
Residual resistance ratio
Encyclopedia
Residual-resistivity ratio (also known as Residual-resistance ratio or just RRR) is usually defined as the ratio of the resistivity
of a material at room temperature and at 0 K
. Of course, 0 K can never be reached in practice so some estimation is usually made. Since the RRR can vary quite strongly for a single material depending on the amount of impurities and other crystallographic defects, it serves as a rough index of the purity and overall quality of a sample. Since resistivity usually increases as defect prevalence increases, a large RRR is associated with a pure sample. RRR is also used important for characterizing certain unusual low temperature states such as the Kondo effect
and superconductivity
. Note that since it is a unitless ratio there is no difference between a residual-resistivity and residual-resistance ratio.
varies linearly with temperature. That is, a plot of the resistivity as a function
of temperature is a straight line. If this straight line were extrapolated all the way down to absolute zero, a theoretical RRR could be calculated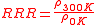
In the simplest case of a good metal that is free of scattering mechanisms one would expect ρ(0K) = 0, which would cause RRR to diverge. However, usually this is not the case because defects such as grain boundaries, impurities, etc. act as scattering sources that contribute a temperature independent ρ0 value. This shifts the intercept of the curve to a higher number, giving a smaller RRR.
In practice the resistivity of a given sample is measured down to as cold as possible, which on typical laboratory instruments is in the range of 2 K (though of course much lower is possible). By this point the linear resistive behavior is usually no longer applicable and by the low T ρ is taken as a good approximation to 0 K.
In the special case of superconducting materials where ρ is always exactly 0 above 0 K the RRR is calculated using the ρ is taken just above the superconducting transition temperature. In the Kondo effect the resistivity begins to increase again with cooling at very low temperatures, and the value of RRR is useful for characterizing this state.
Resistivity
Electrical resistivity is a measure of how strongly a material opposes the flow of electric current. A low resistivity indicates a material that readily allows the movement of electric charge. The SI unit of electrical resistivity is the ohm metre...
of a material at room temperature and at 0 K
Absolute zero
Absolute zero is the theoretical temperature at which entropy reaches its minimum value. The laws of thermodynamics state that absolute zero cannot be reached using only thermodynamic means....
. Of course, 0 K can never be reached in practice so some estimation is usually made. Since the RRR can vary quite strongly for a single material depending on the amount of impurities and other crystallographic defects, it serves as a rough index of the purity and overall quality of a sample. Since resistivity usually increases as defect prevalence increases, a large RRR is associated with a pure sample. RRR is also used important for characterizing certain unusual low temperature states such as the Kondo effect
Kondo effect
In physics, the Kondo effect describes the scattering of conduction electrons in a metal due to magnetic impurities. It is a measure of how electrical resistivity changes with temperature....
and superconductivity
Superconductivity
Superconductivity is a phenomenon of exactly zero electrical resistance occurring in certain materials below a characteristic temperature. It was discovered by Heike Kamerlingh Onnes on April 8, 1911 in Leiden. Like ferromagnetism and atomic spectral lines, superconductivity is a quantum...
. Note that since it is a unitless ratio there is no difference between a residual-resistivity and residual-resistance ratio.
Background
Usually at "warm" temperatures the resistivity of a metalMetal
A metal , is an element, compound, or alloy that is a good conductor of both electricity and heat. Metals are usually malleable and shiny, that is they reflect most of incident light...
varies linearly with temperature. That is, a plot of the resistivity as a function
Function
Function may refer to:*Diatonic function, a term in music theory*Function , explaining why a feature survived selection*Function , or subroutine, a portion of code within a larger program, performs a specific task...
of temperature is a straight line. If this straight line were extrapolated all the way down to absolute zero, a theoretical RRR could be calculated
In the simplest case of a good metal that is free of scattering mechanisms one would expect ρ(0K) = 0, which would cause RRR to diverge. However, usually this is not the case because defects such as grain boundaries, impurities, etc. act as scattering sources that contribute a temperature independent ρ0 value. This shifts the intercept of the curve to a higher number, giving a smaller RRR.
In practice the resistivity of a given sample is measured down to as cold as possible, which on typical laboratory instruments is in the range of 2 K (though of course much lower is possible). By this point the linear resistive behavior is usually no longer applicable and by the low T ρ is taken as a good approximation to 0 K.
In the special case of superconducting materials where ρ is always exactly 0 above 0 K the RRR is calculated using the ρ is taken just above the superconducting transition temperature. In the Kondo effect the resistivity begins to increase again with cooling at very low temperatures, and the value of RRR is useful for characterizing this state.
Examples
- The RRR of copperCopperCopper is a chemical element with the symbol Cu and atomic number 29. It is a ductile metal with very high thermal and electrical conductivity. Pure copper is soft and malleable; an exposed surface has a reddish-orange tarnish...
wireWireA wire is a single, usually cylindrical, flexible strand or rod of metal. Wires are used to bear mechanical loads and to carry electricity and telecommunications signals. Wire is commonly formed by drawing the metal through a hole in a die or draw plate. Standard sizes are determined by various...
is generally ~ 40–50 when used for telephone lineTelephone lineA telephone line or telephone circuit is a single-user circuit on a telephone communication system...
s, etc.

