
Protein efficiency ratio
Encyclopedia
Protein efficiency ratio (PER) is based on the weight gain of a test subject divided by its intake of a particular food protein
during the test period.
From 1919 until very recently, the PER had been a widely used method for evaluating the quality of protein in food.
In the United States
, the food industry had long used the PER as the standard for evaluating the protein quality of food proteins. The U.S. Food and Drug Administration
used the PER as the basis for the percent of the U.S. recommended daily allowance (USRDA) for protein shown on food labels.
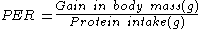
Protein
Proteins are biochemical compounds consisting of one or more polypeptides typically folded into a globular or fibrous form, facilitating a biological function. A polypeptide is a single linear polymer chain of amino acids bonded together by peptide bonds between the carboxyl and amino groups of...
during the test period.
From 1919 until very recently, the PER had been a widely used method for evaluating the quality of protein in food.
In the United States
United States
The United States of America is a federal constitutional republic comprising fifty states and a federal district...
, the food industry had long used the PER as the standard for evaluating the protein quality of food proteins. The U.S. Food and Drug Administration
Food and Drug Administration
The Food and Drug Administration is an agency of the United States Department of Health and Human Services, one of the United States federal executive departments...
used the PER as the basis for the percent of the U.S. recommended daily allowance (USRDA) for protein shown on food labels.
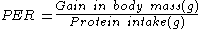
See also
- Protein Digestibility Corrected Amino Acid Score (PDCAAS)
- Net protein utilizationNet protein utilizationThe net protein utilization, or NPU, is the ratio of amino acid converted to proteins to the ratio of amino acids supplied. This figure is somewhat affected by the salvage of essential amino acids within the body, but is profoundly affected by the level of limiting amino acids within a...
- Nitrogen balanceNitrogen balanceNitrogen balance is the measure of nitrogen output subtracted from nitrogen input.Blood urea nitrogen can be used in estimating nitrogen balance, as can the urea concentration in urine....
- Protein digestibility
- ProteinProteinProteins are biochemical compounds consisting of one or more polypeptides typically folded into a globular or fibrous form, facilitating a biological function. A polypeptide is a single linear polymer chain of amino acids bonded together by peptide bonds between the carboxyl and amino groups of...
: Amino AcidAmino acidAmino acids are molecules containing an amine group, a carboxylic acid group and a side-chain that varies between different amino acids. The key elements of an amino acid are carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, and nitrogen...
s - Whey proteinWhey proteinWhey protein is a mixture of globular proteins isolated from whey, the liquid material created as a by-product of cheese production. Some preclinical studies in rodents have suggested that whey protein may possess anti-inflammatory or anti-cancer properties; however, human data is lacking...
- Soy proteinSoy proteinSoy protein is a protein that is isolated from soybean. It is made from dehulled, defatted soybean meal. Dehulled and defatted soybeans are processed into three kinds of high protein commercial products : soy flour, concentrates, and isolates. Soy protein isolate has been used since 1959 in foods ...
- CaseinCaseinCasein is the name for a family of related phosphoprotein proteins . These proteins are commonly found in mammalian milk, making up 80% of the proteins in cow milk and between 60% and 65% of the proteins in human milk....
- Biological valueBiological ValueBiological value is a measure of the proportion of absorbed protein from a food which becomes incorporated into the proteins of the organism's body. It summarises how readily the broken down protein can be used in protein synthesis in the cells of the organism. Proteins are the major source of...

