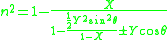Appleton-Hartree equation
Encyclopedia
The Appleton-Hartree equation, sometimes also referred to as the Appleton-Lassen equation is a mathematical expression that describes the refractive index
for electromagnetic wave propagation in a cold magnetized plasma
. The Appleton-Hartree equation was developed independently by several different scientists, including Edward Victor Appleton
, Douglas Hartree
and German radio physicist H. K. Lassen. Lassen's work, completed two years prior to Appleton and five years prior to Hartree, included a more thorough treatment of collisional plasma; but, published only in German, it has not been widely read in the English speaking world of radio physics.
can be written as an expression for the frequency (squared), but it is also common to write it as an expression for the index of refraction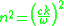 .
.
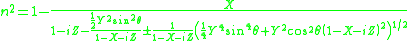
or, alternatively, with damping term Z = 0 and rearranging terms:
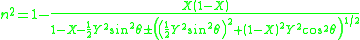
 = complex refractive index
= complex refractive index
 =
= 
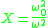
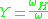
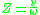
 = electron collision frequency
= electron collision frequency
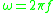 (radial frequency)
(radial frequency)
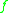 = wave frequency (cycles per second, or Hertz
= wave frequency (cycles per second, or Hertz
)
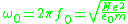 = electron plasma frequency
= electron plasma frequency
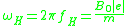 = electron gyro frequency
= electron gyro frequency
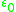 = permittivity of free space
= permittivity of free space
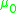 = permeability of free space
= permeability of free space
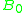 = ambient magnetic field
= ambient magnetic field
strength
 = electron charge
= electron charge
 = electron mass
= electron mass
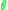 = angle between the ambient magnetic field
= angle between the ambient magnetic field
vector and the wave vector
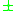 sign in the Appleton-Hartree equation gives two separate solutions for the refractive index. For propagation perpendicular to the magnetic field, i.e.,
sign in the Appleton-Hartree equation gives two separate solutions for the refractive index. For propagation perpendicular to the magnetic field, i.e., 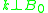 , the '+' sign represents the "ordinary mode," and the '-' sign represents the "extraordinary mode." For propagation parallel to the magnetic field, i.e.,
, the '+' sign represents the "ordinary mode," and the '-' sign represents the "extraordinary mode." For propagation parallel to the magnetic field, i.e., 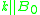 , the '+' sign represents a left-hand circularly polarized mode, and the '-' sign represents a right-hand circularly polarized mode. See the article on electromagnetic electron wave
, the '+' sign represents a left-hand circularly polarized mode, and the '-' sign represents a right-hand circularly polarized mode. See the article on electromagnetic electron wave
s for more detail.
K is the vector of the propagation plane.
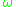 is much smaller than the electron collision frequency
is much smaller than the electron collision frequency  , the plasma can be said to be "collisionless." That is, given the condition
, the plasma can be said to be "collisionless." That is, given the condition
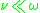 ,
,
we have
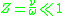 ,
,
so we can neglect the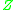 terms in the equation. The Appleton-Hartree equation for a cold, collisionless plasma is therefore,
terms in the equation. The Appleton-Hartree equation for a cold, collisionless plasma is therefore,
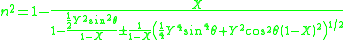
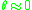 , we can neglect the
, we can neglect the 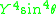 term above. Thus, for quasi-longitudinal propagation in a cold, collisionless plasma, the Appleton-Hartree equation becomes,
term above. Thus, for quasi-longitudinal propagation in a cold, collisionless plasma, the Appleton-Hartree equation becomes,
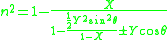
Refractive index
In optics the refractive index or index of refraction of a substance or medium is a measure of the speed of light in that medium. It is expressed as a ratio of the speed of light in vacuum relative to that in the considered medium....
for electromagnetic wave propagation in a cold magnetized plasma
Plasma (physics)
In physics and chemistry, plasma is a state of matter similar to gas in which a certain portion of the particles are ionized. Heating a gas may ionize its molecules or atoms , thus turning it into a plasma, which contains charged particles: positive ions and negative electrons or ions...
. The Appleton-Hartree equation was developed independently by several different scientists, including Edward Victor Appleton
Edward Victor Appleton
Sir Edward Victor Appleton, GBE, KCB, FRS was an English physicist.-Biography:Appleton was born in Bradford, West Yorkshire and educated at Hanson Grammar School. At the age of 18 he won a scholarship to St John's College, Cambridge...
, Douglas Hartree
Douglas Hartree
Douglas Rayner Hartree PhD, FRS was an English mathematician and physicist most famous for the development of numerical analysis and its application to the Hartree-Fock equations of atomic physics and the construction of the meccano differential analyser.-Early life:Douglas Hartree was born in...
and German radio physicist H. K. Lassen. Lassen's work, completed two years prior to Appleton and five years prior to Hartree, included a more thorough treatment of collisional plasma; but, published only in German, it has not been widely read in the English speaking world of radio physics.
