
Potentiostat
Encyclopedia
Electronic hardware
Electronic hardware refers to interconnected electronic components which perform analog and/or logic operations on received and locally stored information to produce as output and/or store resulting new information and/or to provide control for output actuator mechanisms.Electronic hardware can...
required to control a three electrode cell
Voltammetry
Voltammetry is a category of electroanalytical methods used in analytical chemistry and various industrial processes. In voltammetry, information about an analyte is obtained by measuring the current as the potential is varied.- Three electrode system :...
and run most electroanalytical
Electroanalytical method
Electroanalytical methods are a class of techniques in analytical chemistry which study an analyte by measuring the potential and/or current in an electrochemical cell containing the analyte. These methods can be broken down into several categories depending on which aspects of the cell are...
experiments. A Bipotentiostat and polypotentiostat are potentiostats capable of controlling two working electrodes and more than two working electrodes, respectively.
The system functions by maintaining the potential
Voltage
Voltage, otherwise known as electrical potential difference or electric tension is the difference in electric potential between two points — or the difference in electric potential energy per unit charge between two points...
of the working electrode
Working electrode
The working electrode is the electrode in an electrochemical system on which the reaction of interest is occurring. The working electrode is often used in conjunction with an auxiliary electrode, and a reference electrode in a three electrode system...
at a constant level with respect to the reference electrode
Reference electrode
A reference electrode is an electrode which has a stable and well-known electrode potential. The high stability of the electrode potential is usually reached by employing a redox system with constant concentrations of each participants of the redox reaction.There are many ways reference...
by adjusting the current
Electric current
Electric current is a flow of electric charge through a medium.This charge is typically carried by moving electrons in a conductor such as wire...
at an auxiliary electrode
Auxiliary electrode
The Auxiliary electrode, often also called the counter electrode, is an electrode used in a three electrode electrochemical cell for voltammetric analysis or other reactions in which an electrical current is expected to flow...
. It consists of an electric circuit which is usually described in terms of simple op amps.
Primary use
This equipment is fundamental to modern electrochemical studies using three electrode systemsVoltammetry
Voltammetry is a category of electroanalytical methods used in analytical chemistry and various industrial processes. In voltammetry, information about an analyte is obtained by measuring the current as the potential is varied.- Three electrode system :...
for investigations of reaction mechanisms
Electrochemical reaction mechanism
In chemistry, an electrochemical reaction mechanism is the step by step sequence of elementary steps, involving at least one outer sphere electron transfer, by which an overall chemical change occurs .- Overview :...
related to redox
Redox
Redox reactions describe all chemical reactions in which atoms have their oxidation state changed....
chemistry and other chemical
Chemistry
Chemistry is the science of matter, especially its chemical reactions, but also its composition, structure and properties. Chemistry is concerned with atoms and their interactions with other atoms, and particularly with the properties of chemical bonds....
phenomena. The dimensions of the resulting data depend on the experiment. In voltammetry
Voltammetry
Voltammetry is a category of electroanalytical methods used in analytical chemistry and various industrial processes. In voltammetry, information about an analyte is obtained by measuring the current as the potential is varied.- Three electrode system :...
, electric current
Electric current
Electric current is a flow of electric charge through a medium.This charge is typically carried by moving electrons in a conductor such as wire...
in amps
Ampere
The ampere , often shortened to amp, is the SI unit of electric current and is one of the seven SI base units. It is named after André-Marie Ampère , French mathematician and physicist, considered the father of electrodynamics...
is plotted against electric potential
Electric potential
In classical electromagnetism, the electric potential at a point within a defined space is equal to the electric potential energy at that location divided by the charge there...
in voltage
Voltage
Voltage, otherwise known as electrical potential difference or electric tension is the difference in electric potential between two points — or the difference in electric potential energy per unit charge between two points...
. In a bulk electrolysis
Bulk electrolysis
Bulk electrolysis is also known as potentiostatic coulometry or controlled potential coulometry. The experiment is a form of coulometry which generally employees a three electrode system controlled by a potentiostat. In the experiment the working electrode is held at a constant potential and...
total coulombs passed (total electric charge
Electric charge
Electric charge is a physical property of matter that causes it to experience a force when near other electrically charged matter. Electric charge comes in two types, called positive and negative. Two positively charged substances, or objects, experience a mutual repulsive force, as do two...
