
Resolved sideband cooling
Encyclopedia
Laser cooling
Laser cooling refers to the number of techniques in which atomic and molecular samples are cooled through the interaction with one or more laser light fields...
technique that can be used to cool strongly trapped atoms to the quantum ground state
Ground state
The ground state of a quantum mechanical system is its lowest-energy state; the energy of the ground state is known as the zero-point energy of the system. An excited state is any state with energy greater than the ground state...
of their motion. The atoms are usually precooled using the Doppler
Doppler cooling
Doppler cooling is a mechanism that can be used to trap and cool atoms. The term is sometimes used synonymously with laser cooling, though laser cooling includes other techniques.-History:...
laser cooling
Laser cooling
Laser cooling refers to the number of techniques in which atomic and molecular samples are cooled through the interaction with one or more laser light fields...
. Subsequently the resolved sideband
Sideband
In radio communications, a sideband is a band of frequencies higher than or lower than the carrier frequency, containing power as a result of the modulation process. The sidebands consist of all the Fourier components of the modulated signal except the carrier...
cooling is used to cool the atoms beyond the Doppler cooling limit
Doppler cooling limit
Doppler temperature is the minimum temperature achievable with Doppler cooling, one of the methods of laser cooling.When a photon is absorbed by an atom moving in the opposite direction, its velocity is decreased according to the laws of momentum conservation. Accordingly, when a photon is emitted...
.
A cold trapped atom can be treated to a good approximation as a quantum mechanical harmonic oscillator
Harmonic oscillator
In classical mechanics, a harmonic oscillator is a system that, when displaced from its equilibrium position, experiences a restoring force, F, proportional to the displacement, x: \vec F = -k \vec x \, where k is a positive constant....
. If the spontaneous decay rate is much smaller than the vibrational frequency of the atom in the trap, the energy level
Energy level
A quantum mechanical system or particle that is bound -- that is, confined spatially—can only take on certain discrete values of energy. This contrasts with classical particles, which can have any energy. These discrete values are called energy levels...
s of the system can be resolved as consisting of internal levels each corresponding to a ladder of vibrational states.
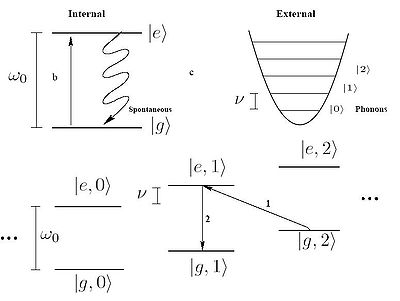
Suppose a two-level atom whose ground state is shown by g and excited state by e. Efficient laser cooling occurs when the frequency of the laser beam is tuned to the red sideband i.e.
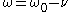 ,
,where
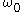 is the internal atomic transition frequency and
is the internal atomic transition frequency and  is the harmonic oscillation frequency of the atom. In this case the atom undergoes the transition
is the harmonic oscillation frequency of the atom. In this case the atom undergoes the transition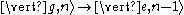 ,
,where
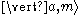 represents the state of an ion whose internal atomic state is a and the motional state is m. This process is labeled '1' in the image to the right.
represents the state of an ion whose internal atomic state is a and the motional state is m. This process is labeled '1' in the image to the right.Subsequent spontaneous emission
Spontaneous emission
Spontaneous emission is the process by which a light source such as an atom, molecule, nanocrystal or nucleus in an excited state undergoes a transition to a state with a lower energy, e.g., the ground state and emits a photon...
occurs predominantly at the carrier frequency if the recoil energy of the atom is negligible compared with the vibrational quantum energy i.e.
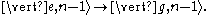
This process is labeled '2' in the image to the right.
The average effect of this mechanism is cooling the ion by one vibrational energy level. When these steps are repeated a sufficient number of times
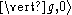 is reached with a high probability.
is reached with a high probability.See also
- Laser coolingLaser coolingLaser cooling refers to the number of techniques in which atomic and molecular samples are cooled through the interaction with one or more laser light fields...
- Amplitude modulationAmplitude modulationAmplitude modulation is a technique used in electronic communication, most commonly for transmitting information via a radio carrier wave. AM works by varying the strength of the transmitted signal in relation to the information being sent...

