
Annihilator method
Encyclopedia
In mathematics
, the annihilator method is a procedure used to find a particular solution to certain types of inhomogeneous ordinary differential equation
s. It is similar to the method of undetermined coefficients
, but instead of guessing the particular solution in the method of undetermined coefficients
, the particular solution is determined systematically in this technique. The phrase undetermined coefficients can also be used to refer to the step in the annihilator method in which the coefficients are calculated.
The annihilator method is used as follows. Given the ODE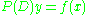 , find another differential operator
, find another differential operator
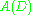 such that
such that 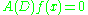 . This operator is called the annihilator, thus giving the method its name. Applying
. This operator is called the annihilator, thus giving the method its name. Applying 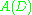 to both sides of the ODE gives a homogeneous ODE
to both sides of the ODE gives a homogeneous ODE 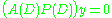 for which we find a solution basis
for which we find a solution basis 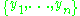 as before. Then the original inhomogeneous ODE is used to construct a system of equations restricting the coefficients of the linear combination to satisfy the ODE.
as before. Then the original inhomogeneous ODE is used to construct a system of equations restricting the coefficients of the linear combination to satisfy the ODE.
This method is not as general as variation of parameters in the sense that an annihilator does not always exist.
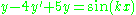 ,
, 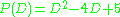 .
.
The simplest annihilator of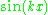 is
is 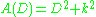 . The zeros of
. The zeros of 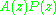 are
are 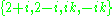 , so the solution basis of
, so the solution basis of 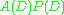 is
is 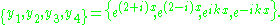
Setting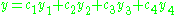 we find
we find
giving the system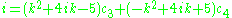
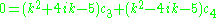
which has solutions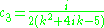 ,
, 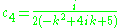
giving the solution set
This solution can be broken down into the homogeneous and nonhomogeneous parts. In particular,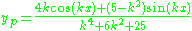 is a particular integral for the nonhomogeneous differential equation, and
is a particular integral for the nonhomogeneous differential equation, and 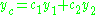 is a complementary solution to the corresponding homogeneous equation. The values of
is a complementary solution to the corresponding homogeneous equation. The values of 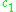 and
and 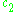 are determined usually through a set of initial conditions. Since this is a second-order equation, two such conditions are necessary to determine these values.
are determined usually through a set of initial conditions. Since this is a second-order equation, two such conditions are necessary to determine these values.
The fundamental solutions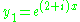 and
and 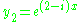 can be further rewritten using Euler's formula
can be further rewritten using Euler's formula
:
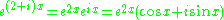
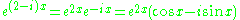
Then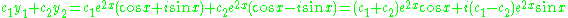 , and a suitable reassignment of the constants gives a simpler and more understandable form of the complementary solution,
, and a suitable reassignment of the constants gives a simpler and more understandable form of the complementary solution, 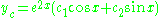 .
.
Mathematics
Mathematics is the study of quantity, space, structure, and change. Mathematicians seek out patterns and formulate new conjectures. Mathematicians resolve the truth or falsity of conjectures by mathematical proofs, which are arguments sufficient to convince other mathematicians of their validity...
, the annihilator method is a procedure used to find a particular solution to certain types of inhomogeneous ordinary differential equation
Ordinary differential equation
In mathematics, an ordinary differential equation is a relation that contains functions of only one independent variable, and one or more of their derivatives with respect to that variable....
s. It is similar to the method of undetermined coefficients
Method of undetermined coefficients
In mathematics, the method of undetermined coefficients, also known as the lucky guess method, is an approach to finding a particular solution to certain inhomogeneous ordinary differential equations and recurrence relations...
, but instead of guessing the particular solution in the method of undetermined coefficients
Method of undetermined coefficients
In mathematics, the method of undetermined coefficients, also known as the lucky guess method, is an approach to finding a particular solution to certain inhomogeneous ordinary differential equations and recurrence relations...
, the particular solution is determined systematically in this technique. The phrase undetermined coefficients can also be used to refer to the step in the annihilator method in which the coefficients are calculated.
The annihilator method is used as follows. Given the ODE
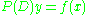 , find another differential operator
, find another differential operatorDifferential operator
In mathematics, a differential operator is an operator defined as a function of the differentiation operator. It is helpful, as a matter of notation first, to consider differentiation as an abstract operation, accepting a function and returning another .This article considers only linear operators,...
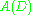 such that
such that 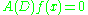 . This operator is called the annihilator, thus giving the method its name. Applying
. This operator is called the annihilator, thus giving the method its name. Applying 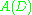 to both sides of the ODE gives a homogeneous ODE
to both sides of the ODE gives a homogeneous ODE 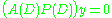 for which we find a solution basis
for which we find a solution basis 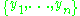 as before. Then the original inhomogeneous ODE is used to construct a system of equations restricting the coefficients of the linear combination to satisfy the ODE.
as before. Then the original inhomogeneous ODE is used to construct a system of equations restricting the coefficients of the linear combination to satisfy the ODE.This method is not as general as variation of parameters in the sense that an annihilator does not always exist.
Example
Given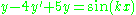 ,
, 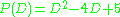 .
.The simplest annihilator of
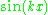 is
is 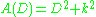 . The zeros of
. The zeros of 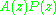 are
are 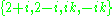 , so the solution basis of
, so the solution basis of 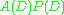 is
is 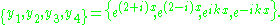
Setting
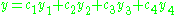 we find
we find
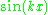 |
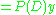 |
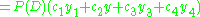 |
|
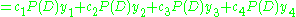 |
|
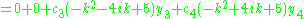 |
|
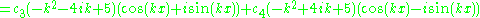 |
giving the system
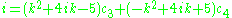
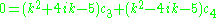
which has solutions
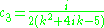 ,
, 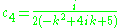
giving the solution set
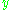 |
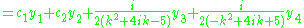 |
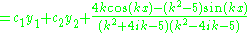 |
|
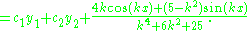 |
This solution can be broken down into the homogeneous and nonhomogeneous parts. In particular,
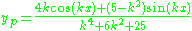 is a particular integral for the nonhomogeneous differential equation, and
is a particular integral for the nonhomogeneous differential equation, and 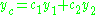 is a complementary solution to the corresponding homogeneous equation. The values of
is a complementary solution to the corresponding homogeneous equation. The values of 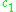 and
and 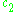 are determined usually through a set of initial conditions. Since this is a second-order equation, two such conditions are necessary to determine these values.
are determined usually through a set of initial conditions. Since this is a second-order equation, two such conditions are necessary to determine these values.The fundamental solutions
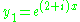 and
and 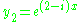 can be further rewritten using Euler's formula
can be further rewritten using Euler's formulaEuler's formula
Euler's formula, named after Leonhard Euler, is a mathematical formula in complex analysis that establishes the deep relationship between the trigonometric functions and the complex exponential function...
:
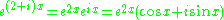
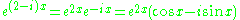
Then
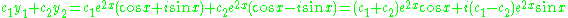 , and a suitable reassignment of the constants gives a simpler and more understandable form of the complementary solution,
, and a suitable reassignment of the constants gives a simpler and more understandable form of the complementary solution, 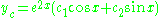 .
.

