
Source function
Encyclopedia
The source function is a characteristic of a stellar atmosphere, and in the case of no scattering
of photons, describes the ratio of the emission coefficient to the absorption coefficient. It is a measure of how photons in a light beam are removed and replaced by new photons by the material it passes through. Its units in the cgs-system are erg s-1 cm-3 sr-1 and in SI are W m-3 sr-1 . The source function can be written
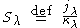
where is the emission coefficient,
is the emission coefficient, 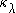 is the absorption coefficient (also known as the opacity
is the absorption coefficient (also known as the opacity
). Putting this into the equation for radiative transfer
we get
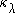
where s is the distance measured along the path traveled by the beam. The minus sign on the left hand side shows that the intensity decreases as the beam travels, due to the absorption of photons.
Scattering
Scattering is a general physical process where some forms of radiation, such as light, sound, or moving particles, are forced to deviate from a straight trajectory by one or more localized non-uniformities in the medium through which they pass. In conventional use, this also includes deviation of...
of photons, describes the ratio of the emission coefficient to the absorption coefficient. It is a measure of how photons in a light beam are removed and replaced by new photons by the material it passes through. Its units in the cgs-system are erg s-1 cm-3 sr-1 and in SI are W m-3 sr-1 . The source function can be written
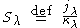
where
 is the emission coefficient,
is the emission coefficient, 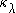 is the absorption coefficient (also known as the opacity
is the absorption coefficient (also known as the opacityOpacity (optics)
Opacity is the measure of impenetrability to electromagnetic or other kinds of radiation, especially visible light. In radiative transfer, it describes the absorption and scattering of radiation in a medium, such as a plasma, dielectric, shielding material, glass, etc...
). Putting this into the equation for radiative transfer
Radiative transfer
Radiative transfer is the physical phenomenon of energy transfer in the form of electromagnetic radiation. The propagation of radiation through a medium is affected by absorption, emission and scattering processes. The equation of radiative transfer describes these interactions mathematically...
we get
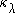
where s is the distance measured along the path traveled by the beam. The minus sign on the left hand side shows that the intensity decreases as the beam travels, due to the absorption of photons.

