Anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction
Encyclopedia
Surgery
Surgery is an ancient medical specialty that uses operative manual and instrumental techniques on a patient to investigate and/or treat a pathological condition such as disease or injury, or to help improve bodily function or appearance.An act of performing surgery may be called a surgical...
tissue graft
Medical grafting
Grafting refers to a surgical procedure to move tissue from one site to another on the body, or from another person, without bringing its own blood supply with it. Instead, a new blood supply grows in after it is placed. A similar technique where tissue is transferred with the blood supply intact...
replacement of the anterior cruciate ligament
Anterior cruciate ligament
The anterior cruciate ligament is a cruciate ligament which is one of the four major ligaments of the human knee. In the quadruped stifle , based on its anatomical position, it is referred to as the cranial cruciate ligament.The ACL originates from deep within the notch of the distal femur...
, located in the knee
Knee
The knee joint joins the thigh with the leg and consists of two articulations: one between the fibula and tibia, and one between the femur and patella. It is the largest joint in the human body and is very complicated. The knee is a mobile trocho-ginglymus , which permits flexion and extension as...
, to restore its function after anterior cruciate ligament injury
Anterior cruciate ligament injury
An injury to the anterior cruciate ligament can be a debilitating musculoskeletal injury to the knee, seen most often in athletes. Non-contact tears and ruptures are the most common causes of ACL injury....
. The torn ligament
Ligament
In anatomy, the term ligament is used to denote any of three types of structures. Most commonly, it refers to fibrous tissue that connects bones to other bones and is also known as articular ligament, articular larua, fibrous ligament, or true ligament.Ligament can also refer to:* Peritoneal...
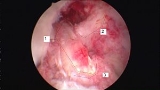
is removed from the knee before the graft is inserted through a hole created by a single hole punch. The surgery is performed arthroscopically
Arthroscopy
Arthroscopy is a minimally invasive surgical procedure in which an examination and sometimes treatment of damage of the interior of a joint is performed using an arthroscope, a type of endoscope that is inserted into the joint through a small incision...
.
An ACL reconstruction is sometimes referred to, incorrectly, as an ACL repair. A torn anterior cruciate ligament cannot be "repaired", and must instead be reconstructed with a tissue graft replacement.
Autograft vs. allograft
- An autograft involves the medical grafting of bone or tissue from the patient's body.
- An allograft is the use of bone or tissue from a donor's (typically a cadaverCadaverA cadaver is a dead human body.Cadaver may also refer to:* Cadaver tomb, tomb featuring an effigy in the form of a decomposing body* Cadaver , a video game* cadaver A command-line WebDAV client for Unix....
's) body.
The patellar tendon, anterior tibialis tendon, or Achilles tendon
Achilles tendon
The Achilles tendon , also known as the calcaneal tendon or the tendo calcaneus, is a tendon of the posterior leg. It serves to attach the plantaris, gastrocnemius and soleus muscles to the calcaneus bone.- Anatomy :The Achilles is the tendonous extension of 3 muscles in the lower leg:...
may be recovered from a cadaver
Cadaver
A cadaver is a dead human body.Cadaver may also refer to:* Cadaver tomb, tomb featuring an effigy in the form of a decomposing body* Cadaver , a video game* cadaver A command-line WebDAV client for Unix....
and used as an allograft in reconstruction. The Achilles tendon, due to its large size, must be shaved to fit within the joint cavity. There is a slight chance of rejection, which would lead to more surgery to remove the graft and replace it.
Sterilization processes exist today that make allografts a safe choice for patients. However, with allografts that are irradiated
Irradiation
Irradiation is the process by which an object is exposed to radiation. The exposure can originate from various sources, including natural sources. Most frequently the term refers to ionizing radiation, and to a level of radiation that will serve a specific purpose, rather than radiation exposure to...
to remove infectious agents, there is a risk of weakening the selected tendon, although for ACL surgery the weakened tendon is generally as strong as the replaced ligament. Even with the extensive and redundant screening process for irradiated donor grafts, a risk of infection remains and it would be cause to remove the graft. Therefore, the option to use an irradiated allograft runs the largest health risk.
Patellar tendon
Tendon
A tendon is a tough band of fibrous connective tissue that usually connects muscle to bone and is capable of withstanding tension. Tendons are similar to ligaments and fasciae as they are all made of collagen except that ligaments join one bone to another bone, and fasciae connect muscles to other...
connects the patella (kneecap) to the tibia
Tibia
The tibia , shinbone, or shankbone is the larger and stronger of the two bones in the leg below the knee in vertebrates , and connects the knee with the ankle bones....
