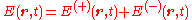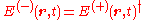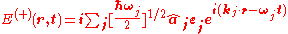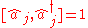Photodetection
Encyclopedia
In his historic paper, entitled " The Quantum Theory of Optical Coherence," Roy J. Glauber
set a solid foundation for the quantum electronics/quantum optics
enterprise. The experimental development of the optical maser
and later laser
at that time had made the classical concept of optical coherence
inadequate. Glauber started from the quantum theory of light detection by considering the process of photoionization in which a photodetector is triggered by an ionizing absorption of a photon. In the quantum theory of radiation, the electric field operator in the Coulomb gauge may be written as the sum of positive and negative frequency parts
where
One may expand in terms of the normal modes as follows:
in terms of the normal modes as follows:
where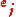 are the unit vectors of polarization; this expansion has the same form as the classical expansion except that now the field amplitudes
are the unit vectors of polarization; this expansion has the same form as the classical expansion except that now the field amplitudes 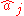 are operators.
are operators.
Glauber showed that, for an ideal photodetector situated at a point in a radiation field, the probability of observing a photoionization event in this detector between time
in a radiation field, the probability of observing a photoionization event in this detector between time  and
and 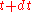 is proportional to
is proportional to 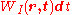 , where
, where
Roy J. Glauber
Roy Jay Glauber is an American theoretical physicist. He is the Mallinckrodt Professor of Physics at Harvard University and Adjunct Professor of Optical Sciences at the University of Arizona...
set a solid foundation for the quantum electronics/quantum optics
Quantum optics
Quantum optics is a field of research in physics, dealing with the application of quantum mechanics to phenomena involving light and its interactions with matter.- History of quantum optics :...
enterprise. The experimental development of the optical maser
Maser
A maser is a device that produces coherent electromagnetic waves through amplification by stimulated emission. Historically, “maser” derives from the original, upper-case acronym MASER, which stands for "Microwave Amplification by Stimulated Emission of Radiation"...
and later laser
Laser
A laser is a device that emits light through a process of optical amplification based on the stimulated emission of photons. The term "laser" originated as an acronym for Light Amplification by Stimulated Emission of Radiation...
at that time had made the classical concept of optical coherence
Coherence (physics)
In physics, coherence is a property of waves that enables stationary interference. More generally, coherence describes all properties of the correlation between physical quantities of a wave....
inadequate. Glauber started from the quantum theory of light detection by considering the process of photoionization in which a photodetector is triggered by an ionizing absorption of a photon. In the quantum theory of radiation, the electric field operator in the Coulomb gauge may be written as the sum of positive and negative frequency parts
where
One may expand
 in terms of the normal modes as follows:
in terms of the normal modes as follows:where
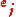 are the unit vectors of polarization; this expansion has the same form as the classical expansion except that now the field amplitudes
are the unit vectors of polarization; this expansion has the same form as the classical expansion except that now the field amplitudes 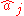 are operators.
are operators.Glauber showed that, for an ideal photodetector situated at a point
 in a radiation field, the probability of observing a photoionization event in this detector between time
in a radiation field, the probability of observing a photoionization event in this detector between time  and
and  is proportional to
is proportional to 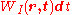 , where
, where-

and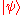 specifies the state of the field. Since the radiation field is a quantum-mechanical one, we do not know the exact properties of the incident light, and the prabability should be averaged, as in the classical theory, to be proportional to
specifies the state of the field. Since the radiation field is a quantum-mechanical one, we do not know the exact properties of the incident light, and the prabability should be averaged, as in the classical theory, to be proportional to
where the angular brackets mean an average over the light field. The significance of the quantum theory of coherence is in the ordering of the creation and destruction operators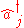 and
and 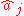 :
:
Since is not equal to
is not equal to 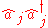 for a light field, the order makes the quantum statistical measurements (such as photon counting) quite different from the classical ones, i.e., the nonclassical properties of light, such as photon antibunchingPhoton antibunchingPhoton antibunching generally refers to a light field with photons more equally spaced than a coherent laser field and a signal at detectors is anticorrelated. More specifically, it can refer to sub-Poisson photon statistics, that is a photon number distribution for which the variance is less than...
for a light field, the order makes the quantum statistical measurements (such as photon counting) quite different from the classical ones, i.e., the nonclassical properties of light, such as photon antibunchingPhoton antibunchingPhoton antibunching generally refers to a light field with photons more equally spaced than a coherent laser field and a signal at detectors is anticorrelated. More specifically, it can refer to sub-Poisson photon statistics, that is a photon number distribution for which the variance is less than...
.
Moreover, Glauber's theory of photodetection is of far-reaching fundamental significance to interpretation of quantum mechanicsInterpretation of quantum mechanicsAn interpretation of quantum mechanics is a set of statements which attempt to explain how quantum mechanics informs our understanding of nature. Although quantum mechanics has held up to rigorous and thorough experimental testing, many of these experiments are open to different interpretations...
. The Glauber detection theory differs from the Born probabilistic interpretation, in that it expresses the meaning of physical law in terms of measured facts (relationships), counting events in the detection processes, without assuming the particle model of matter. These concepts quite naturally lead to a relational approach to quantum physicsRelational approach to quantum physicsThe relational approach to quantum physics is an alternative approach to and interpretation of quantum mechanics. It asserts that the physical world can only be studied accurately in terms of relationships between systems, as all experimentally verifiable facts about the world result explicitly...
. -