Tetraphenylmethane
Encyclopedia
Tetraphenylmethane is an organic compound
consisting of a methane
core with four phenyl substituent
s. It was first synthesized by Moses Gomberg
in 1898.
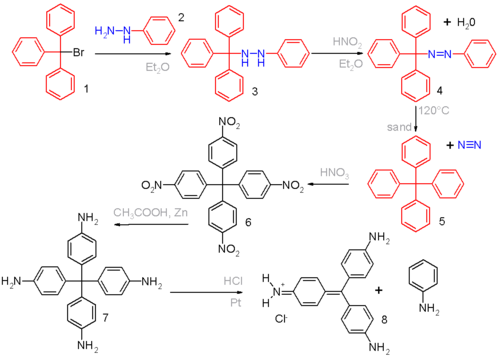
Gomberg's classical organic synthesis
in scheme 1 starts by reacting triphenylmethylbromide 1 with phenylhydrazine
2 to the hydrazine
3. Oxidation with nitrous acid
then produces the azo compound
4 from which on heating above the melting point
, nitrogen
gas evolves with formation of tetraphenylmethane 5.
Gomberg was able to distinguish this compound from triphenylmethane
(elemental analysis
was not an option given the small differences in the hydrogen fractions of 6.29% and 6.60%) by nitration
of 5 with nitric acid
to 6.
A strong base
would be able to abstract the methine proton of the nitrated triphenylmethyl compound if present, forming a strongly colored compound.
He obtained further evidence for the formation of tetraphenylmethane by reducing the nitro groups to amino
groups with zinc
dust in acetic acid
to the leuco dye
7 which on exposure to hydrochloric acid
eliminates aniline
to the known compound pararosanilin 8.
Gomberg's success in synthesizing tetraphenylmethane set him on the attempt to prepare the next homologue hexaphenylethane which led him to the discovery of the triphenylmethyl radical
.
Organic compound
An organic compound is any member of a large class of gaseous, liquid, or solid chemical compounds whose molecules contain carbon. For historical reasons discussed below, a few types of carbon-containing compounds such as carbides, carbonates, simple oxides of carbon, and cyanides, as well as the...
consisting of a methane
Methane
Methane is a chemical compound with the chemical formula . It is the simplest alkane, the principal component of natural gas, and probably the most abundant organic compound on earth. The relative abundance of methane makes it an attractive fuel...
core with four phenyl substituent
Substituent
In organic chemistry and biochemistry, a substituent is an atom or group of atoms substituted in place of a hydrogen atom on the parent chain of a hydrocarbon...
s. It was first synthesized by Moses Gomberg
Moses Gomberg
Moses Gomberg was a chemistry professor at the University of Michigan....
in 1898.
Gomberg's classical organic synthesis
Organic synthesis
Organic synthesis is a special branch of chemical synthesis and is concerned with the construction of organic compounds via organic reactions. Organic molecules can often contain a higher level of complexity compared to purely inorganic compounds, so the synthesis of organic compounds has...
in scheme 1 starts by reacting triphenylmethylbromide 1 with phenylhydrazine
Phenylhydrazine
Phenylhydrazine is the chemical compound with the formula C6H5NHNH2. Organic chemists abbreviate the compound as PhNHNH2.- Chemical properties :...
2 to the hydrazine
Hydrazine
Hydrazine is an inorganic compound with the formula N2H4. It is a colourless flammable liquid with an ammonia-like odor. Hydrazine is highly toxic and dangerously unstable unless handled in solution. Approximately 260,000 tons are manufactured annually...
3. Oxidation with nitrous acid
Nitrous acid
Nitrous acid is a weak and monobasic acid known only in solution and in the form of nitrite salts.Nitrous acid is used to make diazides from amines; this occurs by nucleophilic attack of the amine onto the nitrite, reprotonation by the surrounding solvent, and double-elimination of water...
then produces the azo compound
Azo compound
Azo compounds are compounds bearing the functional group R-N=N-R', in which R and R' can be either aryl or alkyl. IUPAC defines azo compounds as: "Derivatives of diazene , HN=NH, wherein both hydrogens are substituted by hydrocarbyl groups, e.g. PhN=NPh azobenzene or diphenyldiazene." The more...