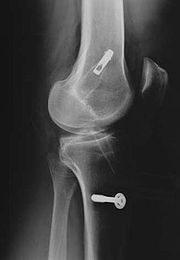
(shin). The graft is taken from the injured knee, but in some circumstances, such as a second operation, the other knee may be used. The middle third of the tendon is used, with bone fragments removed on each end. The graft is then threaded through holes drilled in the tibia and femur
Femur
The femur , or thigh bone, is the most proximal bone of the leg in tetrapod vertebrates capable of walking or jumping, such as most land mammals, birds, many reptiles such as lizards, and amphibians such as frogs. In vertebrates with four legs such as dogs and horses, the femur is found only in...
, and finally screwed into place.
The graft is slightly larger than a hamstring
Hamstring
In human anatomy, the hamstring refers to any one of the three posterior thigh muscles, or to the tendons that make up the borders of the space behind the knee. In modern anatomical contexts, however, they usually refer to the posterior thigh muscles, or the tendons of the semitendinosus, the...
graft, however graft size is not a determinant of outcome. The most important factor in determining the outcome is correct graft placement.
The disadvantages include:
1. Increased wound
Wound
A wound is a type of injury in which skin is torn, cut or punctured , or where blunt force trauma causes a contusion . In pathology, it specifically refers to a sharp injury which damages the dermis of the skin.-Open:...
pain.
2. Increased scar formation as compared to a hamstring tendon operation.
3. Risk of fracturing the patella during harvesting of the graft.
4. Increased risk of tendinitis.
5. Increased levels of pain with activities that require kneeling years after post op.
Hamstring tendon
Gracilis muscle
The gracilis is the most superficial muscle on the medial side of the thigh. It is thin and flattened, broad above, narrow and tapering below.-Origin and insertion:...
tendon for a stronger graft. The semitendinosus is an accessory hamstring (the primary hamstrings are left intact), and the gracilis is actually not a hamstring, but an accessory adductor (the primary adductors are left intact as well). The two tendons are commonly combined and referred to as a four strand hamstring graft, made by a long piece (about 25 cm) which is removed from each tendon. The tendon segments are folded and braided together to form a quadruple thickness strand for the replacement graft. The braided segment is threaded through the heads of tibia and femur and its ends fixated with screws on the opposite sides of the two bones.
Unlike the patellar tendon, the hamstring tendon's fixation to the bone can be affected by motion in the post-operative phase. Therefore, following surgery, a brace is often used to immobilize the knee for one to two weeks while the most critical healing takes place. Evidence suggests that the hamstring tendon graft does just as well, or nearly as well, as the patellar tendon graft in the long-term.
The main surgical wound is over the upper proximal tibia, avoiding the typical pain sensation when one kneels down. The wound is typically smaller than the patellar tendon graft and hence less pain after the operation. A new technique for minimal-invasive harvesting from the back of the knee has been developed in the last years. This technique is faster, easier and produces a significantly smaller wound. Patients are typically discharged from the hospital within two days after surgery.
There seems to be some controversy as to how well a hamstring tendon regenerates after the harvesting. Most studies suggest that the tendon can be regenerated at least partially, while still being inferior in strength to the original tendon.
Choice of graft
No ideal graft site for ACL reconstruction exists; they all have advantages and disadvantages. Patella tendon grafts are still considered the historical "gold standard" for knee stability by surgeons, however they suffer a slightly higher complication rate, including knee pain such as when doing a lunge. Hamstring grafts historically had problems with fixation slippage and stretching out over time. Modern fixation methods of hamstrings avoid graft slippage, producing outcomes that are the same in terms of knee stability with easier rehabilitation, less anterior knee pain and less joint stiffness. An allograft is a graft from a corpse, usually either a patellar tendon, hamstring tendon, and occasionally an achilles tendon. The advantage of an allograft is the patient does not sustain additional injury through removing a tendon, thus making it faster to recover. The disadvantage is the risk of infection by using foreign bodily materials and the graft is known to be slightly weaker. A lesser known, but newer type of graft is a synthetic graft. Little data exists on its strength or reliability, but patients should be aware that the option exists. Typically, age and lifestyle choices help decide the type of graft to be used for ACL reconstruction. The overall factors in knee stability are correct graft placement by the surgeon and treatment of other menisco-ligament injuries in the knee, rather than choice of graft.Recovery
Initial physical therapyPhysical therapy
Physical therapy , often abbreviated PT, is a health care profession. Physical therapy is concerned with identifying and maximizing quality of life and movement potential within the spheres of promotion, prevention, diagnosis, treatment/intervention,and rehabilitation...
consists of range of motion
Range of motion
Range of motion , is the distance that a movable object may normally travel while properly attached to another object. It is also called range of travel, particularly when talking about mechanical devices and in mechanical engineering fields...