Equation
The dispersion relationDispersion relation
In physics and electrical engineering, dispersion most often refers to frequency-dependent effects in wave propagation. Note, however, that there are several other uses of the word "dispersion" in the physical sciences....
can be written as an expression for the frequency (squared), but it is also common to write it as an expression for the index of refraction
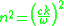 .
.Full Equation
The equation is typically given as follows :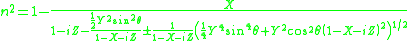
or, alternatively, with damping term Z = 0 and rearranging terms:
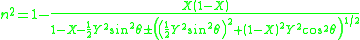
Definition of Terms
 = complex refractive index
= complex refractive index =
= 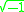
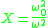
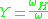
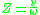
 = electron collision frequency
= electron collision frequency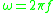 (radial frequency)
(radial frequency)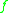 = wave frequency (cycles per second, or Hertz
= wave frequency (cycles per second, or HertzHertz
The hertz is the SI unit of frequency defined as the number of cycles per second of a periodic phenomenon. One of its most common uses is the description of the sine wave, particularly those used in radio and audio applications....
)
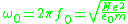 = electron plasma frequency
= electron plasma frequency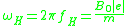 = electron gyro frequency
= electron gyro frequency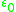 = permittivity of free space
= permittivity of free space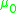 = permeability of free space
= permeability of free space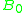 = ambient magnetic field
= ambient magnetic fieldMagnetic field
A magnetic field is a mathematical description of the magnetic influence of electric currents and magnetic materials. The magnetic field at any given point is specified by both a direction and a magnitude ; as such it is a vector field.Technically, a magnetic field is a pseudo vector;...
strength
 = electron charge
= electron charge = electron mass
= electron mass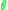 = angle between the ambient magnetic field
= angle between the ambient magnetic fieldMagnetic field
A magnetic field is a mathematical description of the magnetic influence of electric currents and magnetic materials. The magnetic field at any given point is specified by both a direction and a magnitude ; as such it is a vector field.Technically, a magnetic field is a pseudo vector;...
vector and the wave vector
Wave vector
In physics, a wave vector is a vector which helps describe a wave. Like any vector, it has a magnitude and direction, both of which are important: Its magnitude is either the wavenumber or angular wavenumber of the wave , and its direction is ordinarily the direction of wave propagation In...
Modes of Propagation
The presence of the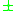 sign in the Appleton-Hartree equation gives two separate solutions for the refractive index. For propagation perpendicular to the magnetic field, i.e.,
sign in the Appleton-Hartree equation gives two separate solutions for the refractive index. For propagation perpendicular to the magnetic field, i.e., 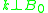 , the '+' sign represents the "ordinary mode," and the '-' sign represents the "extraordinary mode." For propagation parallel to the magnetic field, i.e.,
, the '+' sign represents the "ordinary mode," and the '-' sign represents the "extraordinary mode." For propagation parallel to the magnetic field, i.e., 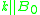 , the '+' sign represents a left-hand circularly polarized mode, and the '-' sign represents a right-hand circularly polarized mode. See the article on electromagnetic electron wave
, the '+' sign represents a left-hand circularly polarized mode, and the '-' sign represents a right-hand circularly polarized mode. See the article on electromagnetic electron waveElectromagnetic electron wave
An electromagnetic electron wave is a wave in a plasma which has a magnetic field component and in which primarily the electrons oscillate.In an unmagnetized plasma, an electromagnetic electron wave is simply a light wave modified by the plasma...
s for more detail.
K is the vector of the propagation plane.
Propagation in a Collisionless Plasma
If the wave frequency of interest is much smaller than the electron collision frequency
is much smaller than the electron collision frequency  , the plasma can be said to be "collisionless." That is, given the condition
, the plasma can be said to be "collisionless." That is, given the condition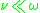 ,
,we have
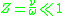 ,
,so we can neglect the
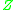 terms in the equation. The Appleton-Hartree equation for a cold, collisionless plasma is therefore,
terms in the equation. The Appleton-Hartree equation for a cold, collisionless plasma is therefore,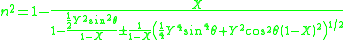
Quasi-Longitudinal Propagation in a Collisionless Plasma
If we further assume that the wave propagation is primarily in the direction of the magnetic field, i.e.,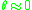 , we can neglect the
, we can neglect the 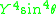 term above. Thus, for quasi-longitudinal propagation in a cold, collisionless plasma, the Appleton-Hartree equation becomes,
term above. Thus, for quasi-longitudinal propagation in a cold, collisionless plasma, the Appleton-Hartree equation becomes,