
Allantoicase
Encyclopedia
In enzymology, an allantoicase is an enzyme
that catalyzes
the chemical reaction
Thus, the two substrates
of this enzyme are allantoate and H2O
, whereas its two products
are (S)-ureidoglycolate and urea
.
This enzyme belongs to the family of hydrolase
s, those acting on carbon-nitrogen bonds other than peptide bonds, specifically in linear amidines. The systematic name of this enzyme class is allantoate amidinohydrolase. This enzyme participates in purine metabolism
by facilitating the utilization of purine
s as secondary nitrogen
sources under nitrogen-limiting conditions. While purine degradation converges to uric acid
in all vertebrates, its further degradation varies from species to species. Uric acid is excreted by birds, reptiles, and some mammal
s that do not have a functional uricase gene, whereas other mammals produce allantoin. Amphibian
s and microorganisms produce ammonia
and carbon dioxide
using the uricolytic pathway. Allantoicase performs the second step in this pathway catalyzing the conversion of allantoate into ureidoglycolate and urea.
have been solved for this class of enzymes, with PDB
accession codes and .
The structure
of allantoicase is best described as being composed of two repeat
s (the allantoicase repeats: AR1 and AR2), which are connected by a flexible linker. The crystal structure, resolved at 2.4A resolution, reveals that AR1 has a very similar fold
to AR2, both repeats being jelly-roll motifs, composed of four-stranded and five-stranded antiparallel
beta-sheets. Each jelly-roll motif has two conserved surface patches that probably constitute the active site
.
Enzyme
Enzymes are proteins that catalyze chemical reactions. In enzymatic reactions, the molecules at the beginning of the process, called substrates, are converted into different molecules, called products. Almost all chemical reactions in a biological cell need enzymes in order to occur at rates...
that catalyzes
Catalysis
Catalysis is the change in rate of a chemical reaction due to the participation of a substance called a catalyst. Unlike other reagents that participate in the chemical reaction, a catalyst is not consumed by the reaction itself. A catalyst may participate in multiple chemical transformations....
the chemical reaction
Chemical reaction
A chemical reaction is a process that leads to the transformation of one set of chemical substances to another. Chemical reactions can be either spontaneous, requiring no input of energy, or non-spontaneous, typically following the input of some type of energy, such as heat, light or electricity...
- allantoate + H2O
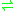 (S)-ureidoglycolate + urea
(S)-ureidoglycolate + urea
Thus, the two substrates
Substrate (biochemistry)
In biochemistry, a substrate is a molecule upon which an enzyme acts. Enzymes catalyze chemical reactions involving the substrate. In the case of a single substrate, the substrate binds with the enzyme active site, and an enzyme-substrate complex is formed. The substrate is transformed into one or...
of this enzyme are allantoate and H2O
Water
Water is a chemical substance with the chemical formula H2O. A water molecule contains one oxygen and two hydrogen atoms connected by covalent bonds. Water is a liquid at ambient conditions, but it often co-exists on Earth with its solid state, ice, and gaseous state . Water also exists in a...
, whereas its two products
Product (chemistry)
Product are formed during chemical reactions as reagents are consumed. Products have lower energy than the reagents and are produced during the reaction according to the second law of thermodynamics. The released energy comes from changes in chemical bonds between atoms in reagent molecules and...
are (S)-ureidoglycolate and urea
Urea
Urea or carbamide is an organic compound with the chemical formula CO2. The molecule has two —NH2 groups joined by a carbonyl functional group....
.
This enzyme belongs to the family of hydrolase
Hydrolase
In biochemistry, a hydrolase is an enzyme that catalyzes the hydrolysis of a chemical bond. For example, an enzyme that catalyzed the following reaction is a hydrolase:-Nomenclature:...
s, those acting on carbon-nitrogen bonds other than peptide bonds, specifically in linear amidines. The systematic name of this enzyme class is allantoate amidinohydrolase. This enzyme participates in purine metabolism
Purine metabolism
-Biosynthesis:Purines are biologically synthesized as nucleotides and in particular as ribotides, i.e. bases attached to ribose 5-phosphate. A key regulatory step is the production of 5-phospho-α-D-ribosyl 1-pyrophosphate by PRPP synthetase, which is activated by inorganic phosphate and...