(ROM) exercises, often with the guidance of a physical therapist. Range of motion exercises are used to regain the flexibility of the ligament, prevent or break down scar tissue
Scar tissue
Scar tissue can refer to:*Granulation tissue, a product of healing in major wounds*The tissue of a scar*"Scar Tissue", a Red Hot Chili Peppers song*Scar Tissue , the autobiography of Anthony Kiedis, lead singer of the Red Hot Chili Peppers...
from forming and reduce loss of muscle
Muscle
Muscle is a contractile tissue of animals and is derived from the mesodermal layer of embryonic germ cells. Muscle cells contain contractile filaments that move past each other and change the size of the cell. They are classified as skeletal, cardiac, or smooth muscles. Their function is to...
tone. Range of motion exercise examples include: quadriceps contractions and straight leg raises. In some cases, a continuous passive motion
Continuous passive motion
Continuous passive motion devices are used during the first phase of rehabilitation following a soft tissue surgical procedure or trauma. The goals of phase 1 rehabilitation are Control post-operative pain, Reduce inflammation, Provide passive motion in a specific plane of movement , and Protect...
(CPM) device is used immediately after surgery to help with flexibility. The preferred method of preventing muscle loss is isometric exercise
Isometric exercise
Isometric exercise or isometrics are a type of strength training in which the joint angle and muscle length do not change during contraction...
s that put zero strain on the knee. Knee extension within two weeks is important with many rehab guidelines.
Approximately six weeks is required for the bone to attach to the graft. However, the patient can typically walk on their own and perform simple physical tasks prior to this with caution, relying on the surgical fixation of the graft until true healing (graft attachment to bone) has taken place. At this stage the first round of physical therapy can begin. This usually consists of careful exercises to regain flexibility and small amounts of strength. One of the more important benchmarks in recovery is the twelve weeks post-surgery period. After this, the patient can typically begin a more aggressive regimen of exercises involving stress on the knee, and increasing resistance. Jogging
Jogging
Jogging is a form of trotting or running at a slow or leisurely pace. The main intention is to increase fitness with less stress on the body than from faster running.-Definition:...
may be incorporated as well.
After four months, more intense activities such as running
Running
Running is a means of terrestrial locomotion allowing humans and other animals to move rapidly on foot. It is simply defined in athletics terms as a gait in which at regular points during the running cycle both feet are off the ground...
are possible without risk. After five months, light ball work may commence as the ligament is nearly regenerated. After six months, the reconstructed ACL is generally at full strength (ligament
Ligament
In anatomy, the term ligament is used to denote any of three types of structures. Most commonly, it refers to fibrous tissue that connects bones to other bones and is also known as articular ligament, articular larua, fibrous ligament, or true ligament.Ligament can also refer to:* Peritoneal...
tissue has fully regrown), and the patient may return to activities involving cutting and twisting if a brace is worn. Recovery varies highly from case to case, and sometimes resumption of stressful activities may take a year or longer.
The reconstructed ACL has a high success rate. Studies show that cases in which the ACL retears are generally caused by a traumatic impact. Some studies indicate that wearing a brace during athletic activity does not reduce probability of re-injury to the ACL, but a study of active post-ACL replacement skiers shows a 300% reduction in re-injury likelihood by using a knee brace after recovery. A sufficiently traumatic impact to retear the ACL is unlikely to be mitigated by the use of a brace.
Phase 1 (0-2 weeks)
The goals of this phase are to:- Eliminate swelling due to activity
- Progress from partial weight bearing to full weight bearing exercises
- Regain normal range of motion
- Increase quadriceps strength
- Increase hamstring strength
Some equipment that can be used and exercises that can be performed are:
- Use of Cryo-cuff
-
- - provides cold compression
- Isometric Contraction of Quads
- Quad Sets
- - stand against wall, push extended knee against rolled towel
- - progress to straight leg raised to 30deg.
- Wall Slides
- - To increase knee flexion
- Assisted Knee Flexion
- Towel Squeeze
- - Sit in chair, squeeze rolled towel between knees for 5 seconds. Relax & repeat.
