
Space Network
Encyclopedia

NASA
The National Aeronautics and Space Administration is the agency of the United States government that is responsible for the nation's civilian space program and for aeronautics and aerospace research...
program that combines space and ground elements to support spacecraft communications in Earth
Earth
Earth is the third planet from the Sun, and the densest and fifth-largest of the eight planets in the Solar System. It is also the largest of the Solar System's four terrestrial planets...
vicinity. The SN Project Office at Goddard Space Flight Center
Goddard Space Flight Center
The Goddard Space Flight Center is a major NASA space research laboratory established on May 1, 1959 as NASA's first space flight center. GSFC employs approximately 10,000 civil servants and contractors, and is located approximately northeast of Washington, D.C. in Greenbelt, Maryland, USA. GSFC,...
(GSFC) manages the SN, which consists of:
- The geosynchronous Tracking and Data Relay SatelliteTracking and Data Relay SatelliteA Tracking and Data Relay Satellite is a type of communications satellite that forms part of the Tracking and Data Relay Satellite System used by NASA and other United States government agencies for communications to and from independent "User Platforms" such as satellites, balloons, aircraft,...
s (TDRS), - Supporting ground terminal systems,
- The Bilateration Ranging and Transponder System (BRTS),
- Merritt Island Launch Annex (MILA) relay,
- Network Control Center Data SystemNetwork Control Center Data SystemThe Network Control Center Data System is an element of NASA's Space Network ground segment. Collocated with the White Sands Tracking and Data Relay Satellite System, the NCCDS is the operations control facility for the network...
(NCCDS).
Satellite generations
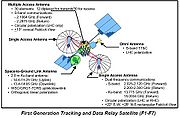
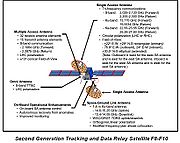
Tracking and Data Relay Satellite
A Tracking and Data Relay Satellite is a type of communications satellite that forms part of the Tracking and Data Relay Satellite System used by NASA and other United States government agencies for communications to and from independent "User Platforms" such as satellites, balloons, aircraft,...
(TDRS) currently consists of first generation (F1-F7), and second generation (F8-F10) satellites.
The space segment of the SN consists of up to six operational relay satellites in geosynchronous orbit. These communications satellites are allocated longitudes for relaying forward and return service signals to and from customers, any entity with an Earth-orbiting satellite that has an agreement with SN to use its communications services, for data transfer and tracking. An additional TDRS, F1, provides dedicated support to the National Science Foundation
National Science Foundation
The National Science Foundation is a United States government agency that supports fundamental research and education in all the non-medical fields of science and engineering. Its medical counterpart is the National Institutes of Health...
(NSF) through the use of the WSC Alternate Relay Terminal (WART). Additional spare TDRSs may be in geosynchronous orbit.
All first generation TDRSs (F1-F7, also known as TDRS A-G) carry functionally identical payloads and all second generation TDRSs (F8-F10, also known as TDRS H-J) carry functionally identical payloads.
A third generation, TDRS K and L, are planned for launch 2012-2013. See TDRS launch history.
Click on the figures to the right, which identify the pertinent communications components and associated parameters of the orbiting relay platforms.
Coverage
For spacecraft operating in a low earth orbitLow Earth orbit
A low Earth orbit is generally defined as an orbit within the locus extending from the Earth’s surface up to an altitude of 2,000 km...
(LEO) 73 km to 3000 km altitude, the SN is capable of providing tracking and data acquisition services over 100% of the spacecraft’s orbit. Spacecraft sent to more distant or exotic destinations rely on either Deep Space Network
Deep Space Network
The Deep Space Network, or DSN, is a world-wide network of large antennas and communication facilities that supports interplanetary spacecraft missions. It also performs radio and radar astronomy observations for the exploration of the solar system and the universe, and supports selected...
or their own custom, dedicated networks.
See also
- Deep Space NetworkDeep Space NetworkThe Deep Space Network, or DSN, is a world-wide network of large antennas and communication facilities that supports interplanetary spacecraft missions. It also performs radio and radar astronomy observations for the exploration of the solar system and the universe, and supports selected...
- Near Earth NetworkNear Earth NetworkThe Near Earth Network provides orbital communications support for Near-Earth orbiting customer platforms via various NASA ground stations.NASA's NEN consists of ground stations in:...
- Indian Deep Space NetworkIndian Deep Space NetworkThe Indian Deep Space Network is a network of large antennas and communication facilities that supports the interplanetary spacecraft missions of India. It is located at Byalalu, a village about 100 km from Bangalore, India. It was officially inaugurated on 17 October 2008 by ISRO chairman...
- Tracking and Data Relay SatelliteTracking and Data Relay SatelliteA Tracking and Data Relay Satellite is a type of communications satellite that forms part of the Tracking and Data Relay Satellite System used by NASA and other United States government agencies for communications to and from independent "User Platforms" such as satellites, balloons, aircraft,...
- Eastern Range
- SCaNSpace Communications and Navigation ProgramThe Space Communications and Navigation program places the three prime NASA space communications networks, Space Network , Near Earth Network , and the Deep Space Network , under one Management and Systems Engineering umbrella. It was established in 2006...
Program

