
R (cross section ratio)
Encyclopedia
R is the ratio of the hadron
ic cross section
to the muon
cross section in electron
–positron
collisions:
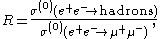
where the superscript (0) indicates that the cross section has been corrected for initial state radiation.
R is an important input in the calculation of the anomalous magnetic dipole moment
. Experimental values have been measured for center-of-mass energies from 400 MeV to 150 GeV.
R also provides experimental confirmation of the electric charge of quark
s, in particular the charm quark and bottom quark, and the existence of three quark colors. A naive calculation of R yields
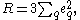
where the sum is over all quark flavors with mass less than the beam energy. eq is the electric charge of the quark, and the factor of 3 accounts for the three colors of the quarks. QCD
corrections to this naive formula have been calculated.
Hadron
In particle physics, a hadron is a composite particle made of quarks held together by the strong force...
ic cross section
Cross section (physics)
A cross section is the effective area which governs the probability of some scattering or absorption event. Together with particle density and path length, it can be used to predict the total scattering probability via the Beer-Lambert law....
to the muon
Muon
The muon |mu]] used to represent it) is an elementary particle similar to the electron, with a unitary negative electric charge and a spin of ½. Together with the electron, the tau, and the three neutrinos, it is classified as a lepton...
cross section in electron
Electron
The electron is a subatomic particle with a negative elementary electric charge. It has no known components or substructure; in other words, it is generally thought to be an elementary particle. An electron has a mass that is approximately 1/1836 that of the proton...
–positron
Positron
The positron or antielectron is the antiparticle or the antimatter counterpart of the electron. The positron has an electric charge of +1e, a spin of ½, and has the same mass as an electron...
collisions:
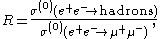
where the superscript (0) indicates that the cross section has been corrected for initial state radiation.
R is an important input in the calculation of the anomalous magnetic dipole moment
Anomalous magnetic dipole moment
In quantum electrodynamics, the anomalous magnetic moment of a particle is a contribution of effects of quantum mechanics, expressed by Feynman diagrams with loops, to the magnetic moment of that particle...
. Experimental values have been measured for center-of-mass energies from 400 MeV to 150 GeV.
R also provides experimental confirmation of the electric charge of quark
Quark
A quark is an elementary particle and a fundamental constituent of matter. Quarks combine to form composite particles called hadrons, the most stable of which are protons and neutrons, the components of atomic nuclei. Due to a phenomenon known as color confinement, quarks are never directly...
s, in particular the charm quark and bottom quark, and the existence of three quark colors. A naive calculation of R yields
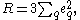
where the sum is over all quark flavors with mass less than the beam energy. eq is the electric charge of the quark, and the factor of 3 accounts for the three colors of the quarks. QCD
Quantum chromodynamics
In theoretical physics, quantum chromodynamics is a theory of the strong interaction , a fundamental force describing the interactions of the quarks and gluons making up hadrons . It is the study of the SU Yang–Mills theory of color-charged fermions...
corrections to this naive formula have been calculated.

