
Standard streams
Encyclopedia
- This article is about standard I/O file descriptors; for System V streams, see STREAMSSTREAMSIn computer networking, STREAMS is the native framework in Unix System V for implementing character devices.STREAMS was designed as a modular architecture for implementing full-duplex I/O between kernel or user space processes and device drivers. Its most frequent uses have been in developing...
.
Unix
Unix is a multitasking, multi-user computer operating system originally developed in 1969 by a group of AT&T employees at Bell Labs, including Ken Thompson, Dennis Ritchie, Brian Kernighan, Douglas McIlroy, and Joe Ossanna...
and Unix-like
Unix-like
A Unix-like operating system is one that behaves in a manner similar to a Unix system, while not necessarily conforming to or being certified to any version of the Single UNIX Specification....
operating systems (and, to some extent, Windows), as well as certain programming language
Programming language
A programming language is an artificial language designed to communicate instructions to a machine, particularly a computer. Programming languages can be used to create programs that control the behavior of a machine and/or to express algorithms precisely....
interfaces, the standard streams are preconnected input and output channels between a computer program and its environment (typically a text terminal) when it begins execution. The three I/O
Input/output
In computing, input/output, or I/O, refers to the communication between an information processing system , and the outside world, possibly a human, or another information processing system. Inputs are the signals or data received by the system, and outputs are the signals or data sent from it...
connections are called standard input (stdin), standard output (stdout) and standard error (stderr).
Background
In most operating systems predating Unix, programs had to explicitly connect to the appropriate input and output data. On many of those systems, this could be an intimidating programming challenge created by OS-specific intricacies such as obtaining control environment settings, accessing a local file table, determining the intended data set, and handling the correct case of a card reader, magnetic tape drive, disk drive, line printer, card punch, or interactive terminal.Unix provided several groundbreaking advances, one of which was to provide abstract devices: it removed the need for a program to know or care what kind of devices it was communicating with. Older operating systems forced upon the programmer a record structure and, frequently non-orthogonal data semantics and device control. Unix eliminated this complexity with the concept of a data stream: an ordered sequence of data bytes which can be read until the end of file
End-of-file
In computing, end of file is a condition in a computer operating system where no more data can be read from a data source...
. A program may also write bytes as desired and need not (and can't easily) declare how many there will be, or how they will be grouped.
Another Unix breakthrough was to automatically associate input and output by default—the program (and programmer) did absolutely nothing to establish input and output for a typical input-process-output program (unless it chose a different paradigm). In contrast, previous operating systems usually required some—often complex—job control language
Job Control Language
Job Control Language is a scripting language used on IBM mainframe operating systems to instruct the system on how to run a batch job or start a subsystem....
to establish connections, or the equivalent burden had to be orchestrated by the program.
Since Unix provided standard streams, the Unix C runtime environment was obligated to support it as well. As a result, most C runtime environments (and C's descendants), regardless of the operating system, provide equivalent functionality.
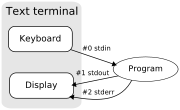
Standard input (stdin)
Standard input is data (often text) going into a program. The program requests data transfers by use of the read operation. Not all programs require input. For example, the dir or ls program (which displays file names contained in a directory) performs its operation without any stream data input.Unless redirected, input is expected from the keyboard
Keyboard (computing)
In computing, a keyboard is a typewriter-style keyboard, which uses an arrangement of buttons or keys, to act as mechanical levers or electronic switches...
which started the program.
The file descriptor
File descriptor
In computer programming, a file descriptor is an abstract indicator for accessing a file. The term is generally used in POSIX operating systems...
for standard input is 0 (zero); the POSIX
POSIX
POSIX , an acronym for "Portable Operating System Interface", is a family of standards specified by the IEEE for maintaining compatibility between operating systems...
Standard output (stdout)
Standard output is the stream where a program writes its output data. The program requests data transfer with the write operation. Not all programs generate output. For example the file rename command (variously called mv, move, ren) is silent on success.Unless redirected
Redirection (Unix)
In computing, redirection is a function common to most command-line interpreters, including the various Unix shells that can redirect standard streams to user-specified locations....
, standard output is the text terminal which initiated the program.
The file descriptor
File descriptor
In computer programming, a file descriptor is an abstract indicator for accessing a file. The term is generally used in POSIX operating systems...
for standard output is 1 (one); the POSIX
POSIX
POSIX , an acronym for "Portable Operating System Interface", is a family of standards specified by the IEEE for maintaining compatibility between operating systems...
