
Ambient isotopy
Encyclopedia
In the mathematical
subject of topology
, an ambient isotopy, also called an h-isotopy, is a kind of continuous distortion of an "ambient space", a manifold
, taking a submanifold
to another submanifold. For example in knot theory
, one considers two knot
s the same if one can distort one knot into the other without breaking it. Such a distortion is an example of an ambient isotopy. More precisely, let N and M be manifolds and g and h be embedding
s of N in M. A continuous map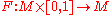
is defined to be an ambient isotopy taking g to h if F0 is the identity map
, each map Ft is a homeomorphism
from M to itself, and F1 ∘ g = h. This implies that the orientation
must be preserved by ambient isotopies. For example, two knots which are mirror image
s of each other are in general not equivalent.
Mathematics
Mathematics is the study of quantity, space, structure, and change. Mathematicians seek out patterns and formulate new conjectures. Mathematicians resolve the truth or falsity of conjectures by mathematical proofs, which are arguments sufficient to convince other mathematicians of their validity...
subject of topology
Topology
Topology is a major area of mathematics concerned with properties that are preserved under continuous deformations of objects, such as deformations that involve stretching, but no tearing or gluing...
, an ambient isotopy, also called an h-isotopy, is a kind of continuous distortion of an "ambient space", a manifold
Manifold
In mathematics , a manifold is a topological space that on a small enough scale resembles the Euclidean space of a specific dimension, called the dimension of the manifold....
, taking a submanifold
Submanifold
In mathematics, a submanifold of a manifold M is a subset S which itself has the structure of a manifold, and for which the inclusion map S → M satisfies certain properties. There are different types of submanifolds depending on exactly which properties are required...
to another submanifold. For example in knot theory
Knot theory
In topology, knot theory is the study of mathematical knots. While inspired by knots which appear in daily life in shoelaces and rope, a mathematician's knot differs in that the ends are joined together so that it cannot be undone. In precise mathematical language, a knot is an embedding of a...
, one considers two knot
Knot (mathematics)
In mathematics, a knot is an embedding of a circle in 3-dimensional Euclidean space, R3, considered up to continuous deformations . A crucial difference between the standard mathematical and conventional notions of a knot is that mathematical knots are closed—there are no ends to tie or untie on a...
s the same if one can distort one knot into the other without breaking it. Such a distortion is an example of an ambient isotopy. More precisely, let N and M be manifolds and g and h be embedding
Embedding
In mathematics, an embedding is one instance of some mathematical structure contained within another instance, such as a group that is a subgroup....
s of N in M. A continuous map
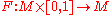
is defined to be an ambient isotopy taking g to h if F0 is the identity map
Identity function
In mathematics, an identity function, also called identity map or identity transformation, is a function that always returns the same value that was used as its argument...
, each map Ft is a homeomorphism
Homeomorphism
In the mathematical field of topology, a homeomorphism or topological isomorphism or bicontinuous function is a continuous function between topological spaces that has a continuous inverse function. Homeomorphisms are the isomorphisms in the category of topological spaces—that is, they are...
from M to itself, and F1 ∘ g = h. This implies that the orientation
Orientation (geometry)
In geometry the orientation, angular position, or attitude of an object such as a line, plane or rigid body is part of the description of how it is placed in the space it is in....
must be preserved by ambient isotopies. For example, two knots which are mirror image
Mirror image
A mirror image is a reflected duplication of an object that appears identical but reversed. As an optical effect it results from reflection off of substances such as a mirror or water. It is also a concept in geometry and can be used as a conceptualization process for 3-D structures...
s of each other are in general not equivalent.

