Active load
Encyclopedia
An active or dynamic load is a component or a circuit behaving as a current-stable nonlinear resistor. This term may refer to a component of circuit design, or to a type of test equipment.
. Most commonly the active load is the output part of a current mirror
and is represented in an idealized manner as a current source. Usually, it is only a constant-current resistor that is a part of the whole current source including a constant voltage source as well (the power supply VCC on the figures below).
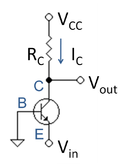
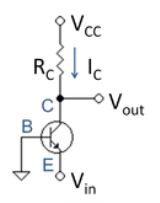
 In Figure 1 the load is a resistor, and the current through the resistor is determined by Ohm's law
In Figure 1 the load is a resistor, and the current through the resistor is determined by Ohm's law
as:
As a consequence of this relation, the voltage drop across the resistor is tied to the current at the Q-point. If the bias current is fixed for some performance reason, any increase in load resistance automatically leads to a lower voltage for Vout. which in turn lowers the voltage drop VCB between collector and base, limiting the signal swing at the amplifier output (if the output swing is larger than VCB, the transistor is driven out of active mode during part of the signal cycle).
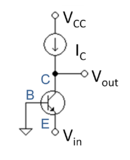
In contrast, using the active load of Figure 2, the AC impedance of the ideal current source is infinite regardless of the voltage drop VCC - Vout, which allows even a large value of VCB. and consequently a large output signal swing.
, which is less ideal in two ways. First, its AC resistance is large, but not infinite. Second, the mirror requires a small voltage drop to maintain operation (to keep the output transistors of the mirror in active mode). As a result, the current mirror does limit the allowable output voltage swing, but this limitation is much less than for a resistor, and also does not depend upon the choice of bias current, leaving more flexibility than a resistor in designing the circuit.
, an active load is used for automatic testing of power supplies and other sources of electrical power to ensure that their output voltage and current are within their specifications over a range of load conditions, from no load to maximum load.
One approach to test loads uses a set of resistor
s of different values, and manual intervention. In contrast, an active load presents to the source a resistance value varied by electronic control, either by an analogue adjusting device such as a multi-turn potentiometer
or, in automated test setups, by a digital computer. The load resistance can often be varied rapidly in order to test the power supply's transient response
.
Just like a resistor, an active load converts the power supply's electrical energy to heat. The heat-dissipating devices (usually transistor
s) in an active load therefore have to be designed to withstand the resulting temperature rise, and are usually cooled by means of heatsinks.
For added convenience, active loads often include circuitry to measure the current and voltage delivered to the inputs, and may display these measurements on numeric readouts.
Circuit design
In circuit design, an active load is a circuit component made up of active devices, such as transistors, intended to present a high small-signal impedance yet not requiring a large DC voltage drop, as would occur if a large resistor were used instead. Such large AC load impedances may be desirable, for example, to increase the AC gain of some types of amplifierAmplifier
Generally, an amplifier or simply amp, is a device for increasing the power of a signal.In popular use, the term usually describes an electronic amplifier, in which the input "signal" is usually a voltage or a current. In audio applications, amplifiers drive the loudspeakers used in PA systems to...
. Most commonly the active load is the output part of a current mirror
Current mirror
A current mirror is a circuit designed to copy a current through one active device by controlling the current in another active device of a circuit, keeping the output current constant regardless of loading. The current being 'copied' can be, and sometimes is, a varying signal current...
and is represented in an idealized manner as a current source. Usually, it is only a constant-current resistor that is a part of the whole current source including a constant voltage source as well (the power supply VCC on the figures below).
Common base example


Ohm's law
Ohm's law states that the current through a conductor between two points is directly proportional to the potential difference across the two points...
as:
-
 .
.
As a consequence of this relation, the voltage drop across the resistor is tied to the current at the Q-point. If the bias current is fixed for some performance reason, any increase in load resistance automatically leads to a lower voltage for Vout. which in turn lowers the voltage drop VCB between collector and base, limiting the signal swing at the amplifier output (if the output swing is larger than VCB, the transistor is driven out of active mode during part of the signal cycle).
In contrast, using the active load of Figure 2, the AC impedance of the ideal current source is infinite regardless of the voltage drop VCC - Vout, which allows even a large value of VCB. and consequently a large output signal swing.
Differential amplifiers
Active loads are frequently used in op-amp differential input stages, in order to enormously increase the gain.Practical limitations
In practice the ideal current source is replaced by a current mirrorCurrent mirror
A current mirror is a circuit designed to copy a current through one active device by controlling the current in another active device of a circuit, keeping the output current constant regardless of loading. The current being 'copied' can be, and sometimes is, a varying signal current...
, which is less ideal in two ways. First, its AC resistance is large, but not infinite. Second, the mirror requires a small voltage drop to maintain operation (to keep the output transistors of the mirror in active mode). As a result, the current mirror does limit the allowable output voltage swing, but this limitation is much less than for a resistor, and also does not depend upon the choice of bias current, leaving more flexibility than a resistor in designing the circuit.
Test equipment
In the area of electronic test equipmentElectronic test equipment
Electronic test equipment is used to create signals and capture responses from electronic Devices Under Test . In this way, the proper operation of the DUT can be proven or faults in the device can be traced and repaired...
, an active load is used for automatic testing of power supplies and other sources of electrical power to ensure that their output voltage and current are within their specifications over a range of load conditions, from no load to maximum load.
One approach to test loads uses a set of resistor
Resistor
A linear resistor is a linear, passive two-terminal electrical component that implements electrical resistance as a circuit element.The current through a resistor is in direct proportion to the voltage across the resistor's terminals. Thus, the ratio of the voltage applied across a resistor's...
s of different values, and manual intervention. In contrast, an active load presents to the source a resistance value varied by electronic control, either by an analogue adjusting device such as a multi-turn potentiometer
Potentiometer
A potentiometer , informally, a pot, is a three-terminal resistor with a sliding contact that forms an adjustable voltage divider. If only two terminals are used , it acts as a variable resistor or rheostat. Potentiometers are commonly used to control electrical devices such as volume controls on...
or, in automated test setups, by a digital computer. The load resistance can often be varied rapidly in order to test the power supply's transient response
Transient response
In electrical engineering and mechanical engineering, a transient response or natural response is the response of a system to a change from equilibrium. The transient response is not necessarily tied to "on/off" events but to any event that affects the equilibrium of the system...
.
Just like a resistor, an active load converts the power supply's electrical energy to heat. The heat-dissipating devices (usually transistor
Transistor
A transistor is a semiconductor device used to amplify and switch electronic signals and power. It is composed of a semiconductor material with at least three terminals for connection to an external circuit. A voltage or current applied to one pair of the transistor's terminals changes the current...
s) in an active load therefore have to be designed to withstand the resulting temperature rise, and are usually cooled by means of heatsinks.
For added convenience, active loads often include circuitry to measure the current and voltage delivered to the inputs, and may display these measurements on numeric readouts.

