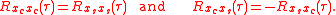Random modulation
Encyclopedia
In the theories of modulation
and of stochastic process
es, random modulation is the creation of a new signal from two other signals by the process of quadrature amplitude modulation
. In particular, the two signals are considered as being random processes. For applications, the two original signals need have a limited frequency range, and these are used to modulate a third sinusoidal (carrier) signal whose frequency is above the range of frequencies contained in the original signals.
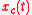 and
and 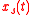 , whose frequency spectrum
, whose frequency spectrum
is non-zero only for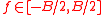 . It applies quadrature modulation
. It applies quadrature modulation
to combine these with a carrier frequency (with
(with 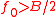 ) to form the signal
) to form the signal  given by
given by
where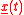 is the equivalent baseband representation of the modulated signal
is the equivalent baseband representation of the modulated signal 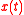

In the following it is assumed that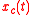 and
and 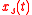 are two real jointly wide sense stationary processes. It can be shown that the new signal
are two real jointly wide sense stationary processes. It can be shown that the new signal 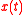 is wide sense stationary if and only if
is wide sense stationary if and only if
 is circular complex, i.e. if and only if
is circular complex, i.e. if and only if 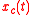 and
and 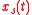 are such that
are such that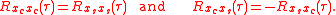
Modulation
In electronics and telecommunications, modulation is the process of varying one or more properties of a high-frequency periodic waveform, called the carrier signal, with a modulating signal which typically contains information to be transmitted...
and of stochastic process
Stochastic process
In probability theory, a stochastic process , or sometimes random process, is the counterpart to a deterministic process...
es, random modulation is the creation of a new signal from two other signals by the process of quadrature amplitude modulation
Quadrature amplitude modulation
Quadrature amplitude modulation is both an analog and a digital modulation scheme. It conveys two analog message signals, or two digital bit streams, by changing the amplitudes of two carrier waves, using the amplitude-shift keying digital modulation scheme or amplitude modulation analog...
. In particular, the two signals are considered as being random processes. For applications, the two original signals need have a limited frequency range, and these are used to modulate a third sinusoidal (carrier) signal whose frequency is above the range of frequencies contained in the original signals.
Details
The random modulation procedure starts with two stochastic baseband signals,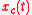 and
and 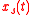 , whose frequency spectrum
, whose frequency spectrumFrequency spectrum
The frequency spectrum of a time-domain signal is a representation of that signal in the frequency domain. The frequency spectrum can be generated via a Fourier transform of the signal, and the resulting values are usually presented as amplitude and phase, both plotted versus frequency.Any signal...
is non-zero only for
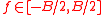 . It applies quadrature modulation
. It applies quadrature modulationQuadrature modulation
Quadrature modulation is the general technique of modulating two carriers.Examples include Quadrature amplitude modulation, Phase-shift keying, and Minimum-shift keying.Constellation diagrams are used to examine the modulation in the 2-D signal space....
to combine these with a carrier frequency
 (with
(with 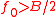 ) to form the signal
) to form the signal  given by
given by
where
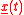 is the equivalent baseband representation of the modulated signal
is the equivalent baseband representation of the modulated signal 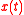

In the following it is assumed that
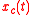 and
and 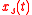 are two real jointly wide sense stationary processes. It can be shown that the new signal
are two real jointly wide sense stationary processes. It can be shown that the new signal 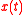 is wide sense stationary if and only if
is wide sense stationary if and only ifIFF
IFF, Iff or iff may refer to:Technology/Science:* Identification friend or foe, an electronic radio-based identification system using transponders...
 is circular complex, i.e. if and only if
is circular complex, i.e. if and only if 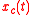 and
and 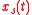 are such that
are such that