by facilitating the utilization of purine
Purine
A purine is a heterocyclic aromatic organic compound, consisting of a pyrimidine ring fused to an imidazole ring. Purines, including substituted purines and their tautomers, are the most widely distributed kind of nitrogen-containing heterocycle in nature....
s as secondary nitrogen
Nitrogen
Nitrogen is a chemical element that has the symbol N, atomic number of 7 and atomic mass 14.00674 u. Elemental nitrogen is a colorless, odorless, tasteless, and mostly inert diatomic gas at standard conditions, constituting 78.08% by volume of Earth's atmosphere...
sources under nitrogen-limiting conditions. While purine degradation converges to uric acid
Uric acid
Uric acid is a heterocyclic compound of carbon, nitrogen, oxygen, and hydrogen with the formula C5H4N4O3. It forms ions and salts known as urates and acid urates such as ammonium acid urate. Uric acid is created when the body breaks down purine nucleotides. High blood concentrations of uric acid...
in all vertebrates, its further degradation varies from species to species. Uric acid is excreted by birds, reptiles, and some mammal
Mammal
Mammals are members of a class of air-breathing vertebrate animals characterised by the possession of endothermy, hair, three middle ear bones, and mammary glands functional in mothers with young...
s that do not have a functional uricase gene, whereas other mammals produce allantoin. Amphibian
Amphibian
Amphibians , are a class of vertebrate animals including animals such as toads, frogs, caecilians, and salamanders. They are characterized as non-amniote ectothermic tetrapods...
s and microorganisms produce ammonia
Ammonia
Ammonia is a compound of nitrogen and hydrogen with the formula . It is a colourless gas with a characteristic pungent odour. Ammonia contributes significantly to the nutritional needs of terrestrial organisms by serving as a precursor to food and fertilizers. Ammonia, either directly or...
and carbon dioxide
Carbon dioxide
Carbon dioxide is a naturally occurring chemical compound composed of two oxygen atoms covalently bonded to a single carbon atom...
using the uricolytic pathway. Allantoicase performs the second step in this pathway catalyzing the conversion of allantoate into ureidoglycolate and urea.
Structural studies
As of late 2007, two structuresTertiary structure
In biochemistry and molecular biology, the tertiary structure of a protein or any other macromolecule is its three-dimensional structure, as defined by the atomic coordinates.-Relationship to primary structure:...
have been solved for this class of enzymes, with PDB
Protein Data Bank
The Protein Data Bank is a repository for the 3-D structural data of large biological molecules, such as proteins and nucleic acids....
accession codes and .
The structure
Secondary structure
In biochemistry and structural biology, secondary structure is the general three-dimensional form of local segments of biopolymers such as proteins and nucleic acids...
of allantoicase is best described as being composed of two repeat
Tandem repeat
Tandem repeats occur in DNA when a pattern of two or more nucleotides is repeated and the repetitions are directly adjacent to each other. -Example:An example would be:in which the sequence A-T-T-C-G is repeated three times.-Terminology:...
s (the allantoicase repeats: AR1 and AR2), which are connected by a flexible linker. The crystal structure, resolved at 2.4A resolution, reveals that AR1 has a very similar fold
Protein folding
Protein folding is the process by which a protein structure assumes its functional shape or conformation. It is the physical process by which a polypeptide folds into its characteristic and functional three-dimensional structure from random coil....
to AR2, both repeats being jelly-roll motifs, composed of four-stranded and five-stranded antiparallel
Antiparallel (biochemistry)
In biochemistry, two molecules are antiparallel if they run side-by-side in opposite directions or when both strands are complimentary to each other....
beta-sheets. Each jelly-roll motif has two conserved surface patches that probably constitute the active site
Active site
In biology the active site is part of an enzyme where substrates bind and undergo a chemical reaction. The majority of enzymes are proteins but RNA enzymes called ribozymes also exist. The active site of an enzyme is usually found in a cleft or pocket that is lined by amino acid residues that...
.

