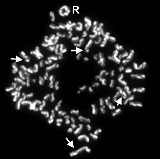
Sister chromatid exchange
Encyclopedia
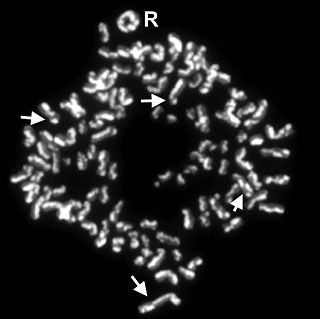
Sister chromatids
Sister chromatids are two identical copies of a chromatid connected by a centromere. Compare sister chromatids to homologous chromosomes, which are the two different copies of the same chromosome that diploid organisms inherit, one from each parent...
.
It was first discovered by using the Giemsa stain
Giemsa stain
Giemsa stain, named after Gustav Giemsa, an early German microbiologist, is used in cytogenetics and for the histopathological diagnosis of malaria and other parasites.-Uses:...
ing method on one chromatid
Chromatid
A chromatid is one of the two identical copies of DNA making up a duplicated chromosome, which are joined at their centromeres, for the process of cell division . They are called sister chromatids so long as they are joined by the centromeres...
belonging to the sister chromatid complex before anaphase
Anaphase
Anaphase, from the ancient Greek ἀνά and φάσις , is the stage of mitosis or meiosis when chromosomes move to opposite poles of the cell....
in mitosis
Mitosis
Mitosis is the process by which a eukaryotic cell separates the chromosomes in its cell nucleus into two identical sets, in two separate nuclei. It is generally followed immediately by cytokinesis, which divides the nuclei, cytoplasm, organelles and cell membrane into two cells containing roughly...
. The staining revealed that few segments were passed to the sister chromatid which were not dyed.
The Giemsa staining was able to stain due to the presence of bromodeoxyuridine
Bromodeoxyuridine
Bromodeoxyuridine is a synthetic nucleoside that is an analogue of thymidine. BrdU is commonly used in the detection of proliferating cells in living tissues....
analogous base which was introduced to the desired chromatid.
The reason for the (SCE) is not known but it is required and used as a mutagen
Mutagen
In genetics, a mutagen is a physical or chemical agent that changes the genetic material, usually DNA, of an organism and thus increases the frequency of mutations above the natural background level. As many mutations cause cancer, mutagens are therefore also likely to be carcinogens...
ic testing of many products. Four to five sister chromatid exchange per chromosome pair, per mitosis is in the normal distribution, 14-100 exchanges is not normal and presents a danger to the organism. SCE is elevated in pathologies including Bloom syndrome
Bloom syndrome
Bloom's syndrome , also known as Bloom–Torre–Machacek syndrome, is a rare autosomal recessive chromosomal disorder characterized by a high frequency of breaks and rearrangements in an affected person's chromosomes. The condition was discovered and first described by dermatologist Dr...
, in which distributions reach 100-160 per chromosome pair per mitosis. Frequent Sister Chromatid Exchange may also be related to formation of tumor
Tumor
A tumor or tumour is commonly used as a synonym for a neoplasm that appears enlarged in size. Tumor is not synonymous with cancer...
s.
Sister chromatid exchange has also been observed more frequently in B51
HLA-B51
HLA-B51 is an HLA-B serotype. The serotype identifies the more common HLA-B*51 gene products.B51 is a split antigen of the broad antigen B5, and is a sister serotype of B52. There are a large number of alleles within the B*51 allele group...
(+) Behçet's disease
Behçet's disease
Behçet's disease is a rare immune-mediated systemic vasculitis that often presents with mucous membrane ulceration and ocular involvements...
.

