
Side looking airborne radar
Encyclopedia
Side-looking airborne radar (SLAR) is an aircraft- or satellite-mounted imaging radar
pointing perpendicular to the direction of flight (hence “side-looking”). A squinted mode is possible also. SLAR can be fitted with a real aperture antenna
(Real Aperture Radar, RAR) or an antenna using synthetic aperture
(SAR).
The platform of the radar moves in direction of the x-axis. The radar “looks” with the looking angle θ (or so called off-nadir angle). The angle α between x-axis and the line of sight (LOS) is called cone angle, the angle φ between the x-axis and the projection of the line of sight to the (x; y)-plane is called azimuth angle. Cone- and azimuth angle are related by cosα = cosφ ∙ cosε. On the earth surface the wave comes in at the (nominal ellipsoidal) incident angle β with respect to the vertical axis at this point. (In some publications the incident angle is denominated to as θi.) The antenna illuminates an area, the so called footprint. The direction of the incoming wave relative to the horizontal plane may be measured also. This angle γ = 90° − β is called grazing angle. The angle ϑ = ε + 90° is used for a mathematical description in a spherical coordinate system.
For the approximation of a flat earth – which is usual for airborne radar with short to medium range – the grazing angle and the depression angle can be assumed to be equal γ = ε and the incident angle is β = 180° – ϑ. The so called LOS-vector is a unit vector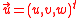 (in the figures shown as a red arrow) pointing from the antenna to a ground scatterer. The variables u, v, w are directional cosines with respect to the x; y; z axes. The variable u is u = cosα with α as the azimuth angle between the line of sight and the x-axis (direction of flight).
(in the figures shown as a red arrow) pointing from the antenna to a ground scatterer. The variables u, v, w are directional cosines with respect to the x; y; z axes. The variable u is u = cosα with α as the azimuth angle between the line of sight and the x-axis (direction of flight).
The range resolution (the ability to separate the pixels of the image perpendicular to the direction of flight) of an SLAR using a step-frequency waveform of bandwidth B is δr = c0/2B, where c0 is the speed of light in free space. The azimutal resolution (better known to as crossrange resolution) is ~rλ/D, where λ is the used wavelength. SAR
refers to a method for improving the crossrange resolution (not range resolution) in SLAR using a real aperture antenna, the crossrange resolution still depends on range r.
Radar
Radar is an object-detection system which uses radio waves to determine the range, altitude, direction, or speed of objects. It can be used to detect aircraft, ships, spacecraft, guided missiles, motor vehicles, weather formations, and terrain. The radar dish or antenna transmits pulses of radio...
pointing perpendicular to the direction of flight (hence “side-looking”). A squinted mode is possible also. SLAR can be fitted with a real aperture antenna
Antenna
Antenna may refer to:-Science and engineering:* Antenna , also known as an aerial, a transducer designed to transmit or receive electromagnetic Antenna (pl. antennas in radio/TV, antennae in biology) may refer to:-Science and engineering:* Antenna (radio), also known as an aerial, a transducer...
(Real Aperture Radar, RAR) or an antenna using synthetic aperture
Synthetic aperture radar
Synthetic-aperture radar is a form of radar whose defining characteristic is its use of relative motion between an antenna and its target region to provide distinctive long-term coherent-signal variations that are exploited to obtain finer spatial resolution than is possible with conventional...
(SAR).
The platform of the radar moves in direction of the x-axis. The radar “looks” with the looking angle θ (or so called off-nadir angle). The angle α between x-axis and the line of sight (LOS) is called cone angle, the angle φ between the x-axis and the projection of the line of sight to the (x; y)-plane is called azimuth angle. Cone- and azimuth angle are related by cosα = cosφ ∙ cosε. On the earth surface the wave comes in at the (nominal ellipsoidal) incident angle β with respect to the vertical axis at this point. (In some publications the incident angle is denominated to as θi.) The antenna illuminates an area, the so called footprint. The direction of the incoming wave relative to the horizontal plane may be measured also. This angle γ = 90° − β is called grazing angle. The angle ϑ = ε + 90° is used for a mathematical description in a spherical coordinate system.
For the approximation of a flat earth – which is usual for airborne radar with short to medium range – the grazing angle and the depression angle can be assumed to be equal γ = ε and the incident angle is β = 180° – ϑ. The so called LOS-vector is a unit vector
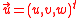 (in the figures shown as a red arrow) pointing from the antenna to a ground scatterer. The variables u, v, w are directional cosines with respect to the x; y; z axes. The variable u is u = cosα with α as the azimuth angle between the line of sight and the x-axis (direction of flight).
(in the figures shown as a red arrow) pointing from the antenna to a ground scatterer. The variables u, v, w are directional cosines with respect to the x; y; z axes. The variable u is u = cosα with α as the azimuth angle between the line of sight and the x-axis (direction of flight).The range resolution (the ability to separate the pixels of the image perpendicular to the direction of flight) of an SLAR using a step-frequency waveform of bandwidth B is δr = c0/2B, where c0 is the speed of light in free space. The azimutal resolution (better known to as crossrange resolution) is ~rλ/D, where λ is the used wavelength. SAR
Synthetic aperture radar
Synthetic-aperture radar is a form of radar whose defining characteristic is its use of relative motion between an antenna and its target region to provide distinctive long-term coherent-signal variations that are exploited to obtain finer spatial resolution than is possible with conventional...
refers to a method for improving the crossrange resolution (not range resolution) in SLAR using a real aperture antenna, the crossrange resolution still depends on range r.

