
Singular isothermal sphere profile
Encyclopedia
The singular isothermal sphere (SIS) profile is the simplest parameterization of the spatial distribution of matter
in an astronomical
system (e.g. galaxies
, clusters of galaxies
, etc.).
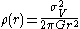
where σV2 is the velocity dispersion
and G is the gravitational constant
. The SIS profile is unphysical because of the singularity
at zero radius and the fact that the corresponding SIS mass
is infinite
. However, it is commonly utilized in the literature due to the simplicity of its form.
Matter
Matter is a general term for the substance of which all physical objects consist. Typically, matter includes atoms and other particles which have mass. A common way of defining matter is as anything that has mass and occupies volume...
in an astronomical
Astronomy
Astronomy is a natural science that deals with the study of celestial objects and phenomena that originate outside the atmosphere of Earth...
system (e.g. galaxies
Galaxy
A galaxy is a massive, gravitationally bound system that consists of stars and stellar remnants, an interstellar medium of gas and dust, and an important but poorly understood component tentatively dubbed dark matter. The word galaxy is derived from the Greek galaxias , literally "milky", a...
, clusters of galaxies
Galaxy groups and clusters
Galaxy groups and clusters are the largest known gravitationally bound objects to have arisen thus far in the process of cosmic structure formation. They form the densest part of the large scale structure of the universe...
, etc.).
Density distribution
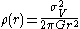
where σV2 is the velocity dispersion
Velocity dispersion
In astronomy, the velocity dispersion σ, is the range of velocities about the mean velocity for a group of objects, such as a cluster of stars about a galaxy...
and G is the gravitational constant
Gravitational constant
The gravitational constant, denoted G, is an empirical physical constant involved in the calculation of the gravitational attraction between objects with mass. It appears in Newton's law of universal gravitation and in Einstein's theory of general relativity. It is also known as the universal...
. The SIS profile is unphysical because of the singularity
Mathematical singularity
In mathematics, a singularity is in general a point at which a given mathematical object is not defined, or a point of an exceptional set where it fails to be well-behaved in some particular way, such as differentiability...
at zero radius and the fact that the corresponding SIS mass
Mass
Mass can be defined as a quantitive measure of the resistance an object has to change in its velocity.In physics, mass commonly refers to any of the following three properties of matter, which have been shown experimentally to be equivalent:...
is infinite
Infinity
Infinity is a concept in many fields, most predominantly mathematics and physics, that refers to a quantity without bound or end. People have developed various ideas throughout history about the nature of infinity...
. However, it is commonly utilized in the literature due to the simplicity of its form.