4 from which on heating above the melting point
Melting point
The melting point of a solid is the temperature at which it changes state from solid to liquid. At the melting point the solid and liquid phase exist in equilibrium. The melting point of a substance depends on pressure and is usually specified at standard atmospheric pressure...
, nitrogen
Nitrogen
Nitrogen is a chemical element that has the symbol N, atomic number of 7 and atomic mass 14.00674 u. Elemental nitrogen is a colorless, odorless, tasteless, and mostly inert diatomic gas at standard conditions, constituting 78.08% by volume of Earth's atmosphere...
gas evolves with formation of tetraphenylmethane 5.
Gomberg was able to distinguish this compound from triphenylmethane
Triphenylmethane
Triphenylmethane, or triphenyl methane, is the hydrocarbon with the formula 3CH. This colorless solid is soluble in nonpolar organic solvents and not in water. Triphenylmethane has the basic skeleton of many synthetic dyes called triarylmethane dyes, many of them are pH indicators, and some display...
(elemental analysis
Elemental analysis
Percent Composition is a process where a sample of some material is analyzed for its elemental and sometimes isotopic composition. Elemental analysis can be qualitative , and it can be quantitative...
was not an option given the small differences in the hydrogen fractions of 6.29% and 6.60%) by nitration
Nitration
Nitration is a general chemical process for the introduction of a nitro group into a chemical compound. The dominant application of nitration is for the production of nitrobenzene, the precursor to methylene diphenyl diisocyanate...
of 5 with nitric acid
Nitric acid
Nitric acid , also known as aqua fortis and spirit of nitre, is a highly corrosive and toxic strong acid.Colorless when pure, older samples tend to acquire a yellow cast due to the accumulation of oxides of nitrogen. If the solution contains more than 86% nitric acid, it is referred to as fuming...
to 6.
A strong base
Base (chemistry)
For the term in genetics, see base A base in chemistry is a substance that can accept hydrogen ions or more generally, donate electron pairs. A soluble base is referred to as an alkali if it contains and releases hydroxide ions quantitatively...
would be able to abstract the methine proton of the nitrated triphenylmethyl compound if present, forming a strongly colored compound.
He obtained further evidence for the formation of tetraphenylmethane by reducing the nitro groups to amino
Amine
Amines are organic compounds and functional groups that contain a basic nitrogen atom with a lone pair. Amines are derivatives of ammonia, wherein one or more hydrogen atoms have been replaced by a substituent such as an alkyl or aryl group. Important amines include amino acids, biogenic amines,...
groups with zinc
Zinc
Zinc , or spelter , is a metallic chemical element; it has the symbol Zn and atomic number 30. It is the first element in group 12 of the periodic table. Zinc is, in some respects, chemically similar to magnesium, because its ion is of similar size and its only common oxidation state is +2...
dust in acetic acid
Acetic acid
Acetic acid is an organic compound with the chemical formula CH3CO2H . It is a colourless liquid that when undiluted is also called glacial acetic acid. Acetic acid is the main component of vinegar , and has a distinctive sour taste and pungent smell...
to the leuco dye
Leuco dye
A leuco dye is a dye whose molecules can acquire two forms, one of which is colorless.For example, the spiro form of an oxazine is a colorless leuco dye; the conjugated system of the oxazine and another aromatic part of the molecule is separated by an sp3-hybridized "spiro" carbon...
7 which on exposure to hydrochloric acid
Hydrochloric acid
Hydrochloric acid is a solution of hydrogen chloride in water, that is a highly corrosive, strong mineral acid with many industrial uses. It is found naturally in gastric acid....
eliminates aniline
Aniline
Aniline, phenylamine or aminobenzene is an organic compound with the formula C6H5NH2. Consisting of a phenyl group attached to an amino group, aniline is the prototypical aromatic amine. Being a precursor to many industrial chemicals, its main use is in the manufacture of precursors to polyurethane...
to the known compound pararosanilin 8.
Gomberg's success in synthesizing tetraphenylmethane set him on the attempt to prepare the next homologue hexaphenylethane which led him to the discovery of the triphenylmethyl radical
Triphenylmethyl radical
The triphenylmethyl radical is a persistent radical and the first-ever radical described in organic chemistry. It can be prepared by homolysis of triphenylmethyl chloride 1 by a metal like silver or zinc in benzene or diethyl ether. The radical 2 forms a chemical equilibrium with the quinoid type...
.