- VMO Strengthening Exercise
- Supported Bilateral Calf-Raises
- - provides cold compression
Phase 2 (2-12 weeks)
The goals of this phase are to:- Regain full knee extension
- Restore knee flexion to +130°
- Perform a full squat properly
- Regain good balance and control
- Reestablish proper gait
- walk with crutches
Some exercises that can be performed are:
- Mini squats
-
- - Progress to full squats → single-leg half squat
- Mini Lunges
- - Progress to full lunges
- Leg Press
- - Double-leg → single
- Step-ups
- - lateral & forward
- Bridges
- - Double-leg → single
- - Floor → Swiss ball
- Hip Abduction w/ Theraband
- Hip Extension w/ Theraband
- Wobble board
- - Assisted → un-assisted → eyes closed (assisted → unassisted)
- Stork Stand
- - Assisted → un-assisted → eyes closed (assisted → unassisted) → unstable surface
- Static Proprioceptive hold/ball throwing
- Functional Exercises that can be performed at this time include:
- - Walking
- - Bike
- - Roman Chair
- - Progress to full squats → single-leg half squat
Phase 3 (3-6 months)
The goals of this phase are to:- Regain full range of motion
- Regain full strength and power
- Increase agility
- allows for adaption to direction change, acceleration and deceleration
- Be able to perform restricted sports-specific drills
- Begin plyometric drills
Some exercises that can be performed are:
- Continue exercises from Phase 2, progress as necessary
- Jump & Land drills
-
- - Jump from block & stick landing
- - Double-leg landing → single-leg
- Plyometric Drills
- - Jumping over blocks, sideways & forward
- - Hopping up & down steps/stairs
Phase 4 (6-12 months)
The goal of this phase is a return to activity, however it requires an ability to perform some functional performance tests such as:- Agility Tests
- Illinois Agility TestIllinois agility testThe Illinois agility test is a fitness test designed to test one's sport agility. It is a simple test which is easy to administer and requires little equipment. It tests the ability to turn in different directions and at different angles....
- Zig Zag Agility Test
- These tests are used to test the ability of the knee to withstand cutting and planting maneuvers
- Standing Vertical Jump
- Here you jump straight in the air from a standing start and land on two feet as stable as possible.
- Heiden Hop Test
- Here you essentially jump as far as possible with the uninjured leg and land on the injured leg. Your ability to stick the landing is indicative of good knee function.
- Isokinetic Testing
- This is used to evaluate muscle strength.
- The individual should have at least 90% quadricep strength of the uninjured leg
- They should also have equal hamstring strength to their uninjured leg as well
Cost and logistics of the procedure
The cost of ACL surgery is an unfortunate reality which affects whether or not a patient proceeds with the operation. The average out-of-pocket cost of ACL reconstruction is $2,339.43, according to a 2010 survey of ACL surgery patients. Insurance companies may or may not cover the various billable components of ACL reconstruction, which may include: pre-op appointments, pre-op physical therapy, ACL reconstruction by the surgeon, an assistant's charge, anesthesia, the hospital or facility fee, rental fees for cryotherapy, prescriptions, transportation, crutches or wheel chair fees, leg brace fees, post op visits (such as to remove drain plugs and monitor swelling), and a physical therapy rehab program.Despite the complexity of the procedure and numerous doctor visits involved, 80% - 90% of patients who have had the surgery said they had favorable results.
External links
- Anterior Cruciate Ligament (ACL) Reconstruction - The KNEEguru
- Dawn Hastreiter, ACL Reconstruction, University of Washington, UWMC Roosevelt Clinic, Musculoskeletal Radiology.
- ACL and Computer Aided ACL Reconstruction Presentation
- Anterior Cruciate Ligament (ACL) Graft Options
- ACL Reconstruction videos
- Arthrosopic Surgery ACL Reconstruction Video
- Information for patients - Anterior Cruciate Ligament Reconstruction - Oxford Clinic
- Patient's comprehensive guide to the ACL - Illinois Sports Medicine and Orthopaedic Center Method for Anterior Cruciate Ligament Reconstruction, ArthrexArthrexArthrex Inc. is a manufacturing company that makes orthopedic surgical supplies. Arthrex began in 1981 as Arthroscopy Excision Instruments Inc. in Munich, Germany. The company moved its headquarters to Naples, Florida in 1991. Its manufacturing arm, Arthrex Manufacturing Inc. was incorporated in...
Corp., issued September 23, 2003 - ACL Post-Surgery Blog
- ACL Diary - Torn ACL Surgery

