.gif)
Sa-sub4 (Luwian hieroglyph)
Encyclopedia
Sa4 is the 4th of 7 hieroglyphs for Sa in the Luwian language
. They are Sa, Sá, Sà, Sa4, Sa5, Sa6, and Sa7.
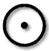


N5
Sa4 of Hieroglyphic Luwian
Sa4 is basically identical to the N5 hieroglyph of Gardiner's Sign List
for the Egyptian language
, which in the hieroglyphs for Ancient Egypt
is the representation of the sun
, (and also Ra
, the sun god). As the representation of the sun in Egypt, it also is translated in many uses for "day", or "time", as word determinative
s.
The day, or time uses being the common ones for Egypt, requires that other more ornate forms of reference to Ra, the sun god, were needed. The solar disc was sometimes put on the head as a 'crown'; the major ornate sun disc representation contained the uraeus
cobra surrounding it, and the cobra being with up-raised head.
Luwian language
Luwian is an extinct language of the Anatolian branch of the Indo-European language family. Luwian is closely related to Hittite, and was among the languages spoken during the second and first millennia BC by population groups in central and western Anatolia and northern Syria...
. They are Sa, Sá, Sà, Sa4, Sa5, Sa6, and Sa7.



Sa4, a glyph similar to Egypt's "sun"
Sa4 of Hieroglyphic Luwian
Sa4 is basically identical to the N5 hieroglyph of Gardiner's Sign List
Gardiner's Sign List
Gardiner's Sign List is a list of common Egyptian hieroglyphs compiled by Sir Alan Gardiner. It is considered a standard reference in the study of Ancient Egyptian hieroglyphs....
for the Egyptian language
Egyptian language
Egyptian is the oldest known indigenous language of Egypt and a branch of the Afroasiatic language family. Written records of the Egyptian language have been dated from about 3400 BC, making it one of the oldest recorded languages known. Egyptian was spoken until the late 17th century AD in the...
, which in the hieroglyphs for Ancient Egypt
Ancient Egypt
Ancient Egypt was an ancient civilization of Northeastern Africa, concentrated along the lower reaches of the Nile River in what is now the modern country of Egypt. Egyptian civilization coalesced around 3150 BC with the political unification of Upper and Lower Egypt under the first pharaoh...
is the representation of the sun
Sun
The Sun is the star at the center of the Solar System. It is almost perfectly spherical and consists of hot plasma interwoven with magnetic fields...
, (and also Ra
Ra
Ra is the ancient Egyptian sun god. By the Fifth Dynasty he had become a major deity in ancient Egyptian religion, identified primarily with the mid-day sun...
, the sun god). As the representation of the sun in Egypt, it also is translated in many uses for "day", or "time", as word determinative
Determinative
A determinative, also known as a taxogram or semagram, is an ideogram used to mark semantic categories of words in logographic scripts which helps to disambiguate interpretation. They have no direct counterpart in spoken language, though they may derive historically from glyphs for real words, and...
s.
The day, or time uses being the common ones for Egypt, requires that other more ornate forms of reference to Ra, the sun god, were needed. The solar disc was sometimes put on the head as a 'crown'; the major ornate sun disc representation contained the uraeus
Uraeus
The Uraeus is the stylized, upright form of an Egyptian spitting cobra , used as a symbol of sovereignty, royalty, deity, and divine authority in ancient Egypt.The Uraeus is a symbol for the goddess Wadjet, who was one of the earliest Egyptian deities and who...
cobra surrounding it, and the cobra being with up-raised head.
Luwian language Sa
The Sa hieroglyphs are used in the Luwian language mostly for the usage of the letter 's'.See also
- Anatolian hieroglyphsAnatolian hieroglyphsAnatolian hieroglyphs are an indigenous logographic script native to central Anatolia, consisting of some 500 signs. They were once commonly known as Hittite hieroglyphs, but the language they encode proved to be Luwian, not Hittite, and the term Luwian hieroglyphs is used in English publications...
- Gardiner's Sign ListGardiner's Sign ListGardiner's Sign List is a list of common Egyptian hieroglyphs compiled by Sir Alan Gardiner. It is considered a standard reference in the study of Ancient Egyptian hieroglyphs....
- Sun (hieroglyph)Sun (hieroglyph)The Ancient Egyptian Sun hieroglyph is Gardiner sign listed no. N5 for the sun-disc; it is also one of the hieroglyphs that refers to the god Ra.-Luwian hieroglyhs, Sa-sub4:...
External links
- The Luwian hieroglyphic script - ancientscripts.com