Standard error (stderr)
Standard error is another output stream typically used by programs to output error messageError message
An error message is information displayed when an unexpected condition occurs, usually on a computer or other device. On modern operating systems with graphical user interfaces, error messages are often displayed using dialog boxes...
s or diagnostics. It is a stream independent of standard output and can be redirected separately. The usual destination is the text terminal which started the program to provide the best chance of being seen even if standard output is redirected (so not readily observed). For example, output of a program in a pipeline
Pipeline (Unix)
In Unix-like computer operating systems , a pipeline is the original software pipeline: a set of processes chained by their standard streams, so that the output of each process feeds directly as input to the next one. Each connection is implemented by an anonymous pipe...
is redirected to input of the next program, but errors from each program still go directly to the text terminal.
It is acceptable—and normal—for standard output and standard error to be directed to the same destination, such as the text terminal. Messages appear in the same order as the program writes them, unless buffering is involved. (For example, a common situation is when the standard error stream is unbuffered but the standard output stream is line-buffered; in this case, text written to standard error later may appear on the terminal earlier, if the standard output stream's buffer is not yet full.)
The file descriptor
File descriptor
In computer programming, a file descriptor is an abstract indicator for accessing a file. The term is generally used in POSIX operating systems...
for standard error is 2; the POSIX
POSIX
POSIX , an acronym for "Portable Operating System Interface", is a family of standards specified by the IEEE for maintaining compatibility between operating systems...
Most shells
Shell (computing)
A shell is a piece of software that provides an interface for users of an operating system which provides access to the services of a kernel. However, the term is also applied very loosely to applications and may include any software that is "built around" a particular component, such as web...
allow both standard output and standard error to be redirected to the same file using
&> filename
Bourne-style shells allow standard error to be redirected to the same destination that standard output is directed to using
2>&1
1950s: Fortran
Fortran has the equivalent of Unix file descriptors:UNIT=5 for stdin, UNIT=6 for stdout and UNIT=0 for stderr.! FORTRAN 77 example
PROGRAM MAIN
READ(UNIT=5,*)NUMBER
WRITE(UNIT=6,'(F5.3)')' NUMBER IS: ',NUMBER
END
1968: ALGOL 68
ALGOL 68ALGOL 68
ALGOL 68 isan imperative computerprogramming language that was conceived as a successor to theALGOL 60 programming language, designed with the goal of a...
's input and output facilities were collectively referred to as the transput. Koster
Cornelis H. A. Koster
Cornelis Hermanus Antonius "Kees" Koster is a professor in the Department of Informatics of the University of Nijmegen in the Netherlands....
coordinated the definition of the transput standard. The model included three standard channels:
stand in, stand out, and stand back.Example:
- ALGOL 68 example #
main:(
REAL number;
getf(stand in,($g$,number));
printf(($"Number is: "g(6,4)"OR "$,number)); # OR #
putf(stand out,($" Number is: "g(6,4)"!"$,number));
newline(stand out)
)
| Input: | Output: |
|---|---|
3.14159 |
Number is: +3.142 OR Number is: +3.142! |
1970s: C and Unix
In the C programming languageC (programming language)
C is a general-purpose computer programming language developed between 1969 and 1973 by Dennis Ritchie at the Bell Telephone Laboratories for use with the Unix operating system....
the standard input, output, and error streams are attached to the existing Unix file descriptors 0, 1 and 2 respectively. In a POSIX
POSIX
POSIX , an acronym for "Portable Operating System Interface", is a family of standards specified by the IEEE for maintaining compatibility between operating systems...
environment the
Magic number (programming)
In computer programming, the term magic number has multiple meanings. It could refer to one or more of the following:* A constant numerical or text value used to identify a file format or protocol; for files, see List of file signatures...
. File pointers stdin, stdout, and stderr are also provided.
1995: Java
In JavaJava (programming language)
Java is a programming language originally developed by James Gosling at Sun Microsystems and released in 1995 as a core component of Sun Microsystems' Java platform. The language derives much of its syntax from C and C++ but has a simpler object model and fewer low-level facilities...
, the standard streams are referred to by (for stdin), (for stdout), and (for stderr).
public static void main(String args[]) {
try {
BufferedReader br =
new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
String s = br.readLine;
double number = Double.parseDouble(s);
System.out.println("Number is:" + number);
} catch (Exception e) {
System.err.println("Error:" + e.getMessage);
}
}
Or you can use the class of package java.util.
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
while(sc.hasNextLine) {
String line = sc.nextLine;
double number = Double.parseDouble(line);
System.out.println("Number is: " + number);
}
}
2000s: .NET
In C# and other .NET.NET Framework
The .NET Framework is a software framework that runs primarily on Microsoft Windows. It includes a large library and supports several programming languages which allows language interoperability...
languages, the standard streams are referred to by
System.Console.In (for stdin), System.Console.Out (for stdout) and System.Console.Error (for stderr). Basic read and write capabilities for the stdin and stdout streams are also accessible directly through the class System.Console (e.g. System.Console.WriteLine can be used instead of System.Console.Out.WriteLine).System.Console.In, System.Console.Out and System.Console.Error are System.IO.TextReader (stdin) and System.IO.TextWriter (stdout, stderr) objects, which only allow access to the underlying standard streams on a text basis. Full binary access to the standard streams must be performed through the System.IO.Stream objects returned by System.Console.OpenStandardInput, System.Console.OpenStandardOutput and System.Console.OpenStandardError respectively.// C# example
public static int Main(string[] args)
{
try {
string s = System.Console.In.ReadLine;
double number = double.Parse(s);
System.Console.Out.WriteLine("Number is: {0:F3}", number);
return 0;
// If Parse threw an exception
} catch (System.ArgumentNullException) {
System.Console.Error.WriteLine("No number was entered!");
} catch (System.FormatException) {
System.Console.Error.WriteLine("The specified value is not a valid number!");
} catch (System.OverflowException) {
System.Console.Error.WriteLine("The specified number is too big!");
}
return -1;
}
' Visual Basic .NET example
Public Function Main As Integer
Dim number As Double
Dim s As String
Try
s = System.Console.In.ReadLine
number = CDbl(s)
System.Console.Out.WriteLine("Number is: {0:F3}", number)
Return 0
Catch e As System.InvalidCastException
' if CDbl threw an exception
System.Console.Error.WriteLine("No number was entered!")
Return 1
End Try
End Function
When applying the
System.Diagnostics.Process classClass (computer science)
In object-oriented programming, a class is a construct that is used as a blueprint to create instances of itself – referred to as class instances, class objects, instance objects or simply objects. A class defines constituent members which enable these class instances to have state and behavior...
one can use the instance properties
Property (programming)
A property, in some object-oriented programming languages, is a special sort of class member, intermediate between a field and a method. Properties are read and written like fields, but property reads and writes are translated to get and set method calls...
StandardInput, StandardOutput, and StandardError of that class to access the standard streams of the process.GUIs
Graphical user interfaceGraphical user interface
In computing, a graphical user interface is a type of user interface that allows users to interact with electronic devices with images rather than text commands. GUIs can be used in computers, hand-held devices such as MP3 players, portable media players or gaming devices, household appliances and...
s (GUIs) rarely make use of the standard streams. Consequently, redirecting GUI programs or constructing a GUI pipeline is neither practical nor useful. The nearest analogy is probably cutting (or copying) from one application and pasting into another. Since manual user operations are required, moving large numbers of pastes is not especially efficient. One notable exception is the dwm
Dwm
dwm is a dynamic tiling window manager for X11 exhibiting the principles of minimalism which is known for having influenced the development of other window managers, including xmonad and awesome. It is externally similar to wmii, but internally much simpler. dwm is written purely in C and, for...
tiling window manager
Tiling window manager
In computing, a tiling window manager is a window manager with an organization of the screen into mutually non-overlapping frames, as opposed to the more popular approach of coordinate-based stacking of overlapping objects that tries to fully emulate the desktop metaphor.-Xerox PARC:Although the...
, which displays data directed through stdin on a status bar.
Some GUI programs, primarily on Unix, still write debug information to standard error. Others may take files to operate from standard in (for example many Unix media players do so).
Popular Windows programs that open a separate console window in addition to their GUI windows are the emulators pSX and DOSBox
DOSBox
DOSBox is emulator software that emulates an IBM PC compatible computer running MS-DOS. It is intended especially for use with old PC games. DOSBox is free software....
.
GTK-server
GTK-server
GTK-server is an open source project released under the GNU General Public License. The GTK-server project aims to bring Graphical User Interface programming to any interpreted language using the GIMP Tool Kit or XForms .-Philosophy:...
can use stdin as communication interface with an interpreted program to realize a GUI.
The Common Lisp Interface Manager paradigm "presents" GUI elements sent to an extended output stream..
iostream Library Standard Streams Naming Convention
iostream library uses c prefix instead of std for naming standard streams. In addition to cin, cout and cerr, it offers the clog standard stream, similar to cerr, but buffered.See also
- Redirection (computing)
- Pipeline (Unix)Pipeline (Unix)In Unix-like computer operating systems , a pipeline is the original software pipeline: a set of processes chained by their standard streams, so that the output of each process feeds directly as input to the next one. Each connection is implemented by an anonymous pipe...
- Stream (computing)
- Input/outputInput/outputIn computing, input/output, or I/O, refers to the communication between an information processing system , and the outside world, possibly a human, or another information processing system. Inputs are the signals or data received by the system, and outputs are the signals or data sent from it...
- C file input/outputC file input/outputThe C programming language provides many standard library functions for file input and output. These functions make up the bulk of the C standard library header...
- SYSIN and SYSOUT
External links
- Standard Output Definition - by The Linux Information Project

