VEST
Encyclopedia
VEST cipher
s are a set of families of general-purpose hardware-dedicated ciphers that support single pass authenticated encryption
and can operate as collision-resistant hash functions
designed by Sean O'Neil, Benjamin Gittins and Howard Landman. VEST cannot be implemented efficiently in software.
VEST is based on a balanced T-function
that can also be described as a bijective nonlinear feedback shift register
with parallel feedback (NLPFSR) or as a substitution-permutation network
, which is assisted by a non-linear RNS
based counter. The four VEST family trees described in the cipher specification are VEST-4, VEST-8, VEST-16, and VEST-32. VEST ciphers support keys and IV
s of variable sizes
and instant re-keying. All VEST ciphers release output on every clock cycle.
All the VEST variants are covered by European Patent Number EP 1820295(B1), owned by Synaptic Laboratories.
VEST was a Phase 2 Candidate in the eSTREAM
competition in the hardware portfolio, but was not a Phase 3 or Focus candidate and so is not part of the final portfolio.
s with prime
periods
, the counter diffusor is a set of 5-to-1 linear combiners with feedback compressing outputs of the 16 counters into 10 bits while at the same time expanding the 8 data inputs into 9 bits, the core accumulator is an NLPFSR accepting 10 bits of the counter diffusor as its input, and the output combiner is a set of 6-to-1 linear combiners.
constructed using non-linear 6-to-1 feedback functions, one for each bit, all of which are updated simultaneously. The VEST-4 core accumulator is illustrated below:
It accepts 10 bits (d0 - d9) as its input. The least significant five bits (p0 - p4) in the accumulator state are updated by a 5x5 substitution box
and linearly combined with the first five input bits on each round. The next five accumulator bits are linearly combined with the next five input bits and with a non-linear function of four of the less significant accumulator bits. In authenticated encryption mode, the ciphertext feedback bits are also linearly fed back into the accumulator (e0 - e3) with a non-linear function of four of the less significant accumulator bits. All the other bits in the VEST accumulator state are linearly combined with non-linear functions of five less significant bits of the accumulator state on each round. The use of only the less significant bits as inputs into the feedback functions for each bit is typical of T-functions and is responsible for the feedback bijectivity. This substitution
operation is followed by a pseudorandom transposition
of all the bits in the state (see picture below).
but authenticating ciphertext rather than plaintext at the same speed and occupying the same area as keystream
generation. However, unkeyed authentication (hashing) is performed only 8 bits at a time by loading the plaintext into the counters rather than directly into the core accumulator.
. Family keying enables the end-user to generate a unique secure cipher for every chip.
 The highly irregular input structure coupled with a unique set of inputs for each feedback function hinders efficient software execution. As a result, all the feedback functions need to be calculated sequentially in software, thus resulting in the hardware-software speed difference being approximately equal to the number of gates occupied by the feedback logic in hardware (see the column "Difference" in the table below).
The highly irregular input structure coupled with a unique set of inputs for each feedback function hinders efficient software execution. As a result, all the feedback functions need to be calculated sequentially in software, thus resulting in the hardware-software speed difference being approximately equal to the number of gates occupied by the feedback logic in hardware (see the column "Difference" in the table below).
The large differential between VEST's optimised hardware execution and equivalently clocked software optimised execution offers a natural resistance against low cost general-purpose software processor clones masquerading as genuine hardware authentication tokens.
In bulk challenge-response scenarios such as RFID authentication applications, bitsliced implementations of VEST ciphers on 32-bit processors which process many independent messages simultaneously are 2-4 times slower per message byte than AES.
hardware according to the evaluation by ETH Zurich.
The authors claim that according to their own implementations using "conservative standard RapidChip design front-end sign-off process", "VEST-32 can effortlessly satisfy a demand for 256-bit secure 10 Gbit/s authenticated encryption @ 167 MHz on 180ηm LSI Logic RapidChip platform ASIC technologies in less than 45K Gates and zero SRAM". On the 110ηm Rapidchip technologies, VEST-32 offers 20 Gbit/s authenticated encryption @ 320 MHz in less than 45 K gates". They also state that unrolling the round function of VEST can halve the clock-speed and reduce power consumption while doubling the output per clock-cycle, at the cost of increased area.
VEST ciphers offer only 1 resynchronisation strategy:
in the paper "Some thoughts on the AES process" and the more conservative guidelines recently proposed by Nicolas Courtois
in the paper “Cryptanalysis of Sfinks”. Although the authors are not publishing their own cryptanalysis, VEST ciphers have survived more than a year of public scrutiny as a part of the eStream competition organised by the ECRYPT. They were advanced to the second phase, albeit not as part of the focus group.
Cipher
In cryptography, a cipher is an algorithm for performing encryption or decryption — a series of well-defined steps that can be followed as a procedure. An alternative, less common term is encipherment. In non-technical usage, a “cipher” is the same thing as a “code”; however, the concepts...
s are a set of families of general-purpose hardware-dedicated ciphers that support single pass authenticated encryption
Authenticated encryption
Authenticated Encryption is a block cipher mode of operation which simultaneously provides confidentiality, integrity and authenticity assurances on the data. It became readily apparent that securely compositing a confidentiality mode with an authentication mode could be error prone and difficult...
and can operate as collision-resistant hash functions
Cryptographic hash function
A cryptographic hash function is a deterministic procedure that takes an arbitrary block of data and returns a fixed-size bit string, the hash value, such that an accidental or intentional change to the data will change the hash value...
designed by Sean O'Neil, Benjamin Gittins and Howard Landman. VEST cannot be implemented efficiently in software.
VEST is based on a balanced T-function
T-function
In cryptography, a T-function is a bijective mapping that updates every bit of the state in a way that can be described as x_i' = x_i + f, or in simple words an update function in which each bit of the state is updated by a linear combination of the same bit and a function of a subset of its less...
that can also be described as a bijective nonlinear feedback shift register
NLFSR
A NLFSR is a common component in modern stream ciphers, especially in RFID and smartcard applications. NLFSRs are known to be more resistant to cryptanalytic attacks than Linear Feedback Shift Registers , although construction of large NLFSRs with guaranteed long periods remains an open...
with parallel feedback (NLPFSR) or as a substitution-permutation network
Substitution-permutation network
In cryptography, an SP-network, or substitution-permutation network , is a series of linked mathematical operations used in block cipher algorithms such as AES .Other ciphers that use SPNs are 3-Way, SAFER, SHARK, and Square....
, which is assisted by a non-linear RNS
Residue number system
A residue number system represents a large integer using a set of smaller integers, so that computation may be performed more efficiently...
based counter. The four VEST family trees described in the cipher specification are VEST-4, VEST-8, VEST-16, and VEST-32. VEST ciphers support keys and IV
Initialization vector
In cryptography, an initialization vector is a fixed-size input to a cryptographic primitive that is typically required to be random or pseudorandom...
s of variable sizes
Key size
In cryptography, key size or key length is the size measured in bits of the key used in a cryptographic algorithm . An algorithm's key length is distinct from its cryptographic security, which is a logarithmic measure of the fastest known computational attack on the algorithm, also measured in bits...
and instant re-keying. All VEST ciphers release output on every clock cycle.
All the VEST variants are covered by European Patent Number EP 1820295(B1), owned by Synaptic Laboratories.
VEST was a Phase 2 Candidate in the eSTREAM
ESTREAM
eSTREAM is a project to "identify new stream ciphers suitable for widespread adoption", organised by the EU ECRYPT network. It was set up as a result of the failure of all six stream ciphers submitted to the NESSIE project. The call for primitives was first issued in November 2004. The project was...
competition in the hardware portfolio, but was not a Phase 3 or Focus candidate and so is not part of the final portfolio.
Overview
| Cipher: | VEST-4 | VEST-8 | VEST-16 | VEST-32 | AES-128 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Output, bits per call: | 4 | 8 | 16 | 32 | 128 |
| Claimed security, bits: | 80 | 128 | 160 | 256 | 128 |
| Recommended key length, bits: | 160 | 256 | 320 | 512 | 128 |
| Recommended hash length, bits: | 160 | 256 | 320 | 512 | |
| Counter size, bits: | 163 | 163 | 171 | 171 | |
| Core size, bits: | 83 | 211 | 331 | 587 | |
| State size, bits: | 256 | 384 | 512 | 768 | 128 |
Overall Structure
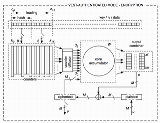
VEST ciphers consist of four components: a non-linear counter, a linear counter diffusor, a bijective non-linear accumulator with a large state and a linear output combiner (as illustrated by the image on the top-right corner of this page). The RNS counter consists of sixteen NLFSRNLFSR
A NLFSR is a common component in modern stream ciphers, especially in RFID and smartcard applications. NLFSRs are known to be more resistant to cryptanalytic attacks than Linear Feedback Shift Registers , although construction of large NLFSRs with guaranteed long periods remains an open...
s with prime
Prime number
A prime number is a natural number greater than 1 that has no positive divisors other than 1 and itself. A natural number greater than 1 that is not a prime number is called a composite number. For example 5 is prime, as only 1 and 5 divide it, whereas 6 is composite, since it has the divisors 2...
periods
Frequency
Frequency is the number of occurrences of a repeating event per unit time. It is also referred to as temporal frequency.The period is the duration of one cycle in a repeating event, so the period is the reciprocal of the frequency...
