Barker code
Encyclopedia
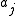 for
for 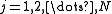
such that
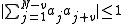
for all
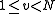 .
.Known Barker codes
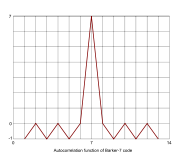
Here is a table of all known Barker codes, where negations and reversals of the codes have been omitted. A Barker code has a maximum autocorrelation sequence which has sidelobes no larger than 2, and which thus has better RMS performance than the codes below. The table below shows all known Barker codes; it is conjectured that no other perfect binary phase codes exist.| Length | Codes | |
|---|---|---|
| 2 | +1 −1 | +1 +1 |
| 3 | +1 +1 −1 | |
| 4 | +1 +1 −1 +1 | +1 +1 +1 −1 |
| 5 | +1 +1 +1 −1 +1 | |
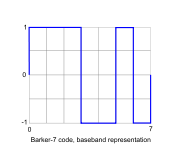
| 7 | +1 +1 +1 −1 −1 +1 −1 | |
| 11 | +1 +1 +1 −1 −1 −1 +1 −1 −1 +1 −1 | |
| 13 | +1 +1 +1 +1 +1 −1 −1 +1 +1 −1 +1 −1 +1 | |
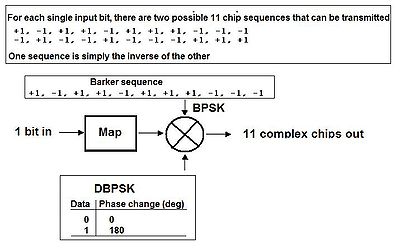
Barker codes of length 11 and 13 are used in direct-sequence spread spectrum
Direct-sequence spread spectrum
In telecommunications, direct-sequence spread spectrum is a modulation technique. As with other spread spectrum technologies, the transmitted signal takes up more bandwidth than the information signal that is being modulated. The name 'spread spectrum' comes from the fact that the carrier signals...
and pulse compression radar
Pulse compression
Pulse compression is a signal processing technique mainly used in radar, sonar and echography to increase the range resolution as well as the signal to noise ratio...
systems because of their low autocorrelation
Autocorrelation
Autocorrelation is the cross-correlation of a signal with itself. Informally, it is the similarity between observations as a function of the time separation between them...
properties.
The +ve and -ve amplitudes of the pulses forming the Barker codes imply the use of biphase modulation; that is, the change of phase in the carrier wave
Carrier wave
In telecommunications, a carrier wave or carrier is a waveform that is modulated with an input signal for the purpose of conveying information. This carrier wave is usually a much higher frequency than the input signal...
is 180 degrees.
A Barker code resembles a discrete version of a continuous chirp
Chirp
A chirp is a signal in which the frequency increases or decreases with time. In some sources, the term chirp is used interchangeably with sweep signal. It is commonly used in sonar and radar, but has other applications, such as in spread spectrum communications...
, another low-autocorrelation signal used in other pulse compression radars.
Pseudorandom number sequences can be thought of as cyclic Barker Codes, having perfect (and uniform) cyclic autocorrelation sidelobes. Very long pseudorandom number sequences can be constructed.
Similar to the Barker Codes are the complementary sequences, which cancel sidelobes exactly; the pair of 4 baud Barker Codes in the table form a complementary pair. There is a simple constructive method to create arbitrarily long complementary sequences.
Barker Modulation