Quinoxaline
Encyclopedia
A quinoxaline, also called a benzopyrazine, in organic chemistry
, is a heterocyclic compound containing a ring complex made up of a benzene ring and a pyrazine
ring. It is isomer
ic with quinazoline
, phthalazine and cinnoline
.
Quinoxalines are used as dyes, pharmaceuticals and antibiotics such as echinomycin
, levomycin and actinoleutin.
Some studies were carried out in order to explore the antitumoral properties of quinoxaline compounds: Recently, quinoxalie and its analogues have been investigated as the catalyst's ligands:
They can be formed by condensing
ortho-diamines
with 1,2-diketones
. The parent substance of the group, quinoxaline, results when glyoxal
is condensed with 1,2-diaminobenzene
. Substituted derivatives arise when α-ketonic acid
s, α-chlorketones, α-aldehyde
alcohol
s and α-ketone alcohols are used in place of diketones. Quinoxaline and its analogues may also be form by reduction of amino acids substituted 1,5-difluoro-2,4-dinitrobenzene (DFDNB):
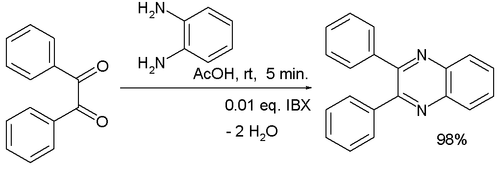
One study used 2-iodoxybenzoic acid
(IBX) as a catalyst in the reaction of benzil
with 1,2-diaminobenzene:
Organic chemistry
Organic chemistry is a subdiscipline within chemistry involving the scientific study of the structure, properties, composition, reactions, and preparation of carbon-based compounds, hydrocarbons, and their derivatives...
, is a heterocyclic compound containing a ring complex made up of a benzene ring and a pyrazine
Pyrazine
Pyrazine is a heterocyclic aromatic organic compound with the chemical formula C4H4N2.Pyrazine is a symmetrical molecule with point group D2h. Derivatives like phenazine are well known for their antitumor, antibiotic and diuretic activity. Pyrazine is less basic in nature than pyridine, pyridazine...
ring. It is isomer
Isomer
In chemistry, isomers are compounds with the same molecular formula but different structural formulas. Isomers do not necessarily share similar properties, unless they also have the same functional groups. There are many different classes of isomers, like stereoisomers, enantiomers, geometrical...
ic with quinazoline
Quinazoline
Quinazoline is a compound made up of two fused six-membered simple aromatic rings, a benzene ring and a pyrimidine ring. Its chemical formula is C8H6N2. Quinazoline is yellow and crystalline...
, phthalazine and cinnoline
Cinnoline
Cinnoline is an aromatic heterocyclic compound with the formula C8H6N2. It is isomeric with quinoxaline, phthalazine and quinazoline.-Properties:...
.
Quinoxalines are used as dyes, pharmaceuticals and antibiotics such as echinomycin
Echinomycin
Echinomycin is a peptide antibiotic. It intercalates into DNA at two specific sites, thereby blocking the binding of hypoxia inducible factor 1 alpha ....
, levomycin and actinoleutin.
Some studies were carried out in order to explore the antitumoral properties of quinoxaline compounds: Recently, quinoxalie and its analogues have been investigated as the catalyst's ligands:
They can be formed by condensing
Condensation reaction
A condensation reaction is a chemical reaction in which two molecules or moieties combine to form one single molecule, together with the loss of a small molecule. When this small molecule is water, it is known as a dehydration reaction; other possible small molecules lost are hydrogen chloride,...
ortho-diamines
Amine
Amines are organic compounds and functional groups that contain a basic nitrogen atom with a lone pair. Amines are derivatives of ammonia, wherein one or more hydrogen atoms have been replaced by a substituent such as an alkyl or aryl group. Important amines include amino acids, biogenic amines,...
with 1,2-diketones
Ketone
In organic chemistry, a ketone is an organic compound with the structure RCR', where R and R' can be a variety of atoms and groups of atoms. It features a carbonyl group bonded to two other carbon atoms. Many ketones are known and many are of great importance in industry and in biology...
. The parent substance of the group, quinoxaline, results when glyoxal
Glyoxal
Glyoxal is an organic compound with the formula OCHCHO. This yellow colored liquid is the smallest dialdehyde . Its tautomer acetylenediol is unstable.-Production:...
is condensed with 1,2-diaminobenzene
O-Phenylenediamine
o-Phenylenediamine is a organic compound with the formula C6H42. This aromatic diamine is an important precursor to many heterocyclic compounds...
. Substituted derivatives arise when α-ketonic acid
Acid
An acid is a substance which reacts with a base. Commonly, acids can be identified as tasting sour, reacting with metals such as calcium, and bases like sodium carbonate. Aqueous acids have a pH of less than 7, where an acid of lower pH is typically stronger, and turn blue litmus paper red...
s, α-chlorketones, α-aldehyde
Aldehyde
An aldehyde is an organic compound containing a formyl group. This functional group, with the structure R-CHO, consists of a carbonyl center bonded to hydrogen and an R group....
alcohol
Alcohol
In chemistry, an alcohol is an organic compound in which the hydroxy functional group is bound to a carbon atom. In particular, this carbon center should be saturated, having single bonds to three other atoms....
s and α-ketone alcohols are used in place of diketones. Quinoxaline and its analogues may also be form by reduction of amino acids substituted 1,5-difluoro-2,4-dinitrobenzene (DFDNB):
One study used 2-iodoxybenzoic acid
2-Iodoxybenzoic acid
IBX acid or 2-iodoxybenzoic acid is an organic compound used in organic synthesis as an oxidizing agent. This Periodinane is especially suited to oxidize alcohols to aldehydes. The IBX acid is prepared from 2-iodobenzoic acid, potassium bromate and sulfuric acid...
(IBX) as a catalyst in the reaction of benzil
Benzil
Benzil is the organic compound with the formula 2, generally abbreviated 2. This yellow solid is one of the most common diketones...
with 1,2-diaminobenzene: