
Revenue Act of 1924
Encyclopedia
Federal government of the United States
The federal government of the United States is the national government of the constitutional republic of fifty states that is the United States of America. The federal government comprises three distinct branches of government: a legislative, an executive and a judiciary. These branches and...
tax
Tax
To tax is to impose a financial charge or other levy upon a taxpayer by a state or the functional equivalent of a state such that failure to pay is punishable by law. Taxes are also imposed by many subnational entities...
rates and established the U.S. Board of Tax Appeals, which was later renamed the United States Tax Court
United States Tax Court
The United States Tax Court is a federal trial court of record established by Congress under Article I of the U.S. Constitution, section 8 of which provides that the Congress has the power to "constitute Tribunals inferior to the supreme Court"...
in 1942. The bill was named after U.S. Secretary of the Treasury Andrew Mellon.
The Revenue Act was applicable to incomes for 1924.
The bottom rate, on income under $4,000, fell from 1.5% to 1.125% (both rates are after reduction by the "earned income credit").
A parallel act, the Indian Citizenship Act of 1924
Indian Citizenship Act of 1924
The Indian Citizenship Act of 1924, also known as the Snyder Act, was proposed by Representative Homer P. Snyder of New York and granted full U.S. citizenship to America's indigenous peoples, called "Indians" in this Act...
), granted all non-citizen resident Indians citizenship. Thus the Revenue Act declared that there were no longer any "Indians, not taxed" to be not counted for purposes of United States Congressional apportionment
United States congressional apportionment
United States congressional apportionment is the process by which seats in the United States House of Representatives are redistributed amongst the 50 states following each constitutionally mandated decennial census. Each state is apportioned a number of seats which approximately corresponds to its...
.
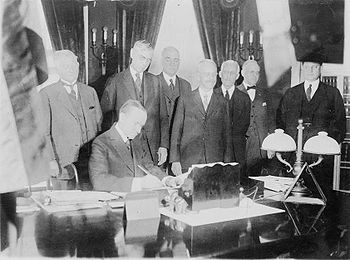
President Calvin Coolidge
Calvin Coolidge
John Calvin Coolidge, Jr. was the 30th President of the United States . A Republican lawyer from Vermont, Coolidge worked his way up the ladder of Massachusetts state politics, eventually becoming governor of that state...
signed the bill into law.
Tax on Individuals
A Normal Tax and a Surtax were levied against the net income of individuals as shown in the following table.| Revenue Act of 1924 Normal Tax and Surtax on Individuals |
|||
| Net Income (dollars) |
Normal Rate (percent) |
Surtax Rate (percent) |
Combined Rate (percent) |
| 0 | 2 | 0 | 2 |
| 4,000 | 4 | 0 | 4 |
| 8,000 | 6 | 0 | 6 |
| 10,000 | 6 | 1 | 7 |
| 14,000 | 6 | 2 | 8 |
| 16,000 | 6 | 3 | 9 |
| 18,000 | 6 | 4 | 10 |
| 20,000 | 6 | 5 | 11 |
| 22,000 | 6 | 6 | 12 |
| 24,000 | 6 | 7 | 13 |
| 26,000 | 6 | 8 | 14 |
| 28,000 | 6 | 9 | 15 |
| 30,000 | 6 | 10 | 16 |
| 34,000 | 6 | 11 | 17 |
| 36,000 | 6 | 12 | 18 |
| 38,000 | 6 | 13 | 19 |
| 42,000 | 6 | 14 | 20 |
| 44,000 | 6 | 15 | 21 |
| 46,000 | 6 | 16 | 22 |
| 48,000 | 6 | 17 | 23 |
| 50,000 | 6 | 18 | 24 |
| 52,000 | 6 | 19 | 25 |
| 56,000 | 6 | 20 | 26 |
| 58,000 | 6 | 21 | 27 |
| 62,000 | 6 | 22 | 28 |
| 64,000 | 6 | 23 | 29 |
| 66,000 | 6 | 24 | 30 |
| 68,000 | 6 | 25 | 31 |
| 70,000 | 6 | 26 | 32 |
| 74,000 | 6 | 27 | 33 |
| 76,000 | 6 | 28 | 34 |
| 80,000 | 6 | 29 | 35 |
| 82,000 | 6 | 30 | 36 |
| 84,000 | 6 | 31 | 37 |
| 88,000 | 6 | 32 | 38 |
| 90,000 | 6 | 33 | 39 |
| 92,000 | 6 | 34 | 40 |
| 94,000 | 6 | 35 | 41 |
| 96,000 | 6 | 36 | 42 |
| 100,000 | 6 | 37 | 43 |
| 200,000 | 6 | 38 | 44 |
| 300,000 | 6 | 39 | 45 |
| 500,000 | 6 | 40 | 46 |
- Exemption of $1,000 for single filers and $2,500 for married couples and heads of family. A $400 exemption for each dependent under 18.