) is plotted against time in seconds even through the experiment measures electric current (ampere
Ampere
The ampere , often shortened to amp, is the SI unit of electric current and is one of the seven SI base units. It is named after André-Marie Ampère , French mathematician and physicist, considered the father of electrodynamics...
s) over time. This is done to show that the experiment is approaching an expected number of coulombs.
Most early potentiostats could function independently, providing data output through a physical data trace. Modern potentiostats are designed to interface with a personal computer
Personal computer
A personal computer is any general-purpose computer whose size, capabilities, and original sales price make it useful for individuals, and which is intended to be operated directly by an end-user with no intervening computer operator...
and operate through a dedicated software package. The automated software allows the user to rapidly shift between experiments and experimental conditions. The computer allows data to be stored and analyzed more effectively, rapidly, and accurately than historic methods.
Significant features
In electrochemical experiments the electrodes are the piece of equipment that comes in immediate contact with the analyteAnalyte
An analyte, or component , is a substance or chemical constituent that is of interest in an analytical procedure. Grammatically, it is important to note that experiments always seek to measure properties of analytes—and that analytes themselves can never be measured. For instance, one cannot...
. For this reason the electrodes are very important for determining the experimental result. The electrode surface may or may not catalyze chemical reactions. The size of the electrodes affects the magnitude of the currents passed which can affect signal to noise. But electrodes are not the only limiting factor for electrochemical experiments, the potentiostat also has a limited range of operation. The following are a few significant features that vary between instruments.
- Electric potential range (measured and applied): while the potential window is mostly based on the solvent window the electronics can also limit the possible range.
- Accuracy in potential (measured and applied): limits of deviations between the actual and reported.
- Range of scan rate: how slow or fast a potential window can be scanned this is most important for experiments that require high scan rates such as those involving ultramicroelectrodeUltramicroelectrodeAn Ultramicroelectrode is a working electrode used in a three electrode system. The small size of UME give them relatively large diffusion layers and small overall currents. These features allow UME to achieve useful steady-state conditions and very high scan rates with limited distortion...
s. - Sample rate: the rate at which potential or voltage can be accurately sampled. This can be important for experiments that need high scan rates such as those involving ultramicroelectrodes.
- File size: a limiting factor can be the file size limit. This would most likely affect the choice of the potential range swept or the potential sample rate.
- Electric current range (measured and applied): the maximum range over which current can be sampled. Applying large currents is important for experiments that pass a great deal of current like a large bulk electrolysisBulk electrolysisBulk electrolysis is also known as potentiostatic coulometry or controlled potential coulometry. The experiment is a form of coulometry which generally employees a three electrode system controlled by a potentiostat. In the experiment the working electrode is held at a constant potential and...
. Measuring small currents is important for experiments that pass small currents like those involving ultramicroelectrodes. - Current resolution: determines the operational range of a specific experiment and the bit resolution of that data in the current dimension.
- Accuracy in current (measured and applied): limits of deviations between the actual and reported.
- Number of working channels: how many working electrodeWorking electrodeThe working electrode is the electrode in an electrochemical system on which the reaction of interest is occurring. The working electrode is often used in conjunction with an auxiliary electrode, and a reference electrode in a three electrode system...
s can the instrument control. A bipotentiostat is necessary to controlling systems with two working electrodes like a rotating ring-disk electrodeRotating ring-disk electrodeA rotating ring-disk electrode is double working electrode used in hydrodynamic voltammetry, very similar to a rotating disk electrode . The electrode actually rotates during experiments inducing a flux of analyte to the electrode...
. A polypotentiostat may be important for controlling some biological experiments with three or more working electrodes. - Footprint: potentiostats include small devices of about 20 x 10 x 5 cm weighing well under a kilogram or a simple board that can be installed in a desktop computer. A large large bench-top model would be on the order of 50 x 20 x 10 cm and weigh up to or more than 5 kilograms.
- Interface: can the instrument run independently or must they be slaved to a personal computer.
- Sweep generator: can the system apply an analogue sweep or does it use a digital staircase generator as an approximation. If it does use a digital staircase then the resolution of the staircase is important.
