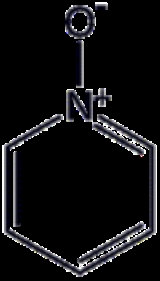
Pyridine-N-oxide
Encyclopedia
Pyridine-N-oxide is the heterocyclic compound
with the formula
C5H5NO. This colourless, hygroscopic solid is the product of the oxidation of pyridine
. It was originally prepared using peracids as the oxidising agent. The molecule is planar. The compound is used infrequently as an oxidizing reagent
in organic synthesis
. It also serves as a ligand
in coordination chemistry.
Heterocyclic compound
A heterocyclic compound is a cyclic compound which has atoms of at least two different elements as members of its ring. The counterparts of heterocyclic compounds are homocyclic compounds, the rings of which are made of a single element....
with the formula
Chemical formula
A chemical formula or molecular formula is a way of expressing information about the atoms that constitute a particular chemical compound....
C5H5NO. This colourless, hygroscopic solid is the product of the oxidation of pyridine
Pyridine
Pyridine is a basic heterocyclic organic compound with the chemical formula C5H5N. It is structurally related to benzene, with one C-H group replaced by a nitrogen atom...
. It was originally prepared using peracids as the oxidising agent. The molecule is planar. The compound is used infrequently as an oxidizing reagent
Reagent
A reagent is a "substance or compound that is added to a system in order to bring about a chemical reaction, or added to see if a reaction occurs." Although the terms reactant and reagent are often used interchangeably, a reactant is less specifically a "substance that is consumed in the course of...
in organic synthesis
Organic synthesis
Organic synthesis is a special branch of chemical synthesis and is concerned with the construction of organic compounds via organic reactions. Organic molecules can often contain a higher level of complexity compared to purely inorganic compounds, so the synthesis of organic compounds has...
. It also serves as a ligand
Ligand
In coordination chemistry, a ligand is an ion or molecule that binds to a central metal atom to form a coordination complex. The bonding between metal and ligand generally involves formal donation of one or more of the ligand's electron pairs. The nature of metal-ligand bonding can range from...
in coordination chemistry.

