
CER-203
Encyclopedia
 |
 |
CER
CER Computers
CER was a series of early computers developed by Mihajlo Pupin Institute in the 1960s and 1970s.Models:* CER-10 - 1960, based on vacuum tubes, transistors, electronic relays, and magnetic core memory...
( – Digital Electronic Computer) model 203 was an early digital computer
Computer
A computer is a programmable machine designed to sequentially and automatically carry out a sequence of arithmetic or logical operations. The particular sequence of operations can be changed readily, allowing the computer to solve more than one kind of problem...
developed by Mihajlo Pupin Institute
Mihajlo Pupin Institute
Mihajlo Pupin Institute is an institute based in Belgrade, Serbia notable for manufacturing numerous computer systems used in Socialist Federal Republic of Yugoslavia - especially early CER and later TIM line of computers. It is named after Mihajlo Idvorski Pupin.The Institute is well known in...
(Serbia
Serbia
Serbia , officially the Republic of Serbia , is a landlocked country located at the crossroads of Central and Southeast Europe, covering the southern part of the Carpathian basin and the central part of the Balkans...
) in 1971. It was designed to process data of medium sized businesses:
- In banks, for managing and processing of accounts, bookkeeping, foreign-currency and interest calculations, amortization plans and statistics
- In manufacturing, for production planning and management, market data processing and forecasting, inventory management, financial document management and process modelling
- In utilities, to calculate water and electricity consumption, to produce various reportsand lists and for technical calculations and design
- In construction industry for network planning method design, financial management and bookkeeping
- In trading companies for payment processing, market analysis, inventory management and customer and partner relationship management
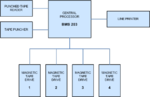
Specifications
Central Processing:- Type: BMS-203
- Number of instructions: 32
- Performance:
- one 16-cycle instruction: 20 μs1 E-6 sA microsecond is an SI unit of time equal to one millionth of a second. Its symbol is µs.A microsecond is equal to 1000 nanoseconds or 1/1000 millisecond...
- one single cycle instruction: 5 μs1 E-6 sA microsecond is an SI unit of time equal to one millionth of a second. Its symbol is µs.A microsecond is equal to 1000 nanoseconds or 1/1000 millisecond...
- addition and/or subtraction of two 15-digit numbers: 20 μs1 E-6 sA microsecond is an SI unit of time equal to one millionth of a second. Its symbol is µs.A microsecond is equal to 1000 nanoseconds or 1/1000 millisecond...
- one 16-cycle instruction: 20 μs
Primary memory:
- Capacity: 8 kilowords
- Speed (cycle time): 1 μs1 E-6 sA microsecond is an SI unit of time equal to one millionth of a second. Its symbol is µs.A microsecond is equal to 1000 nanoseconds or 1/1000 millisecond...
- Complete, autonomous memory error checking
- Parity control
Punched tape
Punched tape
Punched tape or paper tape is an obsolete form of data storage, consisting of a long strip of paper in which holes are punched to store data...
reader:
- DielectricDielectricA dielectric is an electrical insulator that can be polarized by an applied electric field. When a dielectric is placed in an electric field, electric charges do not flow through the material, as in a conductor, but only slightly shift from their average equilibrium positions causing dielectric...
-based reading - Speed: 500 to 1,000 characters per secondSecondThe second is a unit of measurement of time, and is the International System of Units base unit of time. It may be measured using a clock....
- Accepts 5, 7 and 8-channel tapes
Tape puncher:
- Speed: 75 characters per secondSecondThe second is a unit of measurement of time, and is the International System of Units base unit of time. It may be measured using a clock....
Parallel Line Printer
Line printer
The line printer is a form of high speed impact printer in which one line of type is printed at a time. They are mostly associated with the early days of computing, but the technology is still in use...
