Pulse duration
Encyclopedia
In signal processing
and telecommunication
, the term pulse duration has the following meanings:
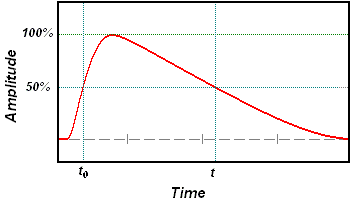
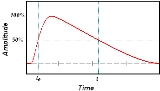
Note: The interval between the 50% points of the final amplitude is usually used to determine or define pulse duration, and this is understood to be the case unless otherwise specified. Other fractions of the final amplitude, e.g., 90% or 1/e
, may also be used, as may the root mean square
(rms) value of the pulse amplitude
.
Signal processing
Signal processing is an area of systems engineering, electrical engineering and applied mathematics that deals with operations on or analysis of signals, in either discrete or continuous time...
and telecommunication
Telecommunication
Telecommunication is the transmission of information over significant distances to communicate. In earlier times, telecommunications involved the use of visual signals, such as beacons, smoke signals, semaphore telegraphs, signal flags, and optical heliographs, or audio messages via coded...
, the term pulse duration has the following meanings:

- In a pulsePulse (signal processing)In signal processing, the term pulse has the following meanings:#A rapid, transient change in the amplitude of a signal from a baseline value to a higher or lower value, followed by a rapid return to the baseline value....
waveformWaveformWaveform means the shape and form of a signal such as a wave moving in a physical medium or an abstract representation.In many cases the medium in which the wave is being propagated does not permit a direct visual image of the form. In these cases, the term 'waveform' refers to the shape of a graph...
, the interval between (a) the timeTimeTime is a part of the measuring system used to sequence events, to compare the durations of events and the intervals between them, and to quantify rates of change such as the motions of objects....
, during the first transition, that the pulse amplitude reaches a specified fraction (level) of its final amplitude, and (b) the time the pulse amplitude drops, on the last transition, to the same level.
Note: The interval between the 50% points of the final amplitude is usually used to determine or define pulse duration, and this is understood to be the case unless otherwise specified. Other fractions of the final amplitude, e.g., 90% or 1/e
E (mathematical constant)
The mathematical constant ' is the unique real number such that the value of the derivative of the function at the point is equal to 1. The function so defined is called the exponential function, and its inverse is the natural logarithm, or logarithm to base...
, may also be used, as may the root mean square
Root mean square
In mathematics, the root mean square , also known as the quadratic mean, is a statistical measure of the magnitude of a varying quantity. It is especially useful when variates are positive and negative, e.g., sinusoids...
(rms) value of the pulse amplitude
Amplitude
Amplitude is the magnitude of change in the oscillating variable with each oscillation within an oscillating system. For example, sound waves in air are oscillations in atmospheric pressure and their amplitudes are proportional to the change in pressure during one oscillation...
.
- In radarRadarRadar is an object-detection system which uses radio waves to determine the range, altitude, direction, or speed of objects. It can be used to detect aircraft, ships, spacecraft, guided missiles, motor vehicles, weather formations, and terrain. The radar dish or antenna transmits pulses of radio...
, measurement of pulse transmission time in microseconds, that is, the time the radar's transmitter is energized during each cycle.

