
Speciation of ions
Encyclopedia
Speciation of ions refers to the changing concentration of varying forms of an ion as the pH of the solution changes.
 The pH
The pH
of a solution of a monoprotic weak acid can be expressed in terms of the extent of dissociation. After rearranging the expression defining the acid dissociation constant
, and putting pH = −log10[H+], one obtains
This is a form of the Henderson-Hasselbalch equation
. It can be deduced from this expression that
It follows that the range of pH within which there is partial dissociation of the acid is about pKa ± 2. This is shown graphically at the right.
A practical application of these results is that the pH transition range of a pH indicator
is approximately pKa ± 1; the colour of the indicator in its acid form is different from the colour of the conjugate base form. In the transition range both forms are in equilibrium, so the colour is intermediate. Outside the transition range the concentration of acid or conjugate base is less than 10% and the colour of the major species dominates.
 A weak acid may be defined as an acid with pKa greater than about −2. An acid with pKa = −2 would be 99% dissociated at pH 0, that is, in a 1 M HCl solution. Any acid with a pKa less than about −2 is said to be a strong acid. Strong acids are said to be fully dissociated. There is no precise pKa value that distinguishes between strong and weak acids because strong acids, such as sulfuric acid
A weak acid may be defined as an acid with pKa greater than about −2. An acid with pKa = −2 would be 99% dissociated at pH 0, that is, in a 1 M HCl solution. Any acid with a pKa less than about −2 is said to be a strong acid. Strong acids are said to be fully dissociated. There is no precise pKa value that distinguishes between strong and weak acids because strong acids, such as sulfuric acid
, are associated in very concentrated solution.
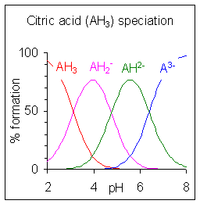
Calculation of the species concentrations for a polyprotic acid is more complicated unless the pK values are separated by four or more, because three or more species may co-exist at a given pH. The example of citric acid
is shown at the right. The pH regions in which the species exist overlap extensively since the difference between successive pKa values is small. A large number of computer programs for the calculation of equilibrium species concentrations have been published. Most of them can handle much more complicated equilibria than acid-base equilibria in solution. For details concerning general purpose programs see computer programs for calculating species concentrations in chemical equilibrium
.

PH
In chemistry, pH is a measure of the acidity or basicity of an aqueous solution. Pure water is said to be neutral, with a pH close to 7.0 at . Solutions with a pH less than 7 are said to be acidic and solutions with a pH greater than 7 are basic or alkaline...
of a solution of a monoprotic weak acid can be expressed in terms of the extent of dissociation. After rearranging the expression defining the acid dissociation constant
Acid dissociation constant
An acid dissociation constant, Ka, is a quantitative measure of the strength of an acid in solution. It is the equilibrium constant for a chemical reaction known as dissociation in the context of acid-base reactions...
, and putting pH = −log10[H+], one obtains
- pH = pKa – log ( [AH]/[A-] )
This is a form of the Henderson-Hasselbalch equation
Henderson-Hasselbalch equation
In chemistry, the Henderson–Hasselbalch equation describes the derivation of pH as a measure of acidity in biological and chemical systems...
. It can be deduced from this expression that
- when the acid is 1% dissociated, that is, when [AH]/[A−] = 100, pH = pKa − 2
- when the acid is 50% dissociated, that is, when [AH]/[A−] = 1, pH = pKa
- when the acid is 99% dissociated, that is, when [AH]/[A−] = 0.01, pH = pKa + 2
It follows that the range of pH within which there is partial dissociation of the acid is about pKa ± 2. This is shown graphically at the right.
A practical application of these results is that the pH transition range of a pH indicator
PH indicator
A pH indicator is a halochromic chemical compound that is added in small amounts to a solution so that the pH of the solution can be determined visually. Hence a pH indicator is a chemical detector for hydronium ions or hydrogen ions in the Arrhenius model. Normally, the indicator causes the...
is approximately pKa ± 1; the colour of the indicator in its acid form is different from the colour of the conjugate base form. In the transition range both forms are in equilibrium, so the colour is intermediate. Outside the transition range the concentration of acid or conjugate base is less than 10% and the colour of the major species dominates.

Sulfuric acid
Sulfuric acid is a strong mineral acid with the molecular formula . Its historical name is oil of vitriol. Pure sulfuric acid is a highly corrosive, colorless, viscous liquid. The salts of sulfuric acid are called sulfates...
, are associated in very concentrated solution.
Calculation of the species concentrations for a polyprotic acid is more complicated unless the pK values are separated by four or more, because three or more species may co-exist at a given pH. The example of citric acid
Citric acid
Citric acid is a weak organic acid. It is a natural preservative/conservative and is also used to add an acidic, or sour, taste to foods and soft drinks...
is shown at the right. The pH regions in which the species exist overlap extensively since the difference between successive pKa values is small. A large number of computer programs for the calculation of equilibrium species concentrations have been published. Most of them can handle much more complicated equilibria than acid-base equilibria in solution. For details concerning general purpose programs see computer programs for calculating species concentrations in chemical equilibrium
Chemical equilibrium
In a chemical reaction, chemical equilibrium is the state in which the concentrations of the reactants and products have not yet changed with time. It occurs only in reversible reactions, and not in irreversible reactions. Usually, this state results when the forward reaction proceeds at the same...
.

