
Sverdrup wave
Encyclopedia
A Sverdrup wave is a wave in the ocean (especially infinite open ocean), which is affected by gravity and Earth's rotation (see Coriolis effect
)
In shallow water gravity wave [or long wave ], (h stands for depth)only gravity effect the wave, the phase velocity
of shallow water gravity wave (c) can be noted as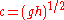
and the group velocity (cg) of shallow water gravity wave can be noted as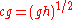 i.e.
i.e. 
where g is gravity, λ is the wavelength
and h is the total depth. But after concerning the inertial acceleration, the result would be different.
Coriolis effect
In physics, the Coriolis effect is a deflection of moving objects when they are viewed in a rotating reference frame. In a reference frame with clockwise rotation, the deflection is to the left of the motion of the object; in one with counter-clockwise rotation, the deflection is to the right...
)
In shallow water gravity wave [or long wave ], (h stands for depth)only gravity effect the wave, the phase velocity
Phase velocity
The phase velocity of a wave is the rate at which the phase of the wave propagates in space. This is the speed at which the phase of any one frequency component of the wave travels. For such a component, any given phase of the wave will appear to travel at the phase velocity...
of shallow water gravity wave (c) can be noted as
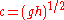
and the group velocity (cg) of shallow water gravity wave can be noted as
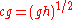 i.e.
i.e. 
where g is gravity, λ is the wavelength
Wavelength
In physics, the wavelength of a sinusoidal wave is the spatial period of the wave—the distance over which the wave's shape repeats.It is usually determined by considering the distance between consecutive corresponding points of the same phase, such as crests, troughs, or zero crossings, and is a...
and h is the total depth. But after concerning the inertial acceleration, the result would be different.

