
Urodynamic testing
Encyclopedia
- incontinenceIncontinenceIncontinence or Incontinent may refer to:*Fecal incontinence, the inability to control one's bowels*Incontinence *Incontinent , a 1981 album by Fad Gadget*Urinary incontinence, the involuntary excretion of urine...
- frequent urinationFrequent urinationFrequent urination, or urinary frequency, is the need to urinate more often than usual. It is often, though not necessarily, associated with urinary incontinence and polyuria.A frequent need to urinate at night is called nocturia...
- sudden, strong urges to urinate
- problems starting a urine stream
- painful urination
- problems emptying your bladder completely
- recurrent urinary tract infections
Urodynamic tests are usually performed in Urology
Urology
Urology is the medical and surgical specialty that focuses on the urinary tracts of males and females, and on the reproductive system of males. Medical professionals specializing in the field of urology are called urologists and are trained to diagnose, treat, and manage patients with urological...
, Gynecology, OB/GYN, Internal medicine
Internal medicine
Internal medicine is the medical specialty dealing with the prevention, diagnosis, and treatment of adult diseases. Physicians specializing in internal medicine are called internists. They are especially skilled in the management of patients who have undifferentiated or multi-system disease processes...
, and Primary care
Primary care
Primary care is the term for the health services by providers who act as the principal point of consultation for patients within a health care system...
offices. Urodynamics will provide the physician with the information necessary to diagnose the cause and nature of a patient's incontinence, thus giving the best treatment options available. Urodynamics is typically conducted by urologists, urogynecologists, or specialist urology nurses.
Purpose of testing
The tests are most often arranged for men with enlarged prostate glands, and for women with incontinence that has either failed conservative treatment or requires surgery.Symptoms reported by the patient are often an unreliable guide to the underlying dysfunction of the lower urinary tract. The purpose of urodynamics is to provide objective confirmation of the pathology that a patient's symptoms would suggest.
For example, a patient complaining of urinary urgency (or rushing to the toilet), with increased frequency of urination can be said on the basis of their symptoms to have overactive bladder syndrome. The cause of this might be detrusor overactivity, in which the bladder muscle (the detrusor) contracts unexpectedly during bladder filling. Urodynamics can be used to confirm the presence of detrusor overactivity, which may help guide treatment. An overactive detrusor can be associated with urge incontinence.
Specific tests
These tests may be as simple as urinating behind a curtain while a doctor or nurse listens or more complicated, involving imaging equipment that films urination and pressure monitors that record the pressures of the bladder and urethra.A typical urodynamic test takes about 30 minutes to perform. It involves the use of a small catheter used to fill the bladder and record measurements. What is done depends on what the presenting problem is, but some of the common tests conducted are;
- Post-void residual volume: Most tests begin with the insertion of a urinary catheter/transducer following complete bladder emptying by the patient. The urine volume is measured (this shows how efficiently the bladder empties). High volumes (180 ml) may be associated with urinary tract infectionUrinary tract infectionA urinary tract infection is a bacterial infection that affects any part of the urinary tract. Symptoms include frequent feeling and/or need to urinate, pain during urination, and cloudy urine. The main causal agent is Escherichia coli...
s. A volume of greater than 50 ml in children has been described as constituting post-void residual urine. High levels can be associated with overflow incontinence.
- The urine is often sent for microscopy and culture to check for infection.
- Uroflowmetry: free uroflowmetry measures how fast the patient can empty his/her bladder. Pressure uroflowmetry again measures the rate of voiding, but with simultaneous assessment of bladder and rectal pressures. It helps demonstrate the reasons for difficulty in voiding, for example bladder muscle weakness or obstruction of the bladder outflow.
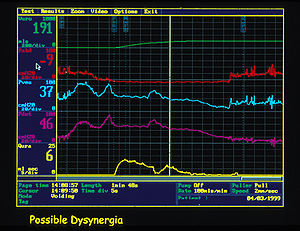
- Multichannel cystometryCystometryCystometry, also known as flow cystometry, is a clinical diagnostic procedure used to evaluate bladder function. Specifically, it measures contractile force of the bladder when voiding...
: measures the pressure in the rectum and in the bladder, using two pressure catheters, to deduce the presence of contractions of the bladder wall, during bladder filling, or during other provocative manoeuvres. The strength of the urethra can also be tested during this phase, using a cough or Valsalva manouvre, to confirm genuine stress incontinence.
- Urethral pressure profilometry: measures strength of sphincter contraction.
- ElectromyographyElectromyographyElectromyography is a technique for evaluating and recording the electrical activity produced by skeletal muscles. EMG is performed using an instrument called an electromyograph, to produce a record called an electromyogram. An electromyograph detects the electrical potential generated by muscle...
(EMG) measurement of electrical activity in the bladder neck.
- Assessing the "tightness" along the length of the urethra.
- FluoroscopyFluoroscopyFluoroscopy is an imaging technique commonly used by physicians to obtain real-time moving images of the internal structures of a patient through the use of a fluoroscope. In its simplest form, a fluoroscope consists of an X-ray source and fluorescent screen between which a patient is placed...
(moving video x-rays) of the bladder and bladder neck during voiding.

