Wagner-Jauregg reaction
Encyclopedia
The Wagner-Jauregg reaction is a classic organic reaction
in organic chemistry
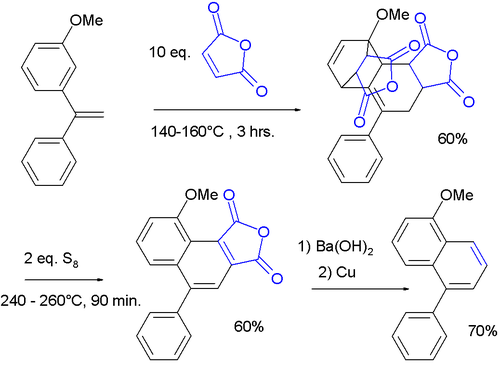
, named after Theodor Wagner-Jauregg, describing the double Diels–Alder reaction of 2 equivalents of maleic anhydride
with a 1,1-diarylethylene. After aromatization of the bis-adduct, the ultimate reaction product is a naphthalene
compound with one phenyl substituent.
The reaction is unusual in that the anhydride reacts with the aromatic ring. The presence of the alpha-phenyl group activates the styryl group for a Diels–Alder reaction even at the expense of its aromaticity. Unactivated styrene reacts instead at the alkene
alone and retains the aromaticity, leading to a Styrene maleic anhydride
copolymer.
In one adaptation, the first rearomatization is accomplished using high temperature and elemental sulfur
, followed by a second rearomatization by decarboxylation
with barium hydroxide
and copper
:
Organic reaction
Organic reactions are chemical reactions involving organic compounds. The basic organic chemistry reaction types are addition reactions, elimination reactions, substitution reactions, pericyclic reactions, rearrangement reactions, photochemical reactions and redox reactions. In organic synthesis,...
in organic chemistry
Organic chemistry
Organic chemistry is a subdiscipline within chemistry involving the scientific study of the structure, properties, composition, reactions, and preparation of carbon-based compounds, hydrocarbons, and their derivatives...
, named after Theodor Wagner-Jauregg, describing the double Diels–Alder reaction of 2 equivalents of maleic anhydride
Maleic anhydride
Maleic anhydride is an organic compound with the formula C2H22O. It is the acid anhydride of maleic acid and in its pure state it is a colourless or white solid with an acrid odour....
with a 1,1-diarylethylene. After aromatization of the bis-adduct, the ultimate reaction product is a naphthalene
Naphthalene
Naphthalene is an organic compound with formula . It is a white crystalline solid with a characteristic odor that is detectable at concentrations as low as 0.08 ppm by mass. As an aromatic hydrocarbon, naphthalene's structure consists of a fused pair of benzene rings...
compound with one phenyl substituent.
The reaction is unusual in that the anhydride reacts with the aromatic ring. The presence of the alpha-phenyl group activates the styryl group for a Diels–Alder reaction even at the expense of its aromaticity. Unactivated styrene reacts instead at the alkene
Alkene
In organic chemistry, an alkene, olefin, or olefine is an unsaturated chemical compound containing at least one carbon-to-carbon double bond...
alone and retains the aromaticity, leading to a Styrene maleic anhydride
Styrene maleic anhydride
Styrene maleic anhydride, also known as SMA or SMAnh, is a synthetic polymer that is built-up of styrene and maleic anhydride monomers. The monomers are almost perfectly alternating, making it an alternating copolymer. It is formed by a radical polymerization, using an organic peroxide as the...
copolymer.
In one adaptation, the first rearomatization is accomplished using high temperature and elemental sulfur
Sulfur
Sulfur or sulphur is the chemical element with atomic number 16. In the periodic table it is represented by the symbol S. It is an abundant, multivalent non-metal. Under normal conditions, sulfur atoms form cyclic octatomic molecules with chemical formula S8. Elemental sulfur is a bright yellow...
, followed by a second rearomatization by decarboxylation
Decarboxylation
Decarboxylation is a chemical reaction that releases carbon dioxide . Usually, decarboxylation refers to a reaction of carboxylic acids, removing a carbon atom from a carbon chain. The reverse process, which is the first chemical step in photosynthesis, is called carbonation, the addition of CO2 to...
with barium hydroxide
Barium hydroxide
Barium hydroxide is the chemical compound with the formula Ba2. Also known as baryta, it is one of the principal compounds of barium. The white granular monohydrate is the usual commercial form.-Preparation:...
and copper
Copper
Copper is a chemical element with the symbol Cu and atomic number 29. It is a ductile metal with very high thermal and electrical conductivity. Pure copper is soft and malleable; an exposed surface has a reddish-orange tarnish...
:


