V-Modell
Encyclopedia
The V-Model is a systems development model
designed to simplify the understanding of the complexity
associated with developing system
s. In systems engineering
it is used to define a uniform procedure for product or project development.
framework.
The VEE represents the sequence of steps in a project life cycle development. It describes the activities and results that have to be produced during product development. The left side of the "V" represents the decomposition of requirements, and creation of system specifications. The right side of the VEE represents integration of parts and their verification. V stands for "Verification and Validation".
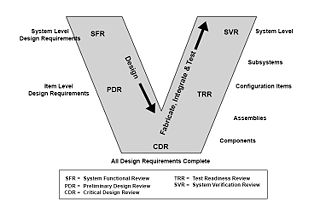
It involved early and comprehensive identification of goals, a concept of operations that describes user needs and the operating environment, thorough and testable system requirements, detailed design, implementation, rigorous acceptance testing of the implemented system to ensure it meets the stated requirements (system verification), measuring its effectiveness in addressing goals (system validation), on-going operation and maintenance, system upgrades over time, and eventual retirement.
The process emphasizes requirements-driven design and testing. All design elements and acceptance tests must be traceable to one or more system requirements and every requirement must be addressed by at least one design element and acceptance test. Such rigor ensures nothing is done unnecessarily and everything that is necessary is accomplished.
The testing stream generally consists of:
The development stream can consist (depending on the system type and the development scope) of customization, configuration or coding.
 The V-model is used to regulate the software development process within the German federal administration. Nowadays it is still the standard for German
The V-model is used to regulate the software development process within the German federal administration. Nowadays it is still the standard for German
federal administration and defense projects, as well as software developers within the region.
The concept of the V-Model was developed simultaneously, but independently, in Germany and in the United States in the late 1980s:
It has now found widespread application in commercial as well as defense programs. Its primary use is in Project Management and throughout the project lifecycle.
One fundamental characteristic of the US V-Model is that time and maturity move from left to right and one cannot move back in time. All iteration is along a vertical line to higher or lower levels in the system hierarchy, as shown in the figure. This has proven to be an important aspect of the model. The expansion of the model to a dual-Vee concept is treated in reference.
As the V-model is publicly available many companies also use it. In project management it is a method comparable to PRINCE2
and describes methods for project management as well as methods for system development. The V-Model while rigid in process, can be very flexible in application, especially as it pertains to the scope outside of the realm of the System Development Lifecycle normal parameters.
Scientific modelling
Scientific modelling is the process of generating abstract, conceptual, graphical and/or mathematical models. Science offers a growing collection of methods, techniques and theory about all kinds of specialized scientific modelling...
designed to simplify the understanding of the complexity
Complexity
In general usage, complexity tends to be used to characterize something with many parts in intricate arrangement. The study of these complex linkages is the main goal of complex systems theory. In science there are at this time a number of approaches to characterizing complexity, many of which are...
associated with developing system
System
System is a set of interacting or interdependent components forming an integrated whole....
s. In systems engineering
Systems engineering
Systems engineering is an interdisciplinary field of engineering that focuses on how complex engineering projects should be designed and managed over the life cycle of the project. Issues such as logistics, the coordination of different teams, and automatic control of machinery become more...
it is used to define a uniform procedure for product or project development.
Overview
The V-model is a graphical representation of the systems development lifecycle. It summarizes the main steps to be taken in conjunction with the corresponding deliverables within computerized system validationComputerized system validation
Computer system validation is the documented process of assuring that a computer system does exactly what it is designed to do in a consistent and reproducible manner....
framework.
The VEE represents the sequence of steps in a project life cycle development. It describes the activities and results that have to be produced during product development. The left side of the "V" represents the decomposition of requirements, and creation of system specifications. The right side of the VEE represents integration of parts and their verification. V stands for "Verification and Validation".
Objectives
The V-Model provides guidance for the planning and realization of projects. The following objectives are intended to be achieved by a project execution:- Minimization of Project Risks: The V-Model improves project transparency and project control by specifying standardized approaches and describing the corresponding results and responsible roles. It permits an early recognition of planning deviations and risks and improves process management, thus reducing the project risk.
- Improvement and Guarantee of Quality: As a standardized process model, the V-Model ensures that the results to be provided are complete and have the desired quality. Defined interim results can be checked at an early stage. Uniform product contents will improve readability, understandability and verifiability.
- Reduction of Total Cost over the Entire Project and System Life Cycle: The effort for the development, production, operation and maintenance of a system can be calculated, estimated and controlled in a transparent manner by applying a standardized process model. The results obtained are uniform and easily retraced. This reduces the acquirers dependency on the supplier and the effort for subsequent activities and projects.
- Improvement of Communication between all Stakeholders: The standardized and uniform description of all relevant elements and terms is the basis for the mutual understanding between all stakeholders. Thus, the frictional loss between user, acquirer, supplier and developer is reduced.
V Model topics

Systems Engineering and verification
The Systems Engineering Process (SEP) provides a path for improving the cost effectiveness of complex systems as experienced by the system owner over the entire life of the system, from conception to retirement.It involved early and comprehensive identification of goals, a concept of operations that describes user needs and the operating environment, thorough and testable system requirements, detailed design, implementation, rigorous acceptance testing of the implemented system to ensure it meets the stated requirements (system verification), measuring its effectiveness in addressing goals (system validation), on-going operation and maintenance, system upgrades over time, and eventual retirement.
The process emphasizes requirements-driven design and testing. All design elements and acceptance tests must be traceable to one or more system requirements and every requirement must be addressed by at least one design element and acceptance test. Such rigor ensures nothing is done unnecessarily and everything that is necessary is accomplished.
