Alpha-particle spectroscopy
Encyclopedia
One method for testing for (and measuring) many alpha emitters is to use alpha-particle spectroscopy. For methods for gamma ray
s and beta particles, please see gamma spectroscopy
and liquid scintillation counting
respectively.
disk which is then dried out to give a uniform coating on the disk. This is then used as the test sample. If the thickness of the layer formed on the disk is too thick then the lines of the spectrum
are broadened to lower energies. This is because some of the energy
of the alpha particle
s is lost during their movement through the layer of active material.
, where the sample is mixed with a scintillation cocktail. When the light
emissions are then counted, some machines will record the amount of light energy per radioactive decay
event. Due to the imperfections of the liquid scintillation method (such as a failure for all the photon
s to be detected, cloudy or coloured samples can be difficult to count) and the fact that random quenching can reduce the number of photon
s generated per radioactive decay, it is possible to get a broadening of the alpha spectra obtained through liquid scintillation. It is likely that these liquid scintillation spectra will be subject to a Gaussian broadening
, rather than the distortion exhibited when the layer of an active material on a disk is too thick.
s such as 239Pu
and 241Am
have more than one alpha line indicates that the nucleus
has the ability to be in different discrete energy level
s (like a molecule can).
Gamma ray
Gamma radiation, also known as gamma rays or hyphenated as gamma-rays and denoted as γ, is electromagnetic radiation of high frequency . Gamma rays are usually naturally produced on Earth by decay of high energy states in atomic nuclei...
s and beta particles, please see gamma spectroscopy
Gamma spectroscopy
Gamma-ray spectroscopy is the quantitative study of the energy spectra of gamma-ray sources, both nuclear laboratory, geochemical, and astrophysical. Gamma rays are the highest-energy form of electromagnetic radiation, being physically exactly like all other forms except for higher photon energy...
and liquid scintillation counting
Liquid scintillation counting
Liquid scintillation counting is a standard laboratory method in the life-sciences for measuring radiation from beta-emitting nuclides. Scintillating materials are also used in differently constructed "counters" in many other fields....
respectively.
Counting using a source in a metal disk
It is common to place a drop of the test solution on a metalMetal
A metal , is an element, compound, or alloy that is a good conductor of both electricity and heat. Metals are usually malleable and shiny, that is they reflect most of incident light...
disk which is then dried out to give a uniform coating on the disk. This is then used as the test sample. If the thickness of the layer formed on the disk is too thick then the lines of the spectrum
Spectrum
A spectrum is a condition that is not limited to a specific set of values but can vary infinitely within a continuum. The word saw its first scientific use within the field of optics to describe the rainbow of colors in visible light when separated using a prism; it has since been applied by...
are broadened to lower energies. This is because some of the energy
Energy
In physics, energy is an indirectly observed quantity. It is often understood as the ability a physical system has to do work on other physical systems...
of the alpha particle
Alpha particle
Alpha particles consist of two protons and two neutrons bound together into a particle identical to a helium nucleus, which is classically produced in the process of alpha decay, but may be produced also in other ways and given the same name...
s is lost during their movement through the layer of active material.
Liquid scintillation
An alternative method is to use internal liquid scintillation countingLiquid scintillation counting
Liquid scintillation counting is a standard laboratory method in the life-sciences for measuring radiation from beta-emitting nuclides. Scintillating materials are also used in differently constructed "counters" in many other fields....
, where the sample is mixed with a scintillation cocktail. When the light
Light
Light or visible light is electromagnetic radiation that is visible to the human eye, and is responsible for the sense of sight. Visible light has wavelength in a range from about 380 nanometres to about 740 nm, with a frequency range of about 405 THz to 790 THz...
emissions are then counted, some machines will record the amount of light energy per radioactive decay
Radioactive decay
Radioactive decay is the process by which an atomic nucleus of an unstable atom loses energy by emitting ionizing particles . The emission is spontaneous, in that the atom decays without any physical interaction with another particle from outside the atom...
event. Due to the imperfections of the liquid scintillation method (such as a failure for all the photon
Photon
In physics, a photon is an elementary particle, the quantum of the electromagnetic interaction and the basic unit of light and all other forms of electromagnetic radiation. It is also the force carrier for the electromagnetic force...
s to be detected, cloudy or coloured samples can be difficult to count) and the fact that random quenching can reduce the number of photon
Photon
In physics, a photon is an elementary particle, the quantum of the electromagnetic interaction and the basic unit of light and all other forms of electromagnetic radiation. It is also the force carrier for the electromagnetic force...
s generated per radioactive decay, it is possible to get a broadening of the alpha spectra obtained through liquid scintillation. It is likely that these liquid scintillation spectra will be subject to a Gaussian broadening
Gaussian broadening
Gaussian broadening refers to broadening effects in spectral lines, these can be produced by Doppler broadening and natural broadening.This effect is similar to Gaussian blur effect in image processing produced by convolution with the Gaussian function....
, rather than the distortion exhibited when the layer of an active material on a disk is too thick.
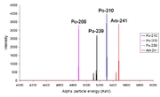
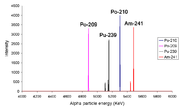
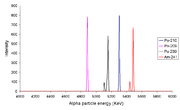
Alpha spectra
From left to right the peaks are due to 209Po, 210Po, 239Pu and 241Am. The fact that isotopeIsotope
Isotopes are variants of atoms of a particular chemical element, which have differing numbers of neutrons. Atoms of a particular element by definition must contain the same number of protons but may have a distinct number of neutrons which differs from atom to atom, without changing the designation...
s such as 239Pu
Plutonium
Plutonium is a transuranic radioactive chemical element with the chemical symbol Pu and atomic number 94. It is an actinide metal of silvery-gray appearance that tarnishes when exposed to air, forming a dull coating when oxidized. The element normally exhibits six allotropes and four oxidation...
and 241Am
Americium
Americium is a synthetic element that has the symbol Am and atomic number 95. This transuranic element of the actinide series is located in the periodic table below the lanthanide element europium, and thus by analogy was named after another continent, America.Americium was first produced in 1944...
have more than one alpha line indicates that the nucleus
Atomic nucleus
The nucleus is the very dense region consisting of protons and neutrons at the center of an atom. It was discovered in 1911, as a result of Ernest Rutherford's interpretation of the famous 1909 Rutherford experiment performed by Hans Geiger and Ernest Marsden, under the direction of Rutherford. The...
has the ability to be in different discrete energy level
Energy level
A quantum mechanical system or particle that is bound -- that is, confined spatially—can only take on certain discrete values of energy. This contrasts with classical particles, which can have any energy. These discrete values are called energy levels...
s (like a molecule can).



