
Tracy–Widom distribution
Encyclopedia
The Tracy–Widom distribution, introduced by , is the probability distribution
of the largest eigenvalue of a random hermitian matrix in the edge scaling limit. It also appears in the distribution of the length of the longest increasing subsequence
of random permutation
s and in current fluctuations of the asymmetric simple exclusion process (ASEP) with step initial condition . See for experimental testing (and verifying) that the interface fluctuations of a growing droplet (or substrate) are described by the TW distribution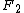 (or
(or 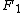 ) as predicted by .
) as predicted by .
The cumulative distribution function
of the Tracy–Widom distribution can be given as the Fredholm determinant
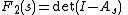
of the operator As on square integrable function on the half line (s, ∞) with kernel given in terms of Airy function
s Ai by
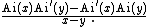
It can also be given as an integral
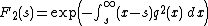
in terms of a solution of a Painlevé equation of type II
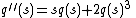
where q, called the Hastings-McLeod solution, satisfies the boundary condition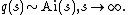
The distribution F2 is associated to unitary ensembles in random matrix theory. There are analogous Tracy–Widom distributions F1 and F4 for orthogonal (β=1) and symplectic ensembles (β=4) that are also expressible in terms of the same Painlevé transcendent q :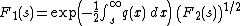
and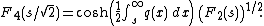
The distribution F1 is of particular interest in multivariate statistics
. For a discussion of the universality of Fβ, β=1,2, and 4, see . For an application of F1 to inferring population structure from genetic data see .
Numerical techniques for obtaining numerical solutions to the Painlevé equations of the types II and V, and numerically evaluating eigenvalue distributions of random matrices in the beta-ensembles were first presented by using MATLAB
. These approximation techniques were further analytically justified in and used to provide numerical evaluation of Painlevé II and Tracy–Widom distributions (for β=1,2, and 4) in S-PLUS
. These distributions have been tabulated in to four significant digits for values of the argument in increments of 0.01; a statistical table for p-values was also given in this work. gave accurate and fast algorithms for the numerical evaluation of Fβ and the density functions fβ(s)=dFβ/ds for β=1,2, and 4. These algorithms can be used to compute numerically the mean
, variance
, skewness
and kurtosis
of the distributions Fβ.
Functions for working with the Tracy-Widom laws are also presented in the R package 'RMTstat' by and MATLAB package 'RMLab' by .
For an extension of the definition of the Tracy–Widom distributions Fβ to all β>0 see .
Probability distribution
In probability theory, a probability mass, probability density, or probability distribution is a function that describes the probability of a random variable taking certain values....
of the largest eigenvalue of a random hermitian matrix in the edge scaling limit. It also appears in the distribution of the length of the longest increasing subsequence
Longest increasing subsequence
The longest increasing subsequence problem is to find a subsequence of a given sequence in which the subsequence elements are in sorted order, lowest to highest, and in which the subsequence is as long as possible...
of random permutation
Permutation
In mathematics, the notion of permutation is used with several slightly different meanings, all related to the act of permuting objects or values. Informally, a permutation of a set of objects is an arrangement of those objects into a particular order...
s and in current fluctuations of the asymmetric simple exclusion process (ASEP) with step initial condition . See for experimental testing (and verifying) that the interface fluctuations of a growing droplet (or substrate) are described by the TW distribution
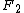 (or
(or 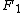 ) as predicted by .
) as predicted by .The cumulative distribution function
Cumulative distribution function
In probability theory and statistics, the cumulative distribution function , or just distribution function, describes the probability that a real-valued random variable X with a given probability distribution will be found at a value less than or equal to x. Intuitively, it is the "area so far"...
of the Tracy–Widom distribution can be given as the Fredholm determinant
Fredholm determinant
In mathematics, the Fredholm determinant is a complex-valued function which generalizes the determinant of a matrix. It is defined for bounded operators on a Hilbert space which differ from the identity operator by a trace-class operator...
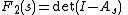
of the operator As on square integrable function on the half line (s, ∞) with kernel given in terms of Airy function
Airy function
In the physical sciences, the Airy function Ai is a special function named after the British astronomer George Biddell Airy...
s Ai by
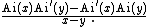
It can also be given as an integral
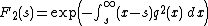
in terms of a solution of a Painlevé equation of type II
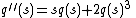
where q, called the Hastings-McLeod solution, satisfies the boundary condition
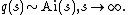
The distribution F2 is associated to unitary ensembles in random matrix theory. There are analogous Tracy–Widom distributions F1 and F4 for orthogonal (β=1) and symplectic ensembles (β=4) that are also expressible in terms of the same Painlevé transcendent q :
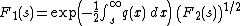
and
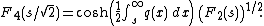
The distribution F1 is of particular interest in multivariate statistics
Multivariate statistics
Multivariate statistics is a form of statistics encompassing the simultaneous observation and analysis of more than one statistical variable. The application of multivariate statistics is multivariate analysis...
. For a discussion of the universality of Fβ, β=1,2, and 4, see . For an application of F1 to inferring population structure from genetic data see .
Numerical techniques for obtaining numerical solutions to the Painlevé equations of the types II and V, and numerically evaluating eigenvalue distributions of random matrices in the beta-ensembles were first presented by using MATLAB
MATLAB
MATLAB is a numerical computing environment and fourth-generation programming language. Developed by MathWorks, MATLAB allows matrix manipulations, plotting of functions and data, implementation of algorithms, creation of user interfaces, and interfacing with programs written in other languages,...
. These approximation techniques were further analytically justified in and used to provide numerical evaluation of Painlevé II and Tracy–Widom distributions (for β=1,2, and 4) in S-PLUS
S-PLUS
S-PLUS is a commercial implementation of the S programming language sold by TIBCO Software Inc..It features object-oriented programming capabilities and advanced analytical algorithms.-Historical timeline:...
. These distributions have been tabulated in to four significant digits for values of the argument in increments of 0.01; a statistical table for p-values was also given in this work. gave accurate and fast algorithms for the numerical evaluation of Fβ and the density functions fβ(s)=dFβ/ds for β=1,2, and 4. These algorithms can be used to compute numerically the mean
Mean
In statistics, mean has two related meanings:* the arithmetic mean .* the expected value of a random variable, which is also called the population mean....
, variance
Variance
In probability theory and statistics, the variance is a measure of how far a set of numbers is spread out. It is one of several descriptors of a probability distribution, describing how far the numbers lie from the mean . In particular, the variance is one of the moments of a distribution...
, skewness
Skewness
In probability theory and statistics, skewness is a measure of the asymmetry of the probability distribution of a real-valued random variable. The skewness value can be positive or negative, or even undefined...
and kurtosis
Kurtosis
In probability theory and statistics, kurtosis is any measure of the "peakedness" of the probability distribution of a real-valued random variable...
of the distributions Fβ.
| β | Mean | Variance | Skewness | Kurtosis |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | -1.2065335745820 | 1.607781034581 | 0.29346452408 | 0.1652429384 |
| 2 | -1.771086807411 | 0.8131947928329 | 0.224084203610 | 0.0934480876 |
| 4 | -2.306884893241 | 0.5177237207726 | 0.16550949435 | 0.0491951565 |
Functions for working with the Tracy-Widom laws are also presented in the R package 'RMTstat' by and MATLAB package 'RMLab' by .
For an extension of the definition of the Tracy–Widom distributions Fβ to all β>0 see .

