
Odd greedy expansion
Encyclopedia
In number theory
, the odd greedy expansion problem concerns a method for forming Egyptian fractions in which all denominators are odd.
If a rational number x/y is a sum of odd unit fractions,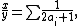
then y must be odd. Conversely, it is known that whenever y is odd, every fraction x/y has a representation of this type in which all the unit fractions are different from each other. For instance, such a representation can be found by replacing the fraction x/y by Ax/Ay where A is a number of the form 35×3i for a sufficiently large i, and then expanding Ax as a sum of divisors of Ay (Breusch 1954; Stewart 1954).
However, there is a simpler greedy algorithm
that has successfully found Egyptian fractions in which all denominators are odd for all instances x/y (with odd y) on which it has been tested: let u be the least odd number that is greater than or equal to y/x, include the fraction 1/u in the expansion, and continue in the same way with the remaining fraction x/y - 1/u. This method is called the odd greedy algorithm and the expansions it creates are called odd greedy expansions.
Stein, Selfridge, Graham
, and others have posed the question of whether the odd greedy algorithm terminates with a finite expansion for every x/y with y odd (Guy 1981). , this question remains open.
Applying the odd greedy algorithm to a fraction with an even denominator produces an infinite series expansion. For instance Sylvester's sequence
can be viewed as generated by the odd greedy expansion of 1/2.
23/4 = 5 3/4; the next larger odd number is 7. So in the first step, we expand
161/5 = 32 1/5; the next larger odd number is 33. So in the next step, we expand
5313/4 = 1328 1/4; the next larger odd number is 1329. So in the third step, we expand
Since the final term in this expansion is a unit fraction, the process terminates with this expansion as its result.
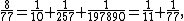
where the left expansion is the greedy expansion and the right expansion is the odd greedy expansion. However, the odd greedy expansion is more typically long, with large denominators. For instance, as Wagon discovered (Guy 1998), the odd greedy expansion for 3/179 has 19 terms, the largest of which is approximately 1.415×10439491. Curiously, the numerators of the fractions to be expanded in each step of the algorithm form a sequence of consecutive integers:
A similar phenomenon occurs with other numbers, such as 5/5809 (an example found independently by K. S. Brown and David Bailey) which has a 31-term expansion. Although the denominators of this expansion are difficult to compute due to their enormous size, the numerator sequence may be found relatively efficiently using modular arithmetic
. Nowakowski (1999) describes several additional examples of this type found by Broadhurst, and notes that K. S. Brown has described methods for finding fractions with arbitrarily long expansions.
Number theory
Number theory is a branch of pure mathematics devoted primarily to the study of the integers. Number theorists study prime numbers as well...
, the odd greedy expansion problem concerns a method for forming Egyptian fractions in which all denominators are odd.
If a rational number x/y is a sum of odd unit fractions,
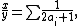
then y must be odd. Conversely, it is known that whenever y is odd, every fraction x/y has a representation of this type in which all the unit fractions are different from each other. For instance, such a representation can be found by replacing the fraction x/y by Ax/Ay where A is a number of the form 35×3i for a sufficiently large i, and then expanding Ax as a sum of divisors of Ay (Breusch 1954; Stewart 1954).
However, there is a simpler greedy algorithm
Greedy algorithm for Egyptian fractions
In mathematics, the greedy algorithm for Egyptian fractions is a greedy algorithm, first described by Fibonacci, for transforming rational numbers into Egyptian fractions. An Egyptian fraction is a representation of an irreducible fraction as a sum of unit fractions, as e.g. 5/6 = 1/2 + 1/3...
that has successfully found Egyptian fractions in which all denominators are odd for all instances x/y (with odd y) on which it has been tested: let u be the least odd number that is greater than or equal to y/x, include the fraction 1/u in the expansion, and continue in the same way with the remaining fraction x/y - 1/u. This method is called the odd greedy algorithm and the expansions it creates are called odd greedy expansions.
Stein, Selfridge, Graham
Ronald Graham
Ronald Lewis Graham is a mathematician credited by the American Mathematical Society as being "one of the principal architects of the rapid development worldwide of discrete mathematics in recent years"...
, and others have posed the question of whether the odd greedy algorithm terminates with a finite expansion for every x/y with y odd (Guy 1981). , this question remains open.
Applying the odd greedy algorithm to a fraction with an even denominator produces an infinite series expansion. For instance Sylvester's sequence
Sylvester's sequence
In number theory, Sylvester's sequence is an integer sequence in which each member of the sequence is the product of the previous members, plus one. The first few terms of the sequence are:...
can be viewed as generated by the odd greedy expansion of 1/2.
Example
Let x/y = 4/23.23/4 = 5 3/4; the next larger odd number is 7. So in the first step, we expand
- 4/23 = 1/7 + 5/161.
161/5 = 32 1/5; the next larger odd number is 33. So in the next step, we expand
- 4/23 = 1/7 + 1/33 + 4/5313.
5313/4 = 1328 1/4; the next larger odd number is 1329. So in the third step, we expand
- 4/23 = 1/7 + 1/33 + 1/1329 + 1/2353659.
Since the final term in this expansion is a unit fraction, the process terminates with this expansion as its result.
Fractions with long expansions
It is possible for the odd greedy algorithm to produce expansions that are shorter than the usual greedy expansion, with smaller denominators (Wagon 1991). For instance,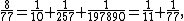
where the left expansion is the greedy expansion and the right expansion is the odd greedy expansion. However, the odd greedy expansion is more typically long, with large denominators. For instance, as Wagon discovered (Guy 1998), the odd greedy expansion for 3/179 has 19 terms, the largest of which is approximately 1.415×10439491. Curiously, the numerators of the fractions to be expanded in each step of the algorithm form a sequence of consecutive integers:
- 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, 15, 16, 17, 18, 1.
A similar phenomenon occurs with other numbers, such as 5/5809 (an example found independently by K. S. Brown and David Bailey) which has a 31-term expansion. Although the denominators of this expansion are difficult to compute due to their enormous size, the numerator sequence may be found relatively efficiently using modular arithmetic
Modular arithmetic
In mathematics, modular arithmetic is a system of arithmetic for integers, where numbers "wrap around" after they reach a certain value—the modulus....
. Nowakowski (1999) describes several additional examples of this type found by Broadhurst, and notes that K. S. Brown has described methods for finding fractions with arbitrarily long expansions.
External links
- MathPages - Odd-Greedy Unit Fraction Expansions, K. S. Brown