The specification stream
The specification stream mainly consists of:- User Requirement Specifications
- Functional Requirement Specifications
- Design Specifications
The testing stream generally consists of:
- Installation Qualification (IQ)
- Operational Qualification (OQ)
- Performance Qualification (PQ)
The development stream can consist (depending on the system type and the development scope) of customization, configuration or coding.
Applications

Germany
Germany , officially the Federal Republic of Germany , is a federal parliamentary republic in Europe. The country consists of 16 states while the capital and largest city is Berlin. Germany covers an area of 357,021 km2 and has a largely temperate seasonal climate...
federal administration and defense projects, as well as software developers within the region.
The concept of the V-Model was developed simultaneously, but independently, in Germany and in the United States in the late 1980s:
- The German V-Model was originally developed by IABG in Ottobrunn, near Munich, in cooperation with the Federal Office for Defense Technology and Procurement in Koblenz, for the Federal Ministry of Defense. It was taken over by the Federal Ministry of the Interior for the civilian public authorities domain in summer 1992.
- The US V-Model, as documented in the 1991 proceedings for the National Council on Systems EngineeringInternational Council on Systems EngineeringThe International Council on Systems Engineering is a non-profit membership organization dedicated to the advancement of systems engineering and to raise the professional stature of systems engineers.- Overview :...
(NCOSE; now INCOSE as of 1995), was developed for satellite systems involving hardware, software, and human interaction. - The V-Model first appeared at HughesHughesHughes may refer to:*Hughes *Hughes Medal*David E. Hughes inventorPlaces:* Hughes Range In Australia:* Division of Hughes, electoral district* Hughes, Australian Capital Territory, suburb of Canberra...
Aircraft circa 1982 as part of the pre-proposal effort for the FAA Advanced Automation System (AAS) program. It eventually formed the test strategy for the Hughes AAS Design Competition Phase (DCP) proposal. It was created to show the test and integration approach which was driven by new challenges to surface latent defects in the software. The need for this new level of latent defect detection was driven by the goal to start automating the thinking and planning processes of the air traffic controller as envisioned by the Automated Enroute Air Traffic Control (AERA) program. The reason the V is so powerful comes from the Hughes culture of coupling all text and analysis to multi dimensional images. It was the foundation of Sequential Thematic Organization of Publications (STOP) created by Hughes in 1963 and used until Hughes was divested by the Howard Hughes Medical InstituteHoward Hughes Medical InstituteHoward Hughes Medical Institute is a United States non-profit medical research organization based in Chevy Chase, Maryland. It was founded by the American businessman Howard Hughes in 1953. It is one of the largest private funding organizations for biological and medical research in the United...
in 1985.
It has now found widespread application in commercial as well as defense programs. Its primary use is in Project Management and throughout the project lifecycle.
One fundamental characteristic of the US V-Model is that time and maturity move from left to right and one cannot move back in time. All iteration is along a vertical line to higher or lower levels in the system hierarchy, as shown in the figure. This has proven to be an important aspect of the model. The expansion of the model to a dual-Vee concept is treated in reference.
As the V-model is publicly available many companies also use it. In project management it is a method comparable to PRINCE2
PRINCE2
PRojects IN Controlled Environments 2 is a structured project management method endorsed by the UK government as the project management standard for public projects. The methodology encompasses the management, control and organisation of a project...
and describes methods for project management as well as methods for system development. The V-Model while rigid in process, can be very flexible in application, especially as it pertains to the scope outside of the realm of the System Development Lifecycle normal parameters.
Advantages
These are the advantages V-Model offers in front of other systems development models:- The users of The V-Model participate in the development and maintenance of The V-Model. A change control board publicly maintains the V-Model. The change control board meets once a year and processes all received change requests on The V-Model.
- At each project start, the V-Model can be tailored into a specific project V-Model, this being possible because the V-Model is organization and project independent.
- The V-Model provides concrete assistance on how to implement an activity and its work steps, defining explicitly the events needed to complete a work step: each activity schema contains instructions, recommendations and detailed explanations of the activity.
Limits
The following aspects are not covered by the V-Model, they must be regulated in addition, or the V-Model must be adapted accordingly :- The placing of contracts for services is not regulated.
- The organization and execution of operation, maintenance, repair and disposal of the system are not covered by the V-Model. However, planning and preparation of a concept for these tasks are regulated in the V-Model.
- The V-Model addresses software development within a project rather than a whole organization.
See also
- RUP (as a supporting software process)
- Systems architectureSystems architectureA system architecture or systems architecture is the conceptual model that defines the structure, behavior, and more views of a system.An architecture description is a formal description and representation of a system, organized in a way that supports reasoning about the structure of the system...
- Systems analysisSystems analysisSystems analysis is the study of sets of interacting entities, including computer systems analysis. This field is closely related to requirements analysis or operations research...
- Systems designSystems designSystems design is the process of defining the architecture, components, modules, interfaces, and data for a system to satisfy specified requirements. One could see it as the application of systems theory to product development...
- Dual Vee ModelDual Vee ModelThe Dual Vee Model builds on the V-Model to cleanly depict the complexity associated with designing and developing systems. In systems engineering it defines a uniform procedure for product or project development. The model depicts concurrent development of a system’s architecture as one Vee with...
External links
- Vee Model of Systems Engineering Design and Integration
- What is the V-model? (in German)
- V-Model XT Documentation (1.3)
- Types of Testing
- Image
- Software Processes (also the V-Modell)
- Death of the V-Model (small software projects but not large systems of systems?)

