with rotational freedom
This uniform polyhedron compound is a symmetric arrangement of 12 pentagrammic crossed antiprisms. It can be constructed by inscribing one pair of pentagrammic crossed antiprisms within a great icosahedron, in each of the six possible ways, and then rotating each by an equal and opposite angle...
.
Cartesian coordinates
Cartesian coordinates for the vertices of this compound are all the cyclic permutations of- (±(2τ−1−(2τ+4)cosθ), ±2(√(5τ+10))sinθ, ±(τ+2+(4τ−2)cosθ))
- (±(2τ−1−(2τ−1)cosθ−τ(√(5τ+10))sinθ), ±(−5τcosθ+τ−1(√(5τ+10))sinθ),
- ±(τ+2+(3−τ)cosθ+(√(5τ+10))sinθ))
- (±(2τ−1+(1+3τ)cosθ−(√(5τ+10))sinθ), ±(−5cosθ−τ(√(5τ+10))sinθ),
- ±(τ+2−(τ+2)cosθ+τ−1(√(5τ+10))sinθ))
- (±(2τ−1+(1+3τ)cosθ+(√(5τ+10))sinθ), ±(5cosθ−τ(√(5τ+10))sinθ),
- ±(τ+2−(τ+2)cosθ−τ−1(√(5τ+10))sinθ))
- (±(2τ−1−(2τ−1)cosθ+τ(√(5τ+10))sinθ), ±(5τcosθ+τ−1(√(5τ+10))sinθ),
- ±(τ+2+(3−τ)cosθ−(√(5τ+10))sinθ))
where τ = (1+√5)/2 is the golden ratio
Golden ratio
In mathematics and the arts, two quantities are in the golden ratio if the ratio of the sum of the quantities to the larger quantity is equal to the ratio of the larger quantity to the smaller one. The golden ratio is an irrational mathematical constant, approximately 1.61803398874989...
(sometimes written φ).

