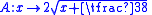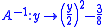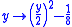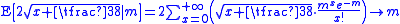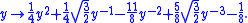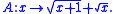Anscombe transform
Encyclopedia
In statistics
, the Anscombe transform, named after Francis Anscombe
, is a variance-stabilizing transformation
that transforms a random variable
with a Poisson distribution
into one with an approximately standard Gaussian distribution. The Anscombe transform is widely used in photon-limited imaging (astronomy, X-ray) where images naturally follow the Poisson law. The Anscombe transform is usually used to pre-process the data in order to make the standard deviation
approximately constant. Then denoising
algorithms designed for the framework of additive white Gaussian noise
are used; the final estimate is then obtained by applying an inverse Anscombe transformation to the denoised data.
the mean and variance
and variance  are not independent:
are not independent:  . The Anscombe transform
. The Anscombe transform
aims at transforming the data so that the variance is set approximately 1 whatever the mean. It transforms Poissonian data to approximately Gaussian data of standard deviation 1. This approximation is valid provided that the mean value of the Poissonian data
of the Poissonian data  is larger than 4.
is larger than 4.
 an estimate of
an estimate of  ), its inverse transform is also needed
), its inverse transform is also needed
in order to return the variance-stabilized and denoised data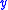 to the original range.
to the original range.
Applying the algebraic inverse
usually introduces undesired bias
to the estimate of the mean , because the forward square-root
, because the forward square-root
transform is not linear. Sometimes using the asymptotically unbiased inverse
mitigates the issue of bias, but this is not the case in photon-limited imaging, for which
the exact unbiased inverse given by the implicit mapping
should be used. A closed-form
approximation of this exact unbiased inverse is
a family of such transformations which includes the Anscombe transform. Another member of the family is the Freeman–Tukey transformation
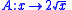
A simplified transformation is
which, while it is not quite so good at stabilizing the variance, has the advantage of being more easily understood.
Statistics
Statistics is the study of the collection, organization, analysis, and interpretation of data. It deals with all aspects of this, including the planning of data collection in terms of the design of surveys and experiments....
, the Anscombe transform, named after Francis Anscombe
Francis Anscombe
Francis John Anscombe was a statistician.Born in Hove in England, Anscombe was educated at Trinity College at Cambridge University...
, is a variance-stabilizing transformation
Variance-stabilizing transformation
In applied statistics, a variance-stabilizing transformation is a data transformation that is specifically chosen either to simplify considerations in graphical exploratory data analysis or to allow the application of simple regression-based or analysis of variance techniques.The aim behind the...
that transforms a random variable
Random variable
In probability and statistics, a random variable or stochastic variable is, roughly speaking, a variable whose value results from a measurement on some type of random process. Formally, it is a function from a probability space, typically to the real numbers, which is measurable functionmeasurable...
with a Poisson distribution
Poisson distribution
In probability theory and statistics, the Poisson distribution is a discrete probability distribution that expresses the probability of a given number of events occurring in a fixed interval of time and/or space if these events occur with a known average rate and independently of the time since...
into one with an approximately standard Gaussian distribution. The Anscombe transform is widely used in photon-limited imaging (astronomy, X-ray) where images naturally follow the Poisson law. The Anscombe transform is usually used to pre-process the data in order to make the standard deviation
Standard deviation
Standard deviation is a widely used measure of variability or diversity used in statistics and probability theory. It shows how much variation or "dispersion" there is from the average...
approximately constant. Then denoising
Noise reduction
Noise reduction is the process of removing noise from a signal.All recording devices, both analogue or digital, have traits which make them susceptible to noise...
algorithms designed for the framework of additive white Gaussian noise
Additive white Gaussian noise
Additive white Gaussian noise is a channel model in which the only impairment to communication is a linear addition of wideband or white noise with a constant spectral density and a Gaussian distribution of amplitude. The model does not account for fading, frequency selectivity, interference,...
are used; the final estimate is then obtained by applying an inverse Anscombe transformation to the denoised data.
Definition
For the Poisson distributionPoisson distribution
In probability theory and statistics, the Poisson distribution is a discrete probability distribution that expresses the probability of a given number of events occurring in a fixed interval of time and/or space if these events occur with a known average rate and independently of the time since...
the mean
 and variance
and variance  are not independent:
are not independent:  . The Anscombe transform
. The Anscombe transformaims at transforming the data so that the variance is set approximately 1 whatever the mean. It transforms Poissonian data to approximately Gaussian data of standard deviation 1. This approximation is valid provided that the mean value
 of the Poissonian data
of the Poissonian data  is larger than 4.
is larger than 4.Inversion
When the Anscombe transform is used in denoising (i.e. when the goal is to obtain from an estimate of
an estimate of  ), its inverse transform is also needed
), its inverse transform is also neededin order to return the variance-stabilized and denoised data
 to the original range.
to the original range.Applying the algebraic inverse
Inverse function
In mathematics, an inverse function is a function that undoes another function: If an input x into the function ƒ produces an output y, then putting y into the inverse function g produces the output x, and vice versa. i.e., ƒ=y, and g=x...
usually introduces undesired bias
Bias of an estimator
In statistics, bias of an estimator is the difference between this estimator's expected value and the true value of the parameter being estimated. An estimator or decision rule with zero bias is called unbiased. Otherwise the estimator is said to be biased.In ordinary English, the term bias is...
to the estimate of the mean
 , because the forward square-root
, because the forward square-roottransform is not linear. Sometimes using the asymptotically unbiased inverse
mitigates the issue of bias, but this is not the case in photon-limited imaging, for which
the exact unbiased inverse given by the implicit mapping
should be used. A closed-form
Closed-form expression
In mathematics, an expression is said to be a closed-form expression if it can be expressed analytically in terms of a bounded number of certain "well-known" functions...
approximation of this exact unbiased inverse is
Alternatives
There are many other possible variance-stabilizing transformations for the Poisson distribution. Bar-Lev and Enis reporta family of such transformations which includes the Anscombe transform. Another member of the family is the Freeman–Tukey transformation
A simplified transformation is
which, while it is not quite so good at stabilizing the variance, has the advantage of being more easily understood.