- Rotating electrode: can the instrument operate a rotating electrode. This is intrinsic for experiments that require a rotating disk electrodeRotating disk electrodeA rotating disk electrode is a hydrodynamic working electrode used in a three electrode system. The electrode rotates during experiments inducing a flux of analyte to the electrode. These working electrodes are used in electrochemical studies when investigating reaction mechanisms related to...
or rotating ring-disk electrodeRotating ring-disk electrodeA rotating ring-disk electrode is double working electrode used in hydrodynamic voltammetry, very similar to a rotating disk electrode . The electrode actually rotates during experiments inducing a flux of analyte to the electrode...
.
Basic relationships
A potentiostat is a controlController (control theory)
In control theory, a controller is a device which monitors and affects the operational conditions of a given dynamical system. The operational conditions are typically referred to as output variables of the system which can be affected by adjusting certain input variables...
and measuring device. It comprises an electric circuit which controls the potential across the cell by sensing changes in its resistance
Electrical resistance
The electrical resistance of an electrical element is the opposition to the passage of an electric current through that element; the inverse quantity is electrical conductance, the ease at which an electric current passes. Electrical resistance shares some conceptual parallels with the mechanical...
, varying accordingly the current supplied to the system: a higher resistance will result in a decreased current, while a lower resistance will result in an increased current, in order to keep the voltage constant as described by Ohm's law
Ohm's law
Ohm's law states that the current through a conductor between two points is directly proportional to the potential difference across the two points...
.
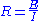
As a result, the variable system resistance
Electrical resistance
The electrical resistance of an electrical element is the opposition to the passage of an electric current through that element; the inverse quantity is electrical conductance, the ease at which an electric current passes. Electrical resistance shares some conceptual parallels with the mechanical...
and the controlled current are inversely proportional
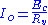
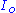 is the output electrical current of the potentiostat
is the output electrical current of the potentiostat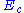 is the voltageVoltageVoltage, otherwise known as electrical potential difference or electric tension is the difference in electric potential between two points — or the difference in electric potential energy per unit charge between two points...
is the voltageVoltageVoltage, otherwise known as electrical potential difference or electric tension is the difference in electric potential between two points — or the difference in electric potential energy per unit charge between two points...
that is kept constant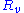 is the electrical resistanceElectrical resistanceThe electrical resistance of an electrical element is the opposition to the passage of an electric current through that element; the inverse quantity is electrical conductance, the ease at which an electric current passes. Electrical resistance shares some conceptual parallels with the mechanical...
is the electrical resistanceElectrical resistanceThe electrical resistance of an electrical element is the opposition to the passage of an electric current through that element; the inverse quantity is electrical conductance, the ease at which an electric current passes. Electrical resistance shares some conceptual parallels with the mechanical...
that varies.
Principles of Operation
Since 1942, when Hickling built the first three electrode potentiostat, substantial progress has been made to improve the instrument. Hickling's device used a third electrode, the reference electrodeReference electrode
A reference electrode is an electrode which has a stable and well-known electrode potential. The high stability of the electrode potential is usually reached by employing a redox system with constant concentrations of each participants of the redox reaction.There are many ways reference...
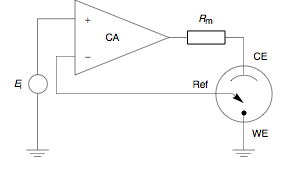
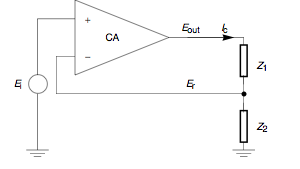
to automatically control the cell potential. Up until the present day his principle has remained in use. At a glance, a potentiostat measures the potential difference between the working and the reference electrode, applies the current through the counter electrode and measures the current as an
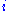
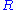 voltage drop over a series resistor (
voltage drop over a series resistor (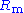 in Fig. 1).
in Fig. 1).The control amplifier CA is responsible for maintaining the voltage between the reference and the working electrode as closely as possible to the voltage of the input source
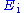 . It adjusts its output to automatically control the cell current so that a condition of equilibrium is satisfied. The theory of operation is best understood using the equations below.
. It adjusts its output to automatically control the cell current so that a condition of equilibrium is satisfied. The theory of operation is best understood using the equations below.Prior to observing the following equations, one may note that, from an electrical point of view, the electrochemical cell and the current measurement resistor
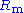 may be regarded as two impedances (Fig. 2).
may be regarded as two impedances (Fig. 2). 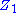 includes
includes 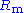 in series with the interfacial impedance of the counter electrode and the solution resistance between the counter and the reference.
in series with the interfacial impedance of the counter electrode and the solution resistance between the counter and the reference. 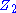
represents the interfacial impedance of the working electrode in series with the solution resistance between the working and the reference
electrodes.
