Staudinger reaction
Overview
Chemical reaction
A chemical reaction is a process that leads to the transformation of one set of chemical substances to another. Chemical reactions can be either spontaneous, requiring no input of energy, or non-spontaneous, typically following the input of some type of energy, such as heat, light or electricity...
in which the combination of an azide
Azide
Azide is the anion with the formula N3−. It is the conjugate base of hydrazoic acid. N3− is a linear anion that is isoelectronic with CO2 and N2O. Per valence bond theory, azide can be described by several resonance structures, an important one being N−=N+=N−...
with a phosphine
Phosphine
Phosphine is the compound with the chemical formula PH3. It is a colorless, flammable, toxic gas. Pure phosphine is odourless, but technical grade samples have a highly unpleasant odor like garlic or rotting fish, due to the presence of substituted phosphine and diphosphine...
or phosphite
Phosphite
A phosphite is a salt of phosphorous acid. The phosphite ion is a polyatomic ion with a phosphorus central atom where phosphorus has an oxidation state of +3...
produces an iminophosphorane intermediate. Combined with the hydrolysis
Hydrolysis
Hydrolysis is a chemical reaction during which molecules of water are split into hydrogen cations and hydroxide anions in the process of a chemical mechanism. It is the type of reaction that is used to break down certain polymers, especially those made by condensation polymerization...
of the aza-ylide to produce a phosphine oxide
Phosphine oxide
Phosphine oxides are either inorganic phosphorus compounds such as phosphoryl trichloride or organophosphorus compounds with the formula OPR3, where R = alkyl or aryl...
and an amine
Amine
Amines are organic compounds and functional groups that contain a basic nitrogen atom with a lone pair. Amines are derivatives of ammonia, wherein one or more hydrogen atoms have been replaced by a substituent such as an alkyl or aryl group. Important amines include amino acids, biogenic amines,...
, this reaction is a mild method of reducing an azide to an amine. Triphenylphosphine
Triphenylphosphine
Triphenylphosphine is a common organophosphorus compound with the formula P3 - often abbreviated to PPh3 or Ph3P. It is widely used in the synthesis of organic and organometallic compounds. PPh3 exists as relatively air stable, colorless crystals at room temperature...
is commonly used as the reducing agent
Reducing agent
A reducing agent is the element or compound in a reduction-oxidation reaction that donates an electron to another species; however, since the reducer loses an electron we say it is "oxidized"...
, yielding triphenylphosphine oxide
Triphenylphosphine oxide
Triphenylphosphine oxide is the chemical compound with the formula OP3. Often chemists abbreviate the formula by writing Ph3PO or PPh3O . This white crystalline compound is a common side product in reactions involving triphenylphosphine...
as the side product in addition to the amine.
The reaction was invented by and named after Hermann Staudinger
Hermann Staudinger
- External links :* Staudinger's * Staudinger's Nobel Lecture *....
.
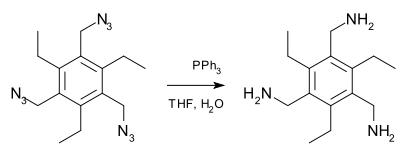
An example of a Staudinger reduction is the organic synthesis
Organic synthesis
Organic synthesis is a special branch of chemical synthesis and is concerned with the construction of organic compounds via organic reactions. Organic molecules can often contain a higher level of complexity compared to purely inorganic compounds, so the synthesis of organic compounds has...
of this pinwheel compound:
The reaction mechanism
Reaction mechanism
In chemistry, a reaction mechanism is the step by step sequence of elementary reactions by which overall chemical change occurs.Although only the net chemical change is directly observable for most chemical reactions, experiments can often be designed that suggest the possible sequence of steps in...
centers around the formation of an iminophosphorane through nucleophilic addition
Nucleophilic addition
In organic chemistry, a nucleophilic addition reaction is an addition reaction where in a chemical compound a π bond is removed by the creation of two new covalent bonds by the addition of a nucleophile....
of the phosphine
Phosphine
Phosphine is the compound with the chemical formula PH3. It is a colorless, flammable, toxic gas. Pure phosphine is odourless, but technical grade samples have a highly unpleasant odor like garlic or rotting fish, due to the presence of substituted phosphine and diphosphine...
at the terminal nitrogen atom of the azide and expulsion of nitrogen.