
Phoenix Network Coordinates
Encyclopedia
Phoenix is a decentralized network coordinate (NC) system based on the matrix factorization model.
Background
- Network coordinates (NC) system is an efficient mechanism for Internet distance (round-trip latency) prediction with scalable measurements. For a network with N hosts, by performing O(N) measurements, all N*N distances can be predicted.
- Use cases: Vuze BitTorrent, application layer multicast, PeerWise overlay, multi-player online gaming.
- Triangle inequality violation (TIV) is widely exist on the Internet due to the current sub-optimal Internet routing.
Model
- Most of the prior NC systems utilize the Euclidean distance model, i.e., embeds N hosts into a d-dimensional Euclidean spaceEuclidean spaceIn mathematics, Euclidean space is the Euclidean plane and three-dimensional space of Euclidean geometry, as well as the generalizations of these notions to higher dimensions...
Rd. Due to the wide existence of TIV on the Internet, the prediction accuracy of such systems is limited. Phoenix chooses Matrix factorization (MF) model, which does not have the constraint of TIV. - The linear dependence among the rows motivates the factorization of Internet distance matrix, i.e., for a system with
 Internet nodes, the
Internet nodes, the  Internet distance matrix D can be factorized into two smaller matrices.
Internet distance matrix D can be factorized into two smaller matrices. 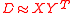 where
where  and
and  are
are  matrices (d << N). This matrix factorization is essentially a problem of linear dimensionality reduction, while Phoenix try to solve it via a distributed way.
matrices (d << N). This matrix factorization is essentially a problem of linear dimensionality reduction, while Phoenix try to solve it via a distributed way.
Design choices in Phoenix
- Different from the existing MF based NC systems such as IDES and DMF, Phoenix introduces a weight to each reference NC and trusts the NCs with higher weight values more than the others. The weight based mechanism can substantially reduce the impact of the error propagation.
- For node discovery, Phoenix utilizes a distributed scheme, so-called Peer exchangePeer exchangePeer exchange or PEX is a communications protocol that augments the BitTorrent file sharing protocol. It allows a group of users that are collaborating to share a given file to do so more swiftly and efficiently....
(PEX), which is used in BitTorrent (protocol). The usage of PEX reduces the load of the tracker, while still ensuring the prediction accuracy under node churn. - Similar to DMF, for avoiding the potential drift of the NCs, Regularization (mathematics)Regularization (mathematics)In mathematics and statistics, particularly in the fields of machine learning and inverse problems, regularization involves introducing additional information in order to solve an ill-posed problem or to prevent overfitting...
is introduced in NC calculation.
See also
- Vivaldi coordinatesVivaldi coordinatesVivaldi Network Coordinates establish a virtual positioning system that has a prime use in networking. The algorithm behind the system uses a distributed technique to estimate propagation times between peers in the network....
- Pharos Network CoordinatesPharos Network CoordinatesPharos is hierarchical and decentralized network coordinate system. With the help of a simple two-level architecture, it achieves much better prediction accuracy then the representative Vivaldi coordinates, and it is incrementally deployable.- Overview :...
- Global network positioningGlobal network positioningGlobal network positioning is a coordinates-based mechanism in a peer-to-peer network architecture which predicts Internet network distance . The mechanism is based on absolute coordinates computed from modeling the Internet as a geometric space...