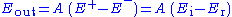 . (1)
. (1)where
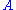 is the amplification factor of the CA. At this point the assumption may be made that a negligible amount of current is flowing through the reference electrode. This correlates to physical phenomenon since the reference electrode is connected to a high impedance electrometer. Thus, the cell current may be described in two ways:
is the amplification factor of the CA. At this point the assumption may be made that a negligible amount of current is flowing through the reference electrode. This correlates to physical phenomenon since the reference electrode is connected to a high impedance electrometer. Thus, the cell current may be described in two ways: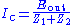 , (2)
, (2)and
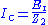 . (3)
. (3)Combining Eqs. (2) and (3) yields Eq. (4):
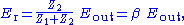 (4)
(4)where
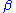 is the fraction of the output voltage of the control amplifier returned to its negative input; namely the feedback factor:
is the fraction of the output voltage of the control amplifier returned to its negative input; namely the feedback factor: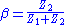 .
.Combining Eqs. (1) and (4) yields Eq. (6):
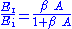 . (6)
. (6)When the quantity
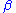
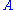 becomes very large with respect to one, Eq. (6) reduces to Eq. (7), which is one of the negative feedback equations:
becomes very large with respect to one, Eq. (6) reduces to Eq. (7), which is one of the negative feedback equations: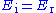 . (7)
. (7)Eq. (7) proves that the control amplifier works to keep the voltage between the reference and the working close to the input source voltage.
See also
- AmperostatAmperostatAn amperostat is a control and measuring device used to keep constant the current flowing though electrolytic cells in coulometric titrations, disregarding changes in the load itself. Synonym is "galvanostat"...
- GalvanostatGalvanostatA galvanostat is a control and measuring device capable of keeping the current through an electrolytic cell in coulometric titrations constant, disregarding changes in the load itself. A synonym is "amperostat"....
- Electroanalytical methodElectroanalytical methodElectroanalytical methods are a class of techniques in analytical chemistry which study an analyte by measuring the potential and/or current in an electrochemical cell containing the analyte. These methods can be broken down into several categories depending on which aspects of the cell are...
- VoltammetryVoltammetryVoltammetry is a category of electroanalytical methods used in analytical chemistry and various industrial processes. In voltammetry, information about an analyte is obtained by measuring the current as the potential is varied.- Three electrode system :...
- Potentiometry
- CoulometryCoulometryCoulometry is the name given to a group of techniques in analytical chemistry that determine the amount of matter transformed during an electrolysis reaction by measuring the amount of electricity consumed or produced....
- PolarographyPolarographyPolarography is a subclass of voltammetry where the working electrode is a dropping mercury electrode or a static mercury drop electrode ., useful for its wide cathodic range and renewable surface...
- Working electrodeWorking electrodeThe working electrode is the electrode in an electrochemical system on which the reaction of interest is occurring. The working electrode is often used in conjunction with an auxiliary electrode, and a reference electrode in a three electrode system...
- Reference electrodeReference electrodeA reference electrode is an electrode which has a stable and well-known electrode potential. The high stability of the electrode potential is usually reached by employing a redox system with constant concentrations of each participants of the redox reaction.There are many ways reference...
- Auxiliary electrodeAuxiliary electrodeThe Auxiliary electrode, often also called the counter electrode, is an electrode used in a three electrode electrochemical cell for voltammetric analysis or other reactions in which an electrical current is expected to flow...
External links
- Genady Ragoisha (webmaster), "potentiodynamic electrochemical impedance spectroscopy (PDEIS)", Physico-Chemical Research Institute, Belarusian State University. A description of the use of a potentiostat in virtual instrumentationVirtual instrumentationVirtual instrumentation is the use of customizable software and modular measurement hardware to create user-defined measurement systems, called virtual instruments....
for electrochemical experiments. - Pierre R. Roberge (Webmaster) "Potentiostat", corrosion-doctors.org Electrochemistry Dictionary.
- "CheapStat: An Open-Source, “Do-It-Yourself” Potentiostat...", Aaron A. Rowe et. al., University of California Santa Barbara
- Potentiostat stability mystery explained

