
Spurline
Encyclopedia
The spurline is a type of radio-frequency and microwave
distributed element filter
with band-stop (notch) characteristics, most commonly used with microstrip
transmission lines. Spurlines usually exhibit moderate to narrow-band rejection, at about 10% around the central frequency.
Spurline filters are very convenient for dense integrated circuits because of their inherently compact design and ease of integration: they occupy surface that corresponds only to a quarter-wavelength transmission line
.
line breaking into a pair of smaller coupled lines that rejoin after a quarter-wavelength distance. Only one of the input ports of the coupled lines is connected to the feed microstrip, as shown in the figure below. The orange area of the illustration is the microstrip transmission line conductor and the gray color the exposed dielectric.
Where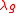 is the wavelength
is the wavelength
corresponding to the central rejection frequency
of the bandstop filter, measured - of course - in the microstrip line material. This is the most important parameter of the filter that sets the rejection band.
The distance between the two coupled lines can be selected appropriately to fine-tune the filter. The smaller the distance, the narrower the stop-band in terms of rejection. Of course that is limited by the circuit-board printing resolution, and it is usually considered at about 10% of the input microstrip width.
The gap between the input microstrip line and the one open-circuited line of the coupler has a negligible effect on the frequency response of the filter. Therefore it is considered approximately equal to the distance of the two coupled lines.
Microwave
Microwaves, a subset of radio waves, have wavelengths ranging from as long as one meter to as short as one millimeter, or equivalently, with frequencies between 300 MHz and 300 GHz. This broad definition includes both UHF and EHF , and various sources use different boundaries...
distributed element filter
Distributed element filter
A distributed element filter is an electronic filter in which capacitance, inductance and resistance are not localised in discrete capacitors, inductors and resistors as they are in conventional filters. Its purpose is to allow a range of signal frequencies to pass, but to block others...
with band-stop (notch) characteristics, most commonly used with microstrip
Microstrip
Microstrip is a type of electrical transmission line which can be fabricated using printed circuit board technology, and is used to convey microwave-frequency signals. It consists of a conducting strip separated from a ground plane by a dielectric layer known as the substrate. Microwave components...
transmission lines. Spurlines usually exhibit moderate to narrow-band rejection, at about 10% around the central frequency.
Spurline filters are very convenient for dense integrated circuits because of their inherently compact design and ease of integration: they occupy surface that corresponds only to a quarter-wavelength transmission line
Transmission line
In communications and electronic engineering, a transmission line is a specialized cable designed to carry alternating current of radio frequency, that is, currents with a frequency high enough that its wave nature must be taken into account...
.
Structure Description
It consists of a normal microstripMicrostrip
Microstrip is a type of electrical transmission line which can be fabricated using printed circuit board technology, and is used to convey microwave-frequency signals. It consists of a conducting strip separated from a ground plane by a dielectric layer known as the substrate. Microwave components...
line breaking into a pair of smaller coupled lines that rejoin after a quarter-wavelength distance. Only one of the input ports of the coupled lines is connected to the feed microstrip, as shown in the figure below. The orange area of the illustration is the microstrip transmission line conductor and the gray color the exposed dielectric.
Where
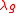 is the wavelength
is the wavelengthWavelength
In physics, the wavelength of a sinusoidal wave is the spatial period of the wave—the distance over which the wave's shape repeats.It is usually determined by considering the distance between consecutive corresponding points of the same phase, such as crests, troughs, or zero crossings, and is a...
corresponding to the central rejection frequency
Frequency
Frequency is the number of occurrences of a repeating event per unit time. It is also referred to as temporal frequency.The period is the duration of one cycle in a repeating event, so the period is the reciprocal of the frequency...
of the bandstop filter, measured - of course - in the microstrip line material. This is the most important parameter of the filter that sets the rejection band.
The distance between the two coupled lines can be selected appropriately to fine-tune the filter. The smaller the distance, the narrower the stop-band in terms of rejection. Of course that is limited by the circuit-board printing resolution, and it is usually considered at about 10% of the input microstrip width.
The gap between the input microstrip line and the one open-circuited line of the coupler has a negligible effect on the frequency response of the filter. Therefore it is considered approximately equal to the distance of the two coupled lines.

