
Cystometry
Encyclopedia
Cystometry, also known as flow cystometry, is a clinical diagnostic procedure used to evaluate bladder function. Specifically, it measures contractile force of the bladder
when voiding
. The resulting chart generated from cystometric analysis is known as a cystometrogram (CMG), which plots volume of liquid emptied from bladder against intravesical
pressure.
 Cystometric analysis is used to evaluate the bladder's capacity to contract and expel urine. It helps determine the source of urinary problems. A normal CMG effectively rules out primary vesical dysfunction. It is used as a component for diagnosis of various disorders including urinary tract infection
Cystometric analysis is used to evaluate the bladder's capacity to contract and expel urine. It helps determine the source of urinary problems. A normal CMG effectively rules out primary vesical dysfunction. It is used as a component for diagnosis of various disorders including urinary tract infection
s, multiple sclerosis
, stroke
, spinal cord
injury, urethra
l obstruction, and overactive bladder
, among others.
s into an emptied bladder through the urethra. In the two catheter method, one catheter transfers liquid while the other is a manometer (pressure sensor). In the single catheter method, a specialized catheter performs both functions. An additional rectal catheter may also be placed for additional data. The bladder will then be filled with saline
and the patient's awareness of the event will be queried. The patient will often be asked to note when presence of liquid is felt, when the bladder feels full, and when the urgency to void is felt. The patient is then asked to void, and both flow and pressure are recorded. These are plotted against each other to create the cystometrogram.
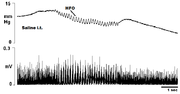 The primary results of cystometric analysis is the cystometrogram. The x-axis is the volume of liquid and the y-axis is the intraluminal pressure of the bladder. In normal patients, the plot is a series of spikes whose local minimums form a non-linear curve resembling an exponential
The primary results of cystometric analysis is the cystometrogram. The x-axis is the volume of liquid and the y-axis is the intraluminal pressure of the bladder. In normal patients, the plot is a series of spikes whose local minimums form a non-linear curve resembling an exponential
growth curve. The spikes correspond to the bladder contractions associated with the micturation reflex
. The curve formed by the bottom of the plot reflects the level of pressure necessary to void. In normal patients, the first couple hundred milliliters of urine flow with minimal applied pressure. Increasing pressure is necessary to void 200-300 millileters of urine. Beyond that, the pressure necessary to void additional urine rises sharply.
There is also the potential for trauma to the bladder and urethtra, which may result in hematuria
(blood in the urine).
Bladder
Bladder usually refers to an anatomical hollow organBladder may also refer to:-Biology:* Urinary bladder in humans** Urinary bladder ** Bladder control; see Urinary incontinence** Artificial urinary bladder, in humans...
when voiding
Urination
Urination, also known as micturition, voiding, peeing, weeing, pissing, and more rarely, emiction, is the ejection of urine from the urinary bladder through the urethra to the outside of the body. In healthy humans the process of urination is under voluntary control...
. The resulting chart generated from cystometric analysis is known as a cystometrogram (CMG), which plots volume of liquid emptied from bladder against intravesical
Vesical
Vesical refers to the urinary bladder and its relevant and nearby structures and functions, including:* the vesical arteries, which provide the urinary bladder with oxygenated blood** Superior vesical artery*** Middle vesical artery...
pressure.
Use

Urinary tract infection
A urinary tract infection is a bacterial infection that affects any part of the urinary tract. Symptoms include frequent feeling and/or need to urinate, pain during urination, and cloudy urine. The main causal agent is Escherichia coli...
s, multiple sclerosis
Multiple sclerosis
Multiple sclerosis is an inflammatory disease in which the fatty myelin sheaths around the axons of the brain and spinal cord are damaged, leading to demyelination and scarring as well as a broad spectrum of signs and symptoms...
, stroke
Stroke
A stroke, previously known medically as a cerebrovascular accident , is the rapidly developing loss of brain function due to disturbance in the blood supply to the brain. This can be due to ischemia caused by blockage , or a hemorrhage...
, spinal cord
Spinal cord
The spinal cord is a long, thin, tubular bundle of nervous tissue and support cells that extends from the brain . The brain and spinal cord together make up the central nervous system...
injury, urethra
Urethra
In anatomy, the urethra is a tube that connects the urinary bladder to the genitals for the removal of fluids out of the body. In males, the urethra travels through the penis, and carries semen as well as urine...
l obstruction, and overactive bladder
Overactive bladder
Overactive bladder is a urological condition defined by a set of symptoms: urgency, with or without urge incontinence, usually with frequency and nocturia. Frequency is usually defined as urinating more than 8 times a day. The International Continence Society is responsible for this definition...
, among others.
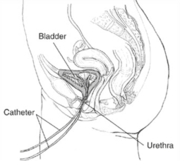
Procedure
The procedure is relatively short, ranging from fifteen minutes to an hour in duration. It involves the insertion of one or two catheterCatheter
In medicine, a catheter is a tube that can be inserted into a body cavity, duct, or vessel. Catheters thereby allow drainage, administration of fluids or gases, or access by surgical instruments. The process of inserting a catheter is catheterization...
s into an emptied bladder through the urethra. In the two catheter method, one catheter transfers liquid while the other is a manometer (pressure sensor). In the single catheter method, a specialized catheter performs both functions. An additional rectal catheter may also be placed for additional data. The bladder will then be filled with saline
Saline (medicine)
In medicine, saline is a general term referring to a sterile solution of sodium chloride in water but is only sterile when it is to be placed intravenously, otherwise, a saline solution is a salt water solution...
and the patient's awareness of the event will be queried. The patient will often be asked to note when presence of liquid is felt, when the bladder feels full, and when the urgency to void is felt. The patient is then asked to void, and both flow and pressure are recorded. These are plotted against each other to create the cystometrogram.
Results

Exponential function
In mathematics, the exponential function is the function ex, where e is the number such that the function ex is its own derivative. The exponential function is used to model a relationship in which a constant change in the independent variable gives the same proportional change In mathematics,...
growth curve. The spikes correspond to the bladder contractions associated with the micturation reflex
Urination
Urination, also known as micturition, voiding, peeing, weeing, pissing, and more rarely, emiction, is the ejection of urine from the urinary bladder through the urethra to the outside of the body. In healthy humans the process of urination is under voluntary control...
. The curve formed by the bottom of the plot reflects the level of pressure necessary to void. In normal patients, the first couple hundred milliliters of urine flow with minimal applied pressure. Increasing pressure is necessary to void 200-300 millileters of urine. Beyond that, the pressure necessary to void additional urine rises sharply.
Risks & Contraindications
As with any catheterization, the primary risk is of urinary tract infection. As a result, the procedure is contraindicated in any patient with an active UTI because the results may be skewed and the infection may spread.There is also the potential for trauma to the bladder and urethtra, which may result in hematuria
Hematuria
In medicine, hematuria, or haematuria, is the presence of red blood cells in the urine. It may be idiopathic and/or benign, or it can be a sign that there is a kidney stone or a tumor in the urinary tract , ranging from trivial to lethal...
(blood in the urine).