667:
- "On the fly" printing
- 128 characters per line
- Removable/replaceable printing cylinder
- Speed:
- 500 lines per minuteMinuteA minute is a unit of measurement of time or of angle. The minute is a unit of time equal to 1/60th of an hour or 60 seconds. In the UTC time scale, a minute on rare occasions has 59 or 61 seconds; see leap second. The minute is not an SI unit; however, it is accepted for use with SI units...
for a character set of 63 characters - 550 lines per minuteMinuteA minute is a unit of measurement of time or of angle. The minute is a unit of time equal to 1/60th of an hour or 60 seconds. In the UTC time scale, a minute on rare occasions has 59 or 61 seconds; see leap second. The minute is not an SI unit; however, it is accepted for use with SI units...
for a character set of 50 characters
- 500 lines per minute
- Automatic paper feeder
- Two line spacing settings
- Programamtic tape for discontinuous paper movement
- Maximum number of carbon copiesCarbon copyCarbon copying, abbreviated cc or c.c., is the technique of using carbon paper to produce one or more copies simultaneously during the creation of paper documents...
: 6
Independent Printer M 30:
- 132 characters per line
- Speed:
- Prints 25 alphanumeric characters per secondSecondThe second is a unit of measurement of time, and is the International System of Units base unit of time. It may be measured using a clock....
- Prints 33 numeric characters per secondSecondThe second is a unit of measurement of time, and is the International System of Units base unit of time. It may be measured using a clock....
- Tabulation speed: 144 characters per secondSecondThe second is a unit of measurement of time, and is the International System of Units base unit of time. It may be measured using a clock....
- Blank printing speed: 100 characters per secondSecondThe second is a unit of measurement of time, and is the International System of Units base unit of time. It may be measured using a clock....
- Prints 25 alphanumeric characters per second
- Maximum number of carbon copiesCarbon copyCarbon copying, abbreviated cc or c.c., is the technique of using carbon paper to produce one or more copies simultaneously during the creation of paper documents...
: 6
Magnetic cassettes 4096:
- Capacity: 600,000 characters
- Variable record length
- Transfer rate: 857 characters per secondSecondThe second is a unit of measurement of time, and is the International System of Units base unit of time. It may be measured using a clock....
- Tape speed: 10 inches per secondSecondThe second is a unit of measurement of time, and is the International System of Units base unit of time. It may be measured using a clock....
Magnetic Tape Drives:
- Data format: 9-track ASCIIASCIIThe American Standard Code for Information Interchange is a character-encoding scheme based on the ordering of the English alphabet. ASCII codes represent text in computers, communications equipment, and other devices that use text...
with inter-record space of 0.6 inches (1.524 cm) - Data density: 556/800 bitBitA bit is the basic unit of information in computing and telecommunications; it is the amount of information stored by a digital device or other physical system that exists in one of two possible distinct states...
s per inch - Capacity per tape: circaCircaCirca , usually abbreviated c. or ca. , means "approximately" in the English language, usually referring to a date...
10,000,000 characters - Tape speed: 24 inches/sSecondThe second is a unit of measurement of time, and is the International System of Units base unit of time. It may be measured using a clock....
, 150 inches/sSecondThe second is a unit of measurement of time, and is the International System of Units base unit of time. It may be measured using a clock....
fast-forward and rewind - Transfer rate: 19.2 kHz
- Tape width: 1/2 inch (1.27 cm)
- Tape length: 2400 ft (731.52 m)
- Working ambient temperature range: 5°C to 40°C
- Relative humidity: up to 80%
- Integrated circuitIntegrated circuitAn integrated circuit or monolithic integrated circuit is an electronic circuit manufactured by the patterned diffusion of trace elements into the surface of a thin substrate of semiconductor material...
control logic - Separate control panel for each drive
- Read/Write Capabilities:
- Read and Write forward
- Read forward
- Read reverse
See also
- CER ComputersCER ComputersCER was a series of early computers developed by Mihajlo Pupin Institute in the 1960s and 1970s.Models:* CER-10 - 1960, based on vacuum tubes, transistors, electronic relays, and magnetic core memory...
- Mihajlo Pupin InstituteMihajlo Pupin InstituteMihajlo Pupin Institute is an institute based in Belgrade, Serbia notable for manufacturing numerous computer systems used in Socialist Federal Republic of Yugoslavia - especially early CER and later TIM line of computers. It is named after Mihajlo Idvorski Pupin.The Institute is well known in...
- History of computer hardware in the SFRYHistory of computer hardware in the SFRYThe Socialist Federal Republic of Yugoslavia was a socialist country that existed in the second half of the 20th century. Being communist meant that strict technology import rules and regulations shaped the development of computer history in the country, unlike in the Western world. However, since...

