
Subcutaneous injection
Encyclopedia
Bolus (medicine)
In medicine, a bolus is the administration of a medication, drug or other compound that is given to raise its concentration in blood to an effective level...
into the subcutis, the layer of skin directly below the dermis
Dermis
The dermis is a layer of skin between the epidermis and subcutaneous tissues, and is composed of two layers, the papillary and reticular dermis...
and epidermis, collectively referred to as the cutis
Cutis
Cutis may refer to several unrelated biological structures:* Cutis , the outermost layers of skin* Cutis , a type of pileipellis with a repent arrangement of hyphaeand to:* Cutiş, a village in Almaşu Commune, Sălaj County, Romania...
. Subcutaneous injections are highly effective in administering vaccines and medications such as insulin
Insulin
Insulin is a hormone central to regulating carbohydrate and fat metabolism in the body. Insulin causes cells in the liver, muscle, and fat tissue to take up glucose from the blood, storing it as glycogen in the liver and muscle....
, morphine
Morphine
Morphine is a potent opiate analgesic medication and is considered to be the prototypical opioid. It was first isolated in 1804 by Friedrich Sertürner, first distributed by same in 1817, and first commercially sold by Merck in 1827, which at the time was a single small chemists' shop. It was more...
, diacetylmorphine and goserelin
Goserelin
Goserelin acetate is an injectable gonadotropin releasing hormone superagonist , also known as a luteinizing hormone releasing hormone agonist. Structurally, it is a decapeptide...
.
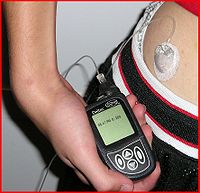
Subcutaneous insulin injections in diabetes mellitus
A person with Type I diabetes mellitusDiabetes mellitus
Diabetes mellitus, often simply referred to as diabetes, is a group of metabolic diseases in which a person has high blood sugar, either because the body does not produce enough insulin, or because cells do not respond to the insulin that is produced...
typically injects insulin subcutaneously. Places on the body where people can inject insulin most easily are:
- The outer area of the upper arm.
- Just above and below the waistWaistThe waist is the part of the abdomen between the rib cage and hips. On proportionate people, the waist is the narrowest part of the torso....
, except the area right around the navelNavelThe navel is a scar on the abdomen caused when the umbilical cord is removed from a newborn baby...
(a 2-inch circle). - The upper area of the buttock, just behind the hip bone.
- The front of the thighThighIn humans the thigh is the area between the pelvis and the knee. Anatomically, it is part of the lower limb.The single bone in the thigh is called the femur...
, midway to the outer side, 4 inches below the top of the thigh to 4 inches above the knee.
These areas can vary with the size of the person. Changing the injection site keeps lumps or small dents called lipodystrophies
Lipodystrophy
Lipodystrophy is a medical condition characterized by abnormal or degenerative conditions of the body's adipose tissue. A more specific term, lipoatrophy is used when describing the loss of fat from one area...
from forming in the skin. However, people should try to use the same body area for injections that are given at the same time each day-for example, always using the abdomen
Abdomen
In vertebrates such as mammals the abdomen constitutes the part of the body between the thorax and pelvis. The region enclosed by the abdomen is termed the abdominal cavity...
for the morning injection or an arm for the evening injection. Using the same body area for these routine injections lessens the possibility of changes in the timing and action of insulin.

