Salla disease
Encyclopedia
Salla disease also called sialic acid storage disease or Finnish type sialuria, is an autosomal
recessive lysosomal storage disease
characterized by early physical impairment
and mental retardation
. It was first described in 1979, after Salla
, a municipality in Finnish Lapland. Salla disease is one of 40 Finnish heritage disease
s and affects approximately 130 individuals, mainly from Finland and Sweden.
, reduced muscle tone and strength, and cognitive impairment. The most severely impaired children do not walk or acquire language, but the typical patient learns to walk and speak and has normal life expectancy. The MRI shows arrested or delayed myelination.
 SD is caused by a mutation
SD is caused by a mutation
in the SLC17A5
gene, located
at human chromosome
6q14-15
. This gene codes for sialin, a lysosomal membrane protein that transports the charged sugar, N-acetylneuraminic acid
(sialic acid), out of lysosome
s. The mutation causes sialic acid
to build up in the cells
.
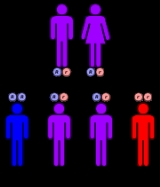
The disease is inherited in an autosomal recessive manner. This means the defective gene responsible for the disorder is located on an autosome
(chromosome 6 is an autosome), and two copies of the defective gene (one inherited from each parent) are required in order to be born with the disorder. The parents of an individual with an autosomal recessive disorder both carry
one copy of the defective gene, but usually do not experience any signs or symptoms of the disorder.
episodes. Physical therapists can assist an affected individual to build muscle strength and coordination, and speech therapists may assist the affected individual in improving his or her speech.
Autosome
An autosome is a chromosome that is not a sex chromosome, or allosome; that is to say, there is an equal number of copies of the chromosome in males and females. For example, in humans, there are 22 pairs of autosomes. In addition to autosomes, there are sex chromosomes, to be specific: X and Y...
recessive lysosomal storage disease
Lysosomal storage disease
Lysosomal storage diseases are a group of approximately 50 rare inherited metabolic disorders that result from defects in lysosomal function...
characterized by early physical impairment
Disability
A disability may be physical, cognitive, mental, sensory, emotional, developmental or some combination of these.Many people would rather be referred to as a person with a disability instead of handicapped...
and mental retardation
Mental retardation
Mental retardation is a generalized disorder appearing before adulthood, characterized by significantly impaired cognitive functioning and deficits in two or more adaptive behaviors...
. It was first described in 1979, after Salla
Salla
Salla is a municipality of Finland, located in Lapland. The municipality has a population of and covers an area of ofwhich is water. The population density is....
, a municipality in Finnish Lapland. Salla disease is one of 40 Finnish heritage disease
Finnish heritage disease
A Finnish heritage disease is a genetic disease or disorder that is part of the Finnish disease heritage. Finnish heritage diseases are significantly more common in people whose ancestors were ethnic Finns, natives of Finland and Sweden. About 40 rare diseases are regarded as Finnish heritage...
s and affects approximately 130 individuals, mainly from Finland and Sweden.
Characteristics
Individuals with Salla disease may present with nystagmus in the first months of life as well as hypotoniaHypotonia
Hypotonia is a state of low muscle tone , often involving reduced muscle strength. Hypotonia is not a specific medical disorder, but a potential manifestation of many different diseases and disorders that affect motor nerve control by the brain or muscle strength...
, reduced muscle tone and strength, and cognitive impairment. The most severely impaired children do not walk or acquire language, but the typical patient learns to walk and speak and has normal life expectancy. The MRI shows arrested or delayed myelination.
Cause and Genetics

Mutation
In molecular biology and genetics, mutations are changes in a genomic sequence: the DNA sequence of a cell's genome or the DNA or RNA sequence of a virus. They can be defined as sudden and spontaneous changes in the cell. Mutations are caused by radiation, viruses, transposons and mutagenic...
in the SLC17A5
SLC17A5
Solute carrier family 17 , member 5, also known as SLC17A5 or sialin, is a protein which in humans is encoded by the SLC17A5 gene.-Further reading:...
gene, located
Locus (genetics)
In the fields of genetics and genetic computation, a locus is the specific location of a gene or DNA sequence on a chromosome. A variant of the DNA sequence at a given locus is called an allele. The ordered list of loci known for a particular genome is called a genetic map...
at human chromosome
Chromosome
A chromosome is an organized structure of DNA and protein found in cells. It is a single piece of coiled DNA containing many genes, regulatory elements and other nucleotide sequences. Chromosomes also contain DNA-bound proteins, which serve to package the DNA and control its functions.Chromosomes...
6q14-15
Chromosome 6 (human)
Chromosome 6 is one of the 23 pairs of chromosomes in humans. People normally have two copies of this chromosome. Chromosome 6 spans more than 170 million base pairs and represents between 5.5 and 6% of the total DNA in cells...
. This gene codes for sialin, a lysosomal membrane protein that transports the charged sugar, N-acetylneuraminic acid
N-Acetylneuraminic acid
N-Acetylneuraminic acid is the predominant sialic acid found in mammalian cells.This negatively charged residue is found in complex glycans on mucins and glycoproteins found at the cell membrane...
(sialic acid), out of lysosome
Lysosome
thumb|350px|Schematic of typical animal cell, showing subcellular components. [[Organelle]]s: [[nucleoli]] [[cell nucleus|nucleus]] [[ribosomes]] [[vesicle |vesicle]] rough [[endoplasmic reticulum]]...
s. The mutation causes sialic acid
Sialic acid
Sialic acid is a generic term for the N- or O-substituted derivatives of neuraminic acid, a monosaccharide with a nine-carbon backbone. It is also the name for the most common member of this group, N-acetylneuraminic acid...
to build up in the cells
Cell (biology)
The cell is the basic structural and functional unit of all known living organisms. It is the smallest unit of life that is classified as a living thing, and is often called the building block of life. The Alberts text discusses how the "cellular building blocks" move to shape developing embryos....
.
The disease is inherited in an autosomal recessive manner. This means the defective gene responsible for the disorder is located on an autosome
Autosome
An autosome is a chromosome that is not a sex chromosome, or allosome; that is to say, there is an equal number of copies of the chromosome in males and females. For example, in humans, there are 22 pairs of autosomes. In addition to autosomes, there are sex chromosomes, to be specific: X and Y...
(chromosome 6 is an autosome), and two copies of the defective gene (one inherited from each parent) are required in order to be born with the disorder. The parents of an individual with an autosomal recessive disorder both carry
Genetic carrier
A genetic carrier , is a person or other organism that has inherited a genetic trait or mutation, but who does not display that trait or show symptoms of the disease. They are, however, able to pass the gene onto their offspring, who may then express the gene...
one copy of the defective gene, but usually do not experience any signs or symptoms of the disorder.
Life Expectancy
The life expectancy for individuals with Salla disease is between the ages of 50 and 60.Diagnosis and Testing
A diagnosis of this disorder can be made by measuring urine to look for elevated levels of free sialic acid. Prenatal testing is also available for known carriers of this disorder.Treatment
There is no cure for Salla Disease. Treatment is limited to controlling the symptoms of this disorder. Anti-convulsant medication may control seizureSeizure
An epileptic seizure, occasionally referred to as a fit, is defined as a transient symptom of "abnormal excessive or synchronous neuronal activity in the brain". The outward effect can be as dramatic as a wild thrashing movement or as mild as a brief loss of awareness...
episodes. Physical therapists can assist an affected individual to build muscle strength and coordination, and speech therapists may assist the affected individual in improving his or her speech.

