
Alpha-aminoadipate pathway
Encyclopedia
Amino acid
Amino acids are molecules containing an amine group, a carboxylic acid group and a side-chain that varies between different amino acids. The key elements of an amino acid are carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, and nitrogen...
L-lysine
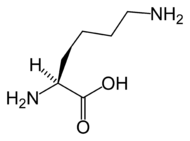
Lysine
Lysine is an α-amino acid with the chemical formula HO2CCH4NH2. It is an essential amino acid, which means that the human body cannot synthesize it. Its codons are AAA and AAG....
. In the eukaryote
Eukaryote
A eukaryote is an organism whose cells contain complex structures enclosed within membranes. Eukaryotes may more formally be referred to as the taxon Eukarya or Eukaryota. The defining membrane-bound structure that sets eukaryotic cells apart from prokaryotic cells is the nucleus, or nuclear...
s, this pathway is unique to the higher fungi (containing chitin
Chitin
Chitin n is a long-chain polymer of a N-acetylglucosamine, a derivative of glucose, and is found in many places throughout the natural world...
in their cell walls) and the euglenid
Euglenid
Euglenoids are one of the best-known groups of flagellates, commonly found in freshwater especially when it is rich in organic materials, with a few marine and endosymbiotic members. Most euglenids are unicellular. Many euglenids have chloroplasts and produce energy through photosynthesis, but...
s. It has also been reported from bacteria of the genus Thermus. The precursor
Precursor (chemistry)
In chemistry, a precursor is a compound that participates in the chemical reaction that produces another compound. In biochemistry, the term "precursor" is used more specifically to refer to a chemical compound preceding another in a metabolic pathway....
compound for L-lysine is α-ketoglutarate; the seven enzyme
Enzyme
Enzymes are proteins that catalyze chemical reactions. In enzymatic reactions, the molecules at the beginning of the process, called substrates, are converted into different molecules, called products. Almost all chemical reactions in a biological cell need enzymes in order to occur at rates...
s involved are, sequentially: homocitrate synthase
Homocitrate synthase
In enzymology, a homocitrate synthase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reactionThe 3 substrates of this enzyme are acetyl-CoA, H2O, and 2-oxoglutarate, whereas its two products are -2-hydroxybutane-1,2,4-tricarboxylate and CoA....
, homoaconitase
Homoaconitate hydratase
In enzymology, a homoaconitate hydratase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction-1-hydroxybutane-1,2,4-tricarboxylate \rightleftharpoons -but-1-ene-1,2,4-tricarboxylate + H2O...
, homoisocitrate dehydrogenase
Homoisocitrate dehydrogenase
In enzymology, a homoisocitrate dehydrogenase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction-1-hydroxybutane-1,2,4-tricarboxylate + NAD+ \rightleftharpoons 2-oxoadipate + CO2 + NADH + H+...
; α-aminoadipate aminotransferase; α-aminoadipate reductase, saccharopine reductase, and saccharopine dehydrogenase
Saccharopine dehydrogenase
Saccharopine dehydrogenase is an enzyme involved in the metabolism of lysine, via saccharopine.It can be classified under , , , and ....
.