, the counter diffusor is a set of 5-to-1 linear combiners with feedback compressing outputs of the 16 counters into 10 bits while at the same time expanding the 8 data inputs into 9 bits, the core accumulator is an NLPFSR accepting 10 bits of the counter diffusor as its input, and the output combiner is a set of 6-to-1 linear combiners.
Accumulator
The core accumulator in VEST ciphers can be seen as a SPNSubstitution-permutation network
In cryptography, an SP-network, or substitution-permutation network , is a series of linked mathematical operations used in block cipher algorithms such as AES .Other ciphers that use SPNs are 3-Way, SAFER, SHARK, and Square....
constructed using non-linear 6-to-1 feedback functions, one for each bit, all of which are updated simultaneously. The VEST-4 core accumulator is illustrated below:
It accepts 10 bits (d0 - d9) as its input. The least significant five bits (p0 - p4) in the accumulator state are updated by a 5x5 substitution box
Substitution box
In cryptography, an S-Box is a basic component of symmetric key algorithms which performs substitution. In block ciphers, they are typically used to obscure the relationship between the key and the ciphertext — Shannon's property of confusion...
and linearly combined with the first five input bits on each round. The next five accumulator bits are linearly combined with the next five input bits and with a non-linear function of four of the less significant accumulator bits. In authenticated encryption mode, the ciphertext feedback bits are also linearly fed back into the accumulator (e0 - e3) with a non-linear function of four of the less significant accumulator bits. All the other bits in the VEST accumulator state are linearly combined with non-linear functions of five less significant bits of the accumulator state on each round. The use of only the less significant bits as inputs into the feedback functions for each bit is typical of T-functions and is responsible for the feedback bijectivity. This substitution
Substitution
Substitution may refer to:- Sciences :* Substitution , a syntactic transformation on strings of symbols of a formal language* Substitution of variables* Substitution cipher, a method of encryption...
operation is followed by a pseudorandom transposition
Transposition
Transposition may refer to:Mathematics* Transposition , a permutation which exchanges two elements and keeps all others fixed* Transposition, producing the transpose of a matrix AT, which is computed by swapping columns for rows in the matrix AGames* Transposition , different moves or a different...
of all the bits in the state (see picture below).
Data authentication
VEST ciphers can be executed in their native authenticated encryption mode similar to that of PhelixPhelix
Phelix is a high-speed stream cipher with a built-in single-pass message authentication code functionality, submitted in 2004 to the eSTREAM contest by Doug Whiting, Bruce Schneier, Stefan Lucks, and Frédéric Muller. The cipher uses only the operations of addition modulo 232, exclusive or, and...
but authenticating ciphertext rather than plaintext at the same speed and occupying the same area as keystream
Keystream
In cryptography, a keystream is a stream of random or pseudorandom characters that are combined with a plaintext message to produce an encrypted message ....
generation. However, unkeyed authentication (hashing) is performed only 8 bits at a time by loading the plaintext into the counters rather than directly into the core accumulator.
Family keying
The four root VEST cipher families are referred to as VEST-4, VEST-8, VEST-16, and VEST-32. Each of the four family trees of VEST ciphers supports family keying to generate other independent cipher families of the same size. The family-keying process is a standard method to generate cipher families with unique substitutions and unique counters with different periodsFrequency
Frequency is the number of occurrences of a repeating event per unit time. It is also referred to as temporal frequency.The period is the duration of one cycle in a repeating event, so the period is the reciprocal of the frequency...
. Family keying enables the end-user to generate a unique secure cipher for every chip.
