
True RMS converter
Encyclopedia
Alternating current
In alternating current the movement of electric charge periodically reverses direction. In direct current , the flow of electric charge is only in one direction....
signal it is often necessary to convert the signal into a direct current
Direct current
Direct current is the unidirectional flow of electric charge. Direct current is produced by such sources as batteries, thermocouples, solar cells, and commutator-type electric machines of the dynamo type. Direct current may flow in a conductor such as a wire, but can also flow through...
signal of equivalent value (known as the root mean square
Root mean square
In mathematics, the root mean square , also known as the quadratic mean, is a statistical measure of the magnitude of a varying quantity. It is especially useful when variates are positive and negative, e.g., sinusoids...
, RMS value). This process can be quite complex (see root mean square
Root mean square
In mathematics, the root mean square , also known as the quadratic mean, is a statistical measure of the magnitude of a varying quantity. It is especially useful when variates are positive and negative, e.g., sinusoids...
for a detailed mathematical explanation). Most low cost instrumentation and signal converters (for example handheld multimeter
Multimeter
A multimeter or a multitester, also known as a VOM , is an electronic measuring instrument that combines several measurement functions in one unit. A typical multimeter may include features such as the ability to measure voltage, current and resistance...
s of the sort used by maintenance engineers) carry out this conversion by filtering the signal into an average value and applying a correction factor.
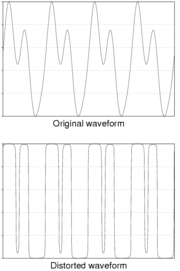
The value of the correction factor applied is only correct if the input signal is sinusoidal. The true RMS value is actually proportional to the square-root of the average of the square of the curve, and not to the average of the absolute value of the curve. For any given waveform
Waveform
Waveform means the shape and form of a signal such as a wave moving in a physical medium or an abstract representation.In many cases the medium in which the wave is being propagated does not permit a direct visual image of the form. In these cases, the term 'waveform' refers to the shape of a graph...
, the ratio of these two averages will be constant and, as most measurements are carried out on what are (nominally) sine waves, the correction factor assumes this waveform; but any distortion or offsets will lead to errors. Although in most cases this produces adequate results, a correct conversion or the measurement of non sine wave values, requires a more complex and costly converter, known as a True RMS converter.
Thermal converters
The RMS value of an alternating currentAlternating current
In alternating current the movement of electric charge periodically reverses direction. In direct current , the flow of electric charge is only in one direction....
is also known as its heating value, as it is a voltage which is equivalent to the direct current
Direct current
Direct current is the unidirectional flow of electric charge. Direct current is produced by such sources as batteries, thermocouples, solar cells, and commutator-type electric machines of the dynamo type. Direct current may flow in a conductor such as a wire, but can also flow through...
value that would be required to get the same heating effect. For example, if we applied RMS to a resistive heating element it would heat up by exactly the same amount as if we had applied .
This principle was exploited in early thermal converters. The AC signal would be applied to a small heating element which was twinned with a thermistor
Thermistor
A thermistor is a type of resistor whose resistance varies significantly with temperature, more so than in standard resistors. The word is a portmanteau of thermal and resistor...
which could be used in a DC measuring circuit.
The technique is not particularly precise but it will measure any waveform at any frequency. A big drawback is that it is low impedance, that is the power used to heat the thermistor comes from the circuit being measured. If the circuit being measured can support the heating current, then it is possible to make a post measurement calculation to correct the effect, as the impedance of the heating element is known. If the signal is small then a pre-amplifier is necessary, and the measuring capabilities of the instrument will be limited by this pre-amplifier.
Thermal converters have become quite rare, but as they are inherently simple and cheap they are still used by radio hams and hobbyists, who may remove the thermal element of an old unreliable instrument and incorporate it into a modern design of their own construction.
Analog electronic converters
Analog electronic circuits may use:- an analog multiplierAnalog multiplierIn electronics, an analog multiplier is a device which takes two analog signals and produces an output which is their product. Such circuits can be used to implement related functions such as squares , and square roots....
in a specific configuration which multiplies the input signal by itself (squares it), averages the result with a capacitor, and then calculates the square root of the value (via a multiplier/squarer circuit in the feedback loop of an operational amplifierOperational amplifierAn operational amplifier is a DC-coupled high-gain electronic voltage amplifier with a differential input and, usually, a single-ended output...
, or - a full-wave precision rectifierPrecision rectifierThe precision rectifier, which is also known as a super diode, is a configuration obtained with an operational amplifier in order to have a circuit behaving like an ideal diode and rectifier. It can be useful for high-precision signal processing....
circuit to create the absolute valueAbsolute valueIn mathematics, the absolute value |a| of a real number a is the numerical value of a without regard to its sign. So, for example, the absolute value of 3 is 3, and the absolute value of -3 is also 3...
of the input signal, which is fed into a operational amplifierOperational amplifierAn operational amplifier is a DC-coupled high-gain electronic voltage amplifier with a differential input and, usually, a single-ended output...
arranged to give an exponential transfer function, then doubled in voltage and fed to a log amplifier as a means of deriving the square-law transfer function, before time-averaging and calculating the square root of the voltage, similar to above, or - a field-effect transistorField-effect transistorThe field-effect transistor is a transistor that relies on an electric field to control the shape and hence the conductivity of a channel of one type of charge carrier in a semiconductor material. FETs are sometimes called unipolar transistors to contrast their single-carrier-type operation with...
may be used to directly create the square-law transfer function, before time-averaging.
Unlike thermal converters they are subject to bandwidth limitations which makes them unsuitable for most RF
Radio frequency
Radio frequency is a rate of oscillation in the range of about 3 kHz to 300 GHz, which corresponds to the frequency of radio waves, and the alternating currents which carry radio signals...
work. The circuitry before time averaging is particularly crucial for high frequency performance. The slew rate
Slew rate
In electronics, the slew rate represents the maximum rate of change of a signal at any point in a circuit.Limitations in slew rate capability can give rise to non linear effects in electronic amplifiers...
limitation of the operational amplifier used to create the absolute value (especially at low input signal levels) tends to make the second method the poorest at high frequencies, while the FET method can work close to VHF. Specialist techniques are required to produce sufficiently accurate integrated circuits for complex analog calculations, and very often meters equipped with such circuits offer True RMS conversion as an optional extra with a significant price increase.
Digital RMS converters
If a waveform has been digitized, then the correct RMS value may be calculated directly. Most digital and PC-based oscilloscopeOscilloscope
An oscilloscope is a type of electronic test instrument that allows observation of constantly varying signal voltages, usually as a two-dimensional graph of one or more electrical potential differences using the vertical or 'Y' axis, plotted as a function of time,...
s include a function to give the RMS value of a waveform. Obviously the precision and the bandwidth of the conversion is entirely dependent on the analog to digital conversion. In most cases, true RMS measurements are made on repetitive waveforms, and under such conditions digital oscilloscopes (and a few sophisticated sampling multimeters) are able to achieve very high bandwidths as they sample at a fraction of the signal frequency to obtain a stroboscopic effect.
Weblinks
- Circuit description of a analog true RMS-to-DC converter (National Semiconductor, 1973)