Periods
VEST ciphers are assisted by a non-linear RNS counter with a very long period. According to the authors, determining average periods of VEST ciphers or probabilities of the shortest periods of VEST-16 and VEST-32 falling below their advertised security ratings for some keys remains an open problem and is computationally infeasible. They believe that these probabilities are below 2−160 for VEST-16 and below 2−256 for VEST-32. The shortest theoretically possible periods of VEST-4 and VEST-8 are above their security ratings as can be seen from the following table.| Period: | VEST-4 | VEST-8 | VEST-16 | VEST-32 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Guaranteed Minimum | 2134 | 2134 | 2143 | 2143 |
| Longest Possible | 2251 | 2383 | 2519 | 2791 |
Computational Efficiency in Software
The core accumulator in VEST ciphers has a complex, highly irregular structure that resists its efficient implementation in software.
| Implementation: | Clock | VEST-4 | VEST-8 | VEST-16 | VEST-32 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hardware | 250 MHz | ~1 Gbit/s | ~2 Gbit/s | ~4 Gbit/s | ~8 Gbit/s |
| Software | 250 MHz | < 1.0 Mbit/s | < 0.8 Mbit/s | < 1.1 Mbit/s | < 1.3 Mbit/s |
| Difference | > 1000 x | > 2300 x | > 3500 x | > 6000 x |
The large differential between VEST's optimised hardware execution and equivalently clocked software optimised execution offers a natural resistance against low cost general-purpose software processor clones masquerading as genuine hardware authentication tokens.
In bulk challenge-response scenarios such as RFID authentication applications, bitsliced implementations of VEST ciphers on 32-bit processors which process many independent messages simultaneously are 2-4 times slower per message byte than AES.
Hardware Performance
VEST is submitted to the eStream competition under the Profile II as designed for "hardware applications with restricted resources such as limited storage, gate count, or power consumption", and shows high speeds in FPGA and ASICASIC
ASIC may refer to:* Application-specific integrated circuit, an integrated circuit developed for a particular use, as opposed to a customised general-purpose device.* ASIC programming language, a dialect of BASIC...
hardware according to the evaluation by ETH Zurich.
The authors claim that according to their own implementations using "conservative standard RapidChip design front-end sign-off process", "VEST-32 can effortlessly satisfy a demand for 256-bit secure 10 Gbit/s authenticated encryption @ 167 MHz on 180ηm LSI Logic RapidChip platform ASIC technologies in less than 45K Gates and zero SRAM". On the 110ηm Rapidchip technologies, VEST-32 offers 20 Gbit/s authenticated encryption @ 320 MHz in less than 45 K gates". They also state that unrolling the round function of VEST can halve the clock-speed and reduce power consumption while doubling the output per clock-cycle, at the cost of increased area.
Key Agility
VEST ciphers offer 3 keying strategies:- Instantly loading the entire cipher state with a cryptographically strong key (100% entropy) supplied by a strong key generation or key exchange process;
- Instant reloading of the entire cipher state with a previously securely initialised cipher state;
- Incremental key loading (of an imperfect key) beginning with the least significant bit of the key loaded into the counter 15, sliding the 16-bit window down by one bit on each round until the single bit 1 that follows the most significant bit of the key is loaded into the counter 0. The process ends with 32 additional sealing rounds. The entire cipher state can now be stored for instant reloading.
| Key Bits | Rounds to load a key |
|---|---|
| 80 | 128 |
| 160 | 208 |
| 256 | 304 |
| 320 | 368 |
| 512 | 560 |
VEST ciphers offer only 1 resynchronisation strategy:
- Hashing the (IV) by loading it incrementally 8-bits at a time into the first 8 RNS counters, followed by additional 32 sealing rounds.
| IV Bits | Rounds to load an IV |
|---|---|
| 64 | 40 |
| 128 | 48 |
| 256 | 64 |
History
VEST was designed by Sean O'Neil and submitted to the eStream competition in June 2005. This was the first publication of the cipher.Security
The authors say that VEST security margins are inline with the guidelines proposed by Lars KnudsenLars Knudsen
Lars Ramkilde Knudsen is a Danish researcher in cryptography, particularly interested in the design and analysis of block ciphers, hash functions and message authentication codes .-Academic:...
in the paper "Some thoughts on the AES process" and the more conservative guidelines recently proposed by Nicolas Courtois
Nicolas Courtois
Nicolas Tadeusz Courtois is a cryptographer, a senior lecturer in computer science at University College London.Courtois was one of the co-authors of both the XSL attack against block ciphers such as the Advanced Encryption Standard and the XL system for solving systems of algebraic equations, used...
in the paper “Cryptanalysis of Sfinks”. Although the authors are not publishing their own cryptanalysis, VEST ciphers have survived more than a year of public scrutiny as a part of the eStream competition organised by the ECRYPT. They were advanced to the second phase, albeit not as part of the focus